linux高性能服务器编程之poll
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了linux高性能服务器编程之poll相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.概述:
和select不同的是,poll使用一个pollfd来指向所要监听的fd,事件,返回事件。(pollfd下面详细讲。)
并且poll没有最大的文件描述符数量的限制,是自己定义一个pollfd数组来实现的。
它的缺点和select差不多,即
(1)每次调用poll,都需要把fd集合从用户态拷贝到内核态,这个开销在fd很多时会很大
(2)当要确定一个文件描述符的状态时,都需要在内核遍历传递进来的所有fd,这个开销在fd很多时也很大
二.poll介绍篇:
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
函数功能:监听fds中的所有文件描述符,并当某个文件描述符准备好时对这个文件描述符进行相应的设置。
返回值:成功返回准备好的文件描述符个数,返回0时代表timeout,失败返回-1.
fds参数:输出型参数,保持了相应的fd,放到所监听的事件,fd准备好时返回的事件。
struct pollfd结构体如下:
The set of file descriptors to be monitored is specified in the fds argument, which is an array of structures of the following
form:
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */
short events; /* requested events */
short revents; /* returned events */
};nfds参数:fds数组的大小。
timeout参数:超出时间。单位为毫秒。
三.代码篇:
用poll实现一个较为高效的服务器:
server.c:
1 /**************************************** 2 > File Name:poll_server.c 3 > Author:xiaoxiaohui 4 > mail:[email protected] 5 > Created Time:2016年05月28日 星期六 13时36分52秒 6 ****************************************/ 7 8 #include<stdio.h> 9 #include<poll.h> 10 #include<sys/types.h> 11 #include<sys/socket.h> 12 #include<netinet/in.h> 13 #include<arpa/inet.h> 14 #include<string.h> 15 #include<stdlib.h> 16 #include<unistd.h> 17 18 #define LEN 1024 19 const int PORT = 8080; 20 const char* IP = "127.0.0.1"; 21 const int BACKLOG = 5; 22 struct sockaddr_in local; 23 struct sockaddr_in client; 24 int SIZE_CLIENT = sizeof(client); 25 #define _MAX_ 64 26 struct pollfd pfds[_MAX_]; 27 int timeout = 5000; 28 29 int ListenSock() 30 { 31 int listenSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 32 if(listenSock < 0) 33 { 34 perror("socket"); 35 exit(1); 36 } 37 38 local.sin_family = AF_INET; 39 local.sin_port = htons(PORT); 40 local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(IP); 41 if( bind(listenSock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) 42 { 43 perror("bind"); 44 exit(2); 45 } 46 47 if( listen(listenSock, BACKLOG) < 0) 48 { 49 perror("listen"); 50 exit(3); 51 } 52 53 return listenSock; 54 } 55 56 57 int main() 58 { 59 int listenSock = ListenSock(); //获得一个监听套接字 60 61 pfds[0].fd = listenSock; //对listenSock进行设置 62 pfds[0].events = POLLIN; //listenSock关心只读事件 63 pfds[0].revents = 0; 64 65 int nfds = _MAX_; 66 int index = 1; 67 for(; index < nfds; index++) //初始化pfds中的fd 68 { 69 pfds[index].fd = -1; 70 } 71 72 while(1) 73 { 74 switch( poll(pfds, nfds, timeout)) 75 { 76 case 0: //timeout 77 printf("timeout.......