python-day05
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python-day05相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这周作业所遇到的麻烦,从在主程序中使用return,报return not functions error,明白return 一般只能在函数中使用,表示返回出去
再者就是模块的导入,在模块的导入的时候我们需要注意首先因为这个pycharm解释器的存在所以我们可以看到在sys.path里面自动帮我们添加当前目录进入环境变量,实际上再cmd下是看不到这个存在的,所以要想真正意义上的存在,我们需要使用sys.path.append(path)
并且在导入模块后,如果我们不在各个模块的末尾加上这么一句if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:,,我们会看到有些我们还没有使用这个模块,它就自动调用其中某个函数了,这又是为什么呢接下来我们来揭开它的面纱
模块是对象,并且所有的模块都有一个内置属性 __name__。一个模块的 __name__ 的值取决于您如何应用模块。如果 import 一个模块,那么模块__name__ 的值通常为模块文件名,不带路径或者文件扩展名。但是您也可以像一个标准的程序样直接运行模块,在这 种情况下, __name__ 的值将是一个特别缺省"__main__",示例来源于网络,简单的说就是我们为了避免导入到其他模块中的时候出现非自动调用,我们就需要用上这么一句加以让解释器区分主次
在cmd 中直接运行.py文件,则__name__的值是‘__main__‘;
而在import 一个.py文件后,__name__的值就不是‘__main__‘了;
从而用if __name__ == ‘__main__‘来判断是否是在直接运行该.py文件
如:
#Test.py
class Test:
def __init(self):pass
def f(self):print ‘Hello, World!‘
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
Test().f()
#End
你在cmd中输入:
C:>python Test.py
Hello, World!
说明:"__name__ == ‘__main__‘"是成立的
你再在cmd中输入:
C:>python
>>>import Test
>>>Test.__name__ #Test模块的__name__
‘Test‘
>>>__name__ #当前程序的__name__
‘__main__‘
无论怎样,Test.py中的"__name__ == ‘__main__‘"都不会成立的!
所以,下一行代码永远不会运行到!
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
time模块或者date模块,

1 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_ 2 import time 3 import datetime 4 5 print(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 6 print(time.process_time()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 7 print(time.time()) #返回当前系统时间戳 8 print(time.ctime()) #输出Tue Jan 26 18:23:48 2016 ,当前系统时间 9 print(time.ctime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转为字符串格式 10 print(time.gmtime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转换成struct_time格式 11 print(time.localtime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转换成struct_time格式,但返回 的本地时间 12 print(time.mktime(time.localtime())) #与time.localtime()功能相反,将struct_time格式转回成时间戳格式 13 #time.sleep(4) #sleep 14 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.gmtime()) ) #将struct_time格式转成指定的字符串格式 15 print(time.strptime("2016-01-28","%Y-%m-%d") ) #将字符串格式转换成struct_time格式 16 17 #datetime module 18 19 print(datetime.date.today()) #输出格式 2016-01-26 20 print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()-864400) ) #2016-01-16 将时间戳转成日期格式 21 current_time = datetime.datetime.now() # 22 print(current_time) #输出2016-01-26 19:04:30.335935 23 print(current_time.timetuple()) #返回struct_time格式 24 25 #datetime.replace([year[, month[, day[, hour[, minute[, second[, microsecond[, tzinfo]]]]]]]]) 26 print(current_time.replace(2014,9,12)) #输出2014-09-12 19:06:24.074900,返回当前时间,但指定的值将被替换 27 28 str_to_date = datetime.datetime.strptime("21/11/06 16:30", "%d/%m/%y %H:%M") #将字符串转换成日期格式 29 new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=10) #比现在加10天 30 new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-10) #比现在减10天 31 new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=-10) #比现在减10小时 32 new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=120) #比现在+120s 33 print(new_date)
| Directive | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
%a |
Locale’s abbreviated weekday name. | |
%A |
Locale’s full weekday name. | |
%b |
Locale’s abbreviated month name. | |
%B |
Locale’s full month name. | |
%c |
Locale’s appropriate date and time representation. | |
%d |
Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31]. | |
%H |
Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23]. | |
%I |
Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12]. | |
%j |
Day of the year as a decimal number [001,366]. | |
%m |
Month as a decimal number [01,12]. | |
%M |
Minute as a decimal number [00,59]. | |
%p |
Locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM. | (1) |
%S |
Second as a decimal number [00,61]. | (2) |
%U |
Week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Sunday are considered to be in week 0. | (3) |
%w |
Weekday as a decimal number [0(Sunday),6]. | |
%W |
Week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Monday are considered to be in week 0. | (3) |
%x |
Locale’s appropriate date representation. | |
%X |
Locale’s appropriate time representation. | |
%y |
Year without century as a decimal number [00,99]. | |
%Y |
Year with century as a decimal number. | |
%z |
Time zone offset indicating a positive or negative time difference from UTC/GMT of the form +HHMM or -HHMM, where H represents decimal hour digits and M represents decimal minute digits [-23:59, +23:59]. | |
%Z |
Time zone name (no characters if no time zone exists). |
OS模块
提供对操作系统进行调用的接口

