SPI应用 用SPI控制一个数字电位器
Posted MyAutomation
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SPI应用 用SPI控制一个数字电位器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Controlling a Digital Potentiometer Using SPI
In this tutorial you will learn how to control the AD5206 digital potentiometer(数字电位计) using Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI). For an explanation of SPI see the SPI Library reference.
Digital potentiometers are useful when you need to vary the resistance in a circuit electronically rather than by hand. Example applications include LED dimming调光, audio signal conditioning and tone generation. In this example we will use a six channel digital potentiometer to control the brightness of six LEDs. The steps we will cover for implementing实施 SPI communication can be modified for use with most other SPI devices.
Hardware Required 硬件准备
- Arduino or Genuino board
- AD5206 Digital Potentiometer
- 6 LEDs
- 6 220 ohm resistors
- hook-up wires电子安装线
- breadboard
Introduction to the AD5206 Digital Potentiometer
Click for for the AD5206\'s datasheet.
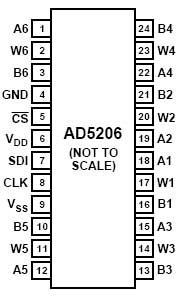

The AD5206 is a 6 channel digital potentiometer. (AD5206是8通道的数字电位器)。 This means it has six variable resistors (potentiometers) built in for individual electronic control. There are three pins on the chip for each of the six internal variable resistors, and they can be interfaced with just as you would use a mechanical potentiometer. The individual variable resistor pins are labeled Ax, Bx and Wx, ie. A1, B1 and W1. For example, in this tutorial we will be using each variable resistor as a voltage divider by pulling one side pin (pin B) high, pulling another side pin (pin A) low and taking the variable voltage output of the center pin (Wiper滑片). In this case, the AD5206 provides a maximum resistance of 10k ohm, delivered in 255 steps (255 being the max, 0 being the least).(可以得到最大电阻10K欧姆,最小0欧模,分为255步幅)
Circuit 电路图
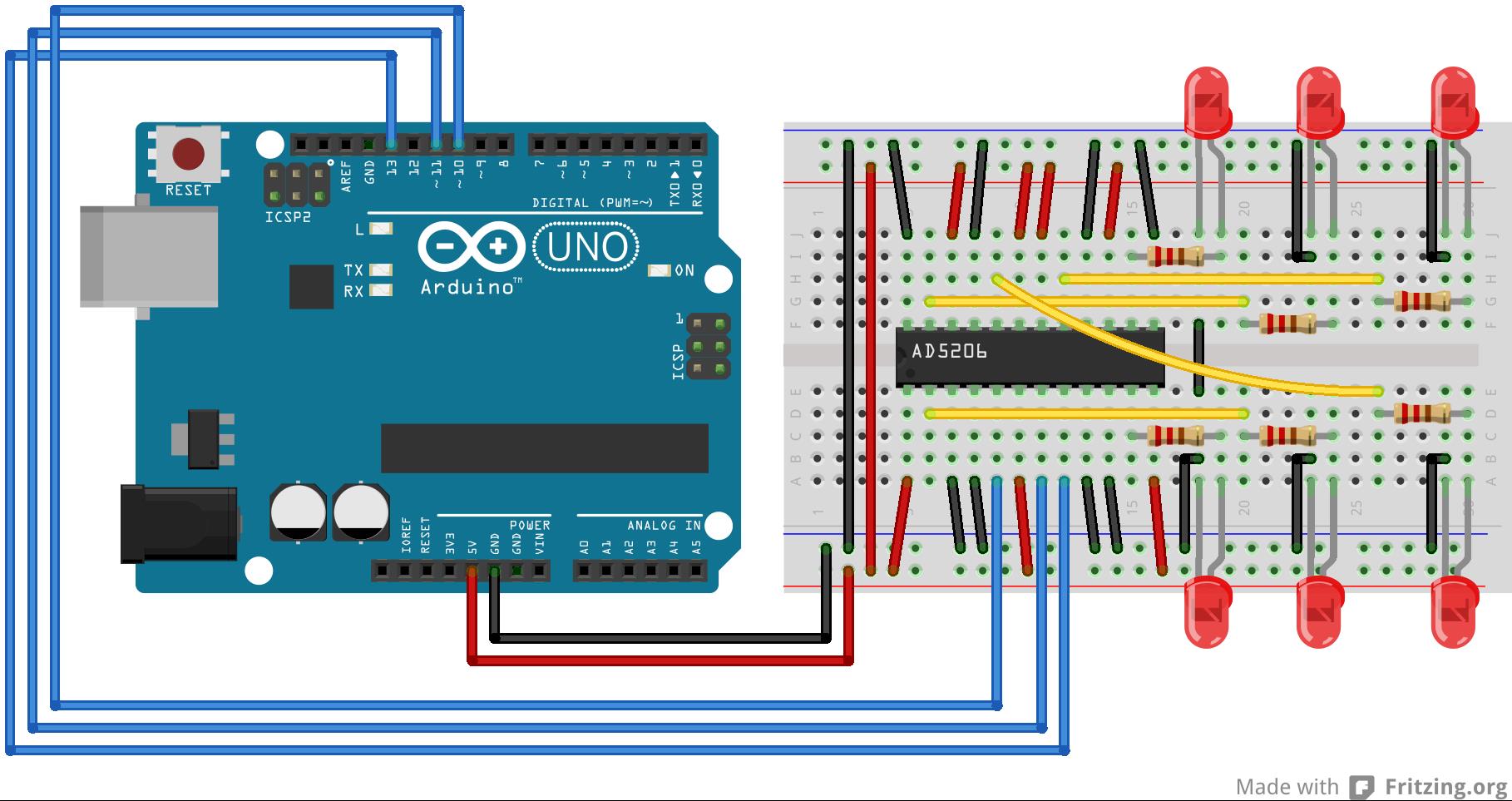
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic 原理图

