hibernate进阶hibernate持久化对象的三种状态
Posted 陈晓婵
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了hibernate进阶hibernate持久化对象的三种状态相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
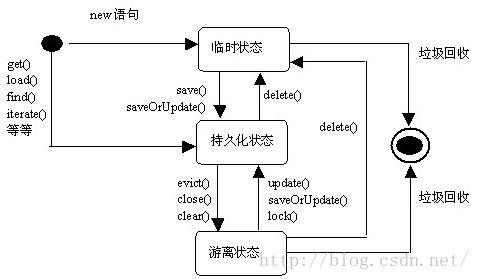
Hibernate持久化对象的三种状态:瞬时对象(Transient Objects),持久化对象(Persist Objects),离线对象(Detached Objects)。
三种状态:
瞬时对象(Transient Objects):使用new 操作符初始化的对象不是立刻就持久的。它们的状态是瞬时的,也就是说他们没有任何跟数据库表相关联的行为,只要应用不在引用这些对象(不再被任何其他对象所引用),它们的状态将会丢失,并由垃圾回收机制回收。持久化对象(Persist Objects):持久实例是任何具有数据库标识的实例。它有持久化管理器session统一管理,持久实例是在事务中进行操作的——它们的状态在事务结束时同数据库进行同步。当事务提交时,通过执行SQL的INSERT,UPDATE和DELETE语句把内存中的状态同步到数据库中。
离线对象(Detached Objects):session关闭之后,持久化对象就变为离线对象。离线表示这个对象不能再与数据库保持同步,它们不再受hibernate管理。
状态转换:
持久化对象的三种状态是可以相互转化的,具体转换过程如图所示:
实例讲解:
TO→PO:
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;"><strong><span style="font-size:18px;">public void testSave1() {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//Transient状态
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setPassword("123");
Date date=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat temp=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String date2=temp.format(date);
Date date3=temp.parse(date2);
user.setCreateTime(date3);
user.setExpireTime(date3);
//Persistent状态
//Persistent状态的对象,当对象的属性发生改变的时候
//hibernate在清理缓存(脏数据检查)的时候,会和数据库同步
session.save(user);
user.setName("lisi");
tx.commit();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx != null) {
tx.rollback();
}
}finally {
HibernateUtils.closeSession(session);
}
//detached状态
}</span></strong></span></strong>输出的结果:
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;"><strong><span style="font-size:18px;">Hibernate: insert into User (name, password, createTime, expireTime, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: update User set name=?, password=?, createTime=?, expireTime=? where id=?</span></strong></span></strong>TO→PO→DO→PO:
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;"> <strong><span style="font-size:18px;">public void testSave3() {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
User user = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
//Transient状态
user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setPassword("123");
Date date=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat temp=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String date2=temp.format(date);
Date date3=temp.parse(date2);
user.setCreateTime(date3);
user.setExpireTime(date3);
//Persistent状态
//Persistent状态的对象,当对象的属性发生改变的时候
//hibernate在清理缓存(脏数据检查)的时候,会和数据库同步
session.save(user);
user.setName("lisi");
tx.commit();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx != null) {
tx.rollback();
}
}finally {
HibernateUtils.closeSession(session);
}
//detached状态
user.setName("wangwu");
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
session.beginTransaction();
//将detached状态的对象重新纳入session管理
//此时将变为persistent状态的对象
//persistent状态的对象,在清理缓存是会和数据库同步
session.update(user);
session.getTransaction().commit();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
session.getTransaction().rollback();
}finally {
HibernateUtils.closeSession(session);
}
} </span></strong></span></strong>
<strong><span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-size:18px;"><strong>Hibernate: insert into User (name, password, createTime, expireTime, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: update User set name=?, password=?, createTime=?, expireTime=? where id=?
Hibernate: update User set name=?, password=?, createTime=?, expireTime=? where id=?</strong></span></span></strong>
总结:
以上是关于hibernate进阶hibernate持久化对象的三种状态的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章