1 os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 2 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd 3 os.curdir 返回当前目录: (‘.‘) 4 os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:(‘..‘) 5 os.makedirs(‘dirname1/dirname2‘) 可生成多层递归目录 6 os.removedirs(‘dirname1‘) 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 7 os.mkdir(‘dirname‘) 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname 8 os.rmdir(‘dirname‘) 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname 9 os.listdir(‘dirname‘) 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 10 os.remove() 删除一个文件 11 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 12 os.stat(‘path/filename‘) 获取文件/目录信息 13 os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\\\",Linux下为"/" 14 os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\\t\\n",Linux下为"\\n" 15 os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 16 os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->‘nt‘; Linux->‘posix‘ 17 os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 18 os.environ 获取系统环境变量 19 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 20 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 21 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 22 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 23 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False 24 os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True 25 os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False 26 os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False 27 os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 28 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 29 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
random模块
随机数

1 import random 2 print random.random() 3 print random.randint(1,2) 4 print random.randrange(1,10)
生成随机验证码

1 import random 2 checkcode = ‘‘ 3 for i in range(4): 4 current = random.randrange(0,4) 5 if current != i: 6 temp = chr(random.randint(65,90)) 7 else: 8 temp = random.randint(0,9) 9 checkcode += str(temp) 10 print checkcode
sys模块
用于提供对Python解释器相关的操作:

1 sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 2 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) 3 sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 4 sys.maxint 最大的Int值 5 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 6 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称 7 sys.stdin 输入相关 8 sys.stdout 输出相关 9 sys.stderror 错误相关
进度百分比

1 import sys 2 import time 3 4 5 def view_bar(num, total): 6 rate = float(num) / float(total) 7 rate_num = int(rate * 100) 8 r = ‘\\r%d%%‘ % (rate_num, ) 9 sys.stdout.write(r) 10 sys.stdout.flush() 11 12 13 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 14 for i in range(0, 100): 15 time.sleep(0.1) 16 view_bar(i, 100)
hashlib
用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法

1 import hashlib 2 3 # ######## md5 ######## 4 hash = hashlib.md5() 5 # help(hash.update) 6 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) 7 print(hash.hexdigest()) 8 print(hash.digest()) 9 10 11 ######## sha1 ######## 12 13 hash = hashlib.sha1() 14 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) 15 print(hash.hexdigest()) 16 17 # ######## sha256 ######## 18 19 hash = hashlib.sha256() 20 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) 21 print(hash.hexdigest()) 22 23 24 # ######## sha384 ######## 25 26 hash = hashlib.sha384() 27 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) 28 print(hash.hexdigest()) 29 30 # ######## sha512 ######## 31 32 hash = hashlib.sha512() 33 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) 34 print(hash.hexdigest())
以上加密算法虽然依然非常厉害,但时候存在缺陷,即:通过撞库可以反解。所以,有必要对加密算法中添加自定义key再来做加密。