1 Code 代码 2 3 /* 4 5 Digital Pot Control 数字电位器的控制 6 7 8 9 This example controls an Analog Devices AD5206 digital potentiometer. 10 11 The AD5206 has 6 potentiometer channels. Each channel\'s pins are labeled 12 13 A - connect this to voltage 14 15 W - this is the pot\'s wiper, which changes when you set it 16 17 B - connect this to ground. 18 19 每隔通道有三个端,A,B,W,A接工作电压,W接滑动端,C接地 20 21 The AD5206 is SPI-compatible, and to command it, you send two bytes, one with the channel number (0 - 5) and one with the resistance value for the channel (0 - 255). 22 23 24 25 The circuit: 26 27 * All A pins of AD5206 connected to +5V 28 29 * All B pins of AD5206 connected to ground 30 31 * An LED and a 220-ohm resisor in series connected from each W pin to ground 32 33 每个W引脚的LED串220欧电阻 34 35 * CS - to digital pin 10 (SS pin) 片选引脚CS接到控制板的引脚10 36 37 * SDI - to digital pin 11 (MOSI pin) SDI引脚接到控制板的引脚11 38 39 * CLK - to digital pin 13 (SCK pin) CLK 引脚接到控制板的引脚13 40 41 42 43 created 10 Aug 2010 44 45 by Tom Igoe 46 47 48 Thanks to Heather Dewey-Hagborg for the original tutorial, 2005 49 50 51 52 */ 53 54 55 56 // inslude the SPI library: 57 58 #include <SPI.h> 59 60 61 62 // set pin 10 as the slave select for the digital pot: 63 64 const int slaveSelectPin = 10; // 从选择引脚 65 66 67 68 void setup() 69 70 { 71 72 pinMode(slaveSelectPin, OUTPUT); // set the slaveSelectPin as an output 73 74 SPI.begin(); // initialize SPI 75 76 } 77 78 79 80 void loop() 81 82 { 83 84 // go through the six channels of the digital pot: 循环数字电位器的六个通道 85 86 for (int channel = 0; channel < 6; channel++) 87 88 { 89 90 // change the resistance on this channel from min to max: 电阻从小到大 91 92 for (int level = 0; level < 255; level++) 93 94 { 95 96 digitalPotWrite(channel, level); 97 98 delay(10); 99 100 } 101 102 delay(100); // wait a second at the top 103 104 // change the resistance on this channel from max to min: 电阻从大到小 105 106 for (int level = 0; level < 255; level++) 107 108 { 109 110 digitalPotWrite(channel, 255 - level); 111 112 delay(10); 113 114 } 115 116 } 117 118 } 119 120 121 122 void digitalPotWrite(int address, int value) 123 124 { 125 126 // take the SS pin low to select the chip: SS引脚置低选中该芯片 127 128 digitalWrite(slaveSelectPin, LOW); 129 130 // send in the address and value via SPI: 131 132 SPI.transfer(address); //传送地址 133 134 SPI.transfer(value); //传送数值 135 136 // take the SS pin high to de-select the chip: SS引脚置高释放该芯片 137 138 digitalWrite(slaveSelectPin, HIGH); 139 140 }
运行效果:从第1通道开始,每个通道的LED,从最暗到最亮,0.1秒后,再从最亮到最暗。
以上是关于SPI应用 用SPI控制一个数字电位器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章