\n"); 78 break; 79 case -1: //error 80 perror("poll"); 81 sleep(1); 82 break; 83 default: 84 for(int i = 0; i < nfds; i++) 85 { 86 if(pfds[i].fd == listenSock && (pfds[i].revents & POLLIN)) //listenSock就绪 87 { 88 int linkSock = accept(listenSock, (struct sockaddr*)&client, &SIZE_CLIENT); 89 if(linkSock < 0) 90 { 91 perror("accept"); 92 break; 93 } 94 printf("a new client is connected\n"); 95 96 int j = 0; 97 for(; j < nfds; j++) 98 { 99 if(pfds[j].fd < 0) 100 { 101 break; 102 } 103 } 104 pfds[j].fd = linkSock; //把linkSock添加到pfds中 105 pfds[j].events = POLLIN; 106 pfds[j].revents = 0; 107 } 108 else if(pfds[i].revents & POLLIN) //数据已经准备好,可以进行读操作 109 { 110 char buf[LEN]; 111 int fd = pfds[i].fd; 112 113 memset(buf, ‘\0‘,LEN); 114 int ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); 115 if(ret > 0) //read success 116 { 117 buf[ret] = ‘\0‘; 118 printf("client# %s\n", buf) ; 119 } 120 else if(ret == 0) //client close 121 { 122 pfds[i].fd = -1; 123 pfds[i].events = 0; 124 pfds[i].events = 0; 125 close(pfds[i].fd); 126 } 127 else //error 128 { 129 perror("read"); 130 continue; 131 } 132 133 write(fd, buf, strlen(buf)); //在此没有考虑POLLOUT事件 134 } 135 } 136 break; 137 } 138 } 139 140 return 0; 141 } 142
client.c:
1 /**************************************** 2 > File Name:client.c 3 > Author:xiaoxiaohui 4 > mail:[email protected] 5 > Created Time:2016年05月23日 星期一 12时30分01秒 6 ****************************************/ 7 8 #include<stdio.h> 9 #include<stdlib.h> 10 #include<string.h> 11 #include<sys/types.h> 12 #include<sys/socket.h> 13 #include<netinet/in.h> 14 #include<arpa/inet.h> 15 #include<sys/time.h> 16 #include<unistd.h> 17 18 #define LEN 1024 19 const int PORT = 8080; 20 const char* IP = "127.0.0.1"; 21 struct sockaddr_in server; 22 int clientSock; 23 char buf[LEN]; 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 clientSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 28 if(clientSock < 0) 29 { 30 perror("socket"); 31 exit(1); 32 } 33 34 server.sin_family = AF_INET; 35 server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(IP); 36 server.sin_port = htons(PORT); 37 38 if ( connect(clientSock, (struct sockaddr*)&server, sizeof(server)) < 0) 39 { 40 perror("connect"); 41 exit(2); 42 } 43 44 while(1) 45 {linux高性能服务器编程之poll 46 memset(buf, ‘\0‘, LEN); 47 printf("please input: "); 48 gets(buf); 49 write(clientSock, buf, strlen(buf)); 50 51 memset(buf, ‘\0‘, LEN); 52 int ret = read(clientSock, buf, LEN); 53 buf[ret] = ‘\0‘; 54 printf("echo: %s\n", buf); 55 } 56 57 return 0; 58 }
Makefile:
1 .PHONY:all 2 all:server client 3 4 server:poll_server.c 5 gcc -o [email protected] $^ -g 6 client:poll_client.c 7 gcc -o [email protected] $^ -g 8 9 .PHONY:clean 10 clean: 11 rm -f server client ~
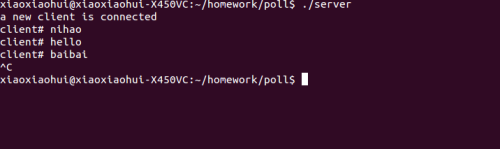
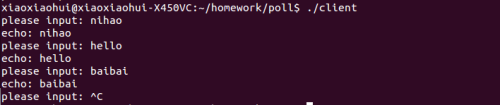
执行结果:
四.总结:
epoll没有reads,writes,exports这三个输入输出型参数,而是用一个pollfd指针来实现这三个参数的功能,所以看上去poll比select更简洁一点。
虽然poll没有文件描述符数量上的限制,但还是存在两个和select一样的缺点,即因为文件描述符是内核管理的,所以在调用poll时会把所有的文件描述符从用户空间拷贝到内核中,当要监测相关文件描述符的状态时,也要在内核中遍历文件描述符集,当要监听的文件描述符集很大时,效率会比较低。
本文出自 “水仙花” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://10704527.blog.51cto.com/10694527/1784666
以上是关于linux高性能服务器编程之poll的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章