1 import hashlib 2 3 # ######## md5 ######## 4 5 hash = hashlib.md5(bytes(‘898oaFs09f‘,encoding="utf-8")) 6 hash.update(bytes(‘admin‘,encoding="utf-8")) 7 print(hash.hexdigest())
python内置还有一个 hmac 模块,它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 进行进一步的处理然后再加密

1 import hmac 2 3 h = hmac.new(bytes(‘898oaFs09f‘,encoding="utf-8")) 4 h.update(bytes(‘admin‘,encoding="utf-8")) 5 print(h.hexdigest())
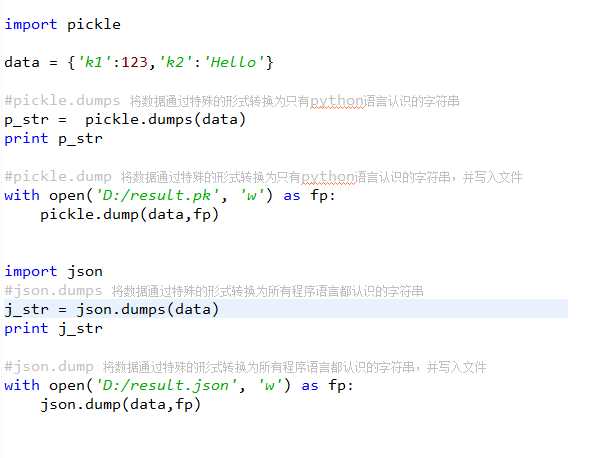
序列化
Python中用于序列化的两个模块
- json 用于【字符串】和 【python基本数据类型】 间进行转换
- pickle 用于【python特有的类型】 和 【python基本数据类型】间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
shutil
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容

1 def copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst, length=16*1024): 2 """copy data from file-like object fsrc to file-like object fdst""" 3 while 1: 4 buf = fsrc.read(length) 5 if not buf: 6 break 7 fdst.write(buf)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
拷贝文件

1 def copyfile(src, dst): 2 """Copy data from src to dst""" 3 if _samefile(src, dst): 4 raise Error("`%s` and `%s` are the same file" % (src, dst)) 5 6 for fn in [src, dst]: 7 try: 8 st = os.stat(fn) 9 except OSError: 10 # File most likely does not exist 11 pass 12 else: 13 # XXX What about other special files? (sockets, devices...) 14 if stat.S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode): 15 raise SpecialFileError("`%s` is a named pipe" % fn) 16 17 with open(src, ‘rb‘) as fsrc: 18 with open(dst, ‘wb‘) as fdst: 19 copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst)
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变

1 def copymode(src, dst): 2 """Copy mode bits from src to dst""" 3 if hasattr(os, ‘chmod‘): 4 st = os.stat(src) 5 mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode) 6 os.chmod(dst, mode)
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags

1 def copystat(src, dst): 2 """Copy all stat info (mode bits, atime, mtime, flags) from src to dst""" 3 st = os.stat(src) 4 mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode) 5 if hasattr(os, ‘utime‘): 6 os.utime(dst, (st.st_atime, st.st_mtime)) 7 if hasattr(os, ‘chmod‘): 8 os.chmod(dst, mode) 9 if hasattr(os, ‘chflags‘) and hasattr(st, ‘st_flags‘): 10 try: 11 os.chflags(dst, st.st_flags) 12 except OSError, why: 13 for err in ‘EOPNOTSUPP‘, ‘ENOTSUP‘: 14 if hasattr(errno, err) and why.errno == getattr(errno, err): 15 break 16 else: 17 raise
shutil.copy(src, dst)
拷贝文件和权限

