进程间的通信----管道
Posted 秋雨丶梧桐
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了进程间的通信----管道相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前提:本文是基于Linux系统下的学习
用户态的进程是如何组织的呢?
所有的用户态进构成了一棵树。进程树。
进程树的树根是init.也就是1号进程。是用户态进程的祖宗进程。
如何查看进程树?
pstree
进程之间的关系 父子进程和兄弟进程
查看进程的信息
ps -aux
实时查看进程的使用情况 top
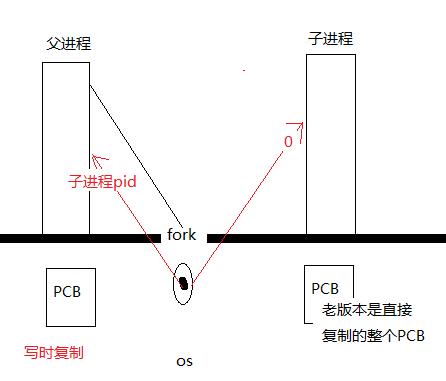
如何创建一个进程?
fork(2) 可以创建一个子进程。
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
功能:创建一个子进程。函数的调用者是父进程,新创建的进程是子进程
参数:void
返回值:
成功 父进程中返回子进程的pid
子进程中返回0
失败 父进程中返回-1. errno被设置
子进程创建失败
进程的终止
return和exit(3)
return 只是从函数调用中返回。结束了函数的执行。在main函数中返回,并没有结束进程
exit(3) 这个函数被调用的时候,结束当前进程。
无名管道和有名管道
无名管道--应用于具有亲属关系的进程间通信
pipe(2) 创建无名管道
pipefd[0] 指向读端;pipefd[1]指向写端
1 //无名管道必须是带有亲属关系的 父子or兄弟 2 //无名管道实现进程间通信 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <stdlib.h> 7 int main(){ 8 char buf[128]; 9 char* msg="hello,father\\n"; 10 int pfd[2