Nginx负载均衡实践之一:基本实现
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Nginx负载均衡实践之一:基本实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
由于现在的网站架构越来越大,基于互联网的用户也是日渐增长,所以传统的单机版服务器已经渐渐不能适应时代发展的需要。最近在和其他企业接触的过程中,发现对于互联网的经验尤为看重,所谓的互联网经验,其实就是指对于高并发,大数据量的处理能力。说到高并发这块,那么负载均衡是肯定不能少的。下面我将会在自己的机器上通过搭建一套单机版的负载均衡实现,来描述这个过程。
安装nginx
首先,我们从官网http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.9.9.zip中下载最新版本,然后解压到文件夹中,我这里为了方便,路径我就定为:E:\\nginx。解压之后,在CMD窗口中,我们通过以下命令来开启Nginx服务:
start nginx --开启nginx nginx -s stop --关闭nginx nginx -s reload --修改配置文件后,重新加载nginx
需要特别注意的是,如果先运行了 nginx –s stop命令后,再运行nginx –s reload命令,会抛出错误信息的,所以在任何时候运行stop命令后,都要再运行以下 start nginx命令,然后再进行其他命令操作。
启动nginx服务之后,我们就可以在任务管理器中看到有两个进程存在:
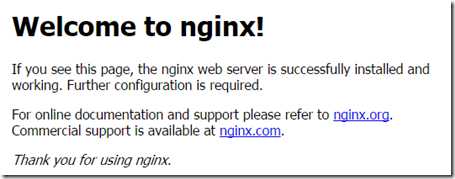
然后我们可以通过在浏览器中打开 http://127.0.0.1访问地址,就可以看到nginx成功访问的信息了。这就表示我们的nginx安装正常,正确。
配置Nginx
接下来,我们就开始通过实例来演示如何进行单机负载均衡的。
首先,我们打开VS2013,创建两个WebApplication,名称分别为WebApplication1,WebApplication2. 这两个WebApplication的正文部分会有不同的标志信息用来表示当前访问的页面是属于二者中的哪一个的。
然后,我们发布网站,打开IIS,分别创建两个网站实例,然后进行指向,绑定地址分别设置为: 127.0.0.1:8100 和 127.0.0.1:8200
最后,我们进入nginx安装目录,打开conf文件夹下的nginx.conf文件,进行如下的配置:
1.添加一个upstream节点,用于标记数据库集群:
upstream test.var{
server 127.0.0.1:8100 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:8200 weight=1;
}
2.在server节点下,修改location节点,访问方式:
#对aspx后缀的进行负载均衡请求
location / {
root /wwwroot;#定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置
index index.aspx index.html index.htm;#定义首页索引文件的名称
proxy_pass http://test.var;
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
这样配置之后,基本就完成了,我附上所有的配置:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘
# ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘
# ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘;
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
upstream test.var{
server 127.0.0.1:8100 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:8200 weight=1;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#location / {
# root html;
# index default.aspx index.html index.htm;
#}
#对aspx后缀的进行负载均衡请求
location / {
root /wwwroot; #定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置
index index.aspx index.html index.htm; #定义首页索引文件的名称
proxy_pass http://test.var;
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the php scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \\.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \\.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root
# concurs with nginx‘s one
#
#location ~ /\\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
访问测试
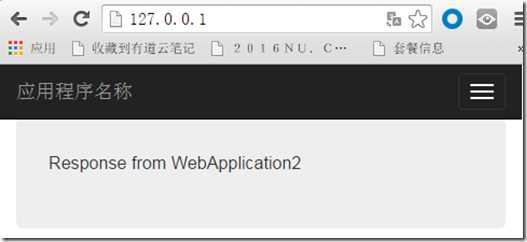
上面配置完毕之后,我们就可以通过访问 127.0.0.1 来访问了:
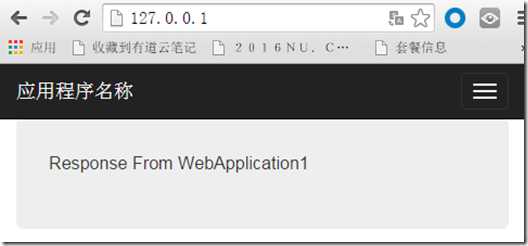
我们可以看到,第一次访问的时候,我们访问的是WebApplication2,然后我们刷新页面:
刷新页面之后,我们看到,访问的是WebApplication1.
这样,当不同用户来访问我们的服务器的时候,由于nginx的负载均衡,使得不同用户访问的服务器是不同的,这也从一定程度上大大缓解了服务器的压力。
接下来,我会讲解对静态资源的缓存,session共享等等,敬请期待。
参考资源
【大型网站技术实践】初级篇:借助Nginx搭建反向代理服务器
以上是关于Nginx负载均衡实践之一:基本实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章