1 def copy(src, dst): 2 """Copy data and mode bits ("cp src dst"). 3 4 The destination may be a directory. 5 6 """ 7 if os.path.isdir(dst): 8 dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src)) 9 copyfile(src, dst) 10 copymode(src, dst)
shutil.copy2(src, dst)
拷贝文件和状态信息

1 def copy2(src, dst): 2 """Copy data and all stat info ("cp -p src dst"). 3 4 The destination may be a directory. 5 6 """ 7 if os.path.isdir(dst): 8 dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src)) 9 copyfile(src, dst) 10 copystat(src, dst)
shutil.ignore_patterns(*patterns)
shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None)
递归的去拷贝文件
例如:copytree(source, destination, ignore=ignore_patterns(‘*.pyc‘, ‘tmp*‘))

1 def ignore_patterns(*patterns): 2 """Function that can be used as copytree() ignore parameter. 3 4 Patterns is a sequence of glob-style patterns 5 that are used to exclude files""" 6 def _ignore_patterns(path, names): 7 ignored_names = [] 8 for pattern in patterns: 9 ignored_names.extend(fnmatch.filter(names, pattern)) 10 return set(ignored_names) 11 return _ignore_patterns 12 13 def copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None): 14 """Recursively copy a directory tree using copy2(). 15 16 The destination directory must not already exist. 17 If exception(s) occur, an Error is raised with a list of reasons. 18 19 If the optional symlinks flag is true, symbolic links in the 20 source tree result in symbolic links in the destination tree; if 21 it is false, the contents of the files pointed to by symbolic 22 links are copied. 23 24 The optional ignore argument is a callable. If given, it 25 is called with the `src` parameter, which is the directory 26 being visited by copytree(), and `names` which is the list of 27 `src` contents, as returned by os.listdir(): 28 29 callable(src, names) -> ignored_names 30 31 Since copytree() is called recursively, the callable will be 32 called once for each directory that is copied. It returns a 33 list of names relative to the `src` directory that should 34 not be copied. 35 36 XXX Consider this example code rather than the ultimate tool. 37 38 """ 39 names = os.listdir(src) 40 if ignore is not None: 41 ignored_names = ignore(src, names) 42 else: 43 ignored_names = set() 44 45 os.makedirs(dst) 46 errors = [] 47 for name in names: 48 if name in ignored_names: 49 continue 50 srcname = os.path.join(src, name) 51 dstname = os.path.join(dst, name) 52 try: 53 if symlinks and os.path.islink(srcname): 54 linkto = os.readlink(srcname) 55 os.symlink(linkto, dstname) 56 elif os.path.isdir(srcname): 57 copytree(srcname, dstname, symlinks, ignore) 58 else: 59 # Will raise a SpecialFileError for unsupported file types 60 copy2(srcname, dstname) 61 # catch the Error from the recursive copytree so that we can 62 # continue with other files 63 except Error, err: 64 errors.extend(err.args[0]) 65 except EnvironmentError, why: 66 errors.append((srcname, dstname, str(why))) 67 try: 68 copystat(src, dst) 69 except OSError, why: 70 if WindowsError is not None and isinstance(why, WindowsError): 71 # Copying file access times may fail on Windows 72 pass 73 else: 74 errors.append((src, dst, str(why))) 75 if errors: 76 raise Error, errors
shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]])
递归的去删除文件

1 def rmtree(path, ignore_errors=False, onerror=None): 2 """Recursively delete a directory tree. 3 4 If ignore_errors is set, errors are ignored; otherwise, if onerror 5 is set, it is called to handle the error with arguments (func, 6 path, exc_info) where func is os.listdir, os.remove, or os.rmdir; 7 path is the argument to that function that caused it to fail; and 8 exc_info is a tuple returned by sys.exc_info(). If ignore_errors 9 is false and onerror is None, an exception is raised. 10 11 """ 12 if ignore_errors: 13 def onerror(*args): 14 pass 15 elif onerror is None: 16 def onerror(*args): 17 raise
以上是关于python-day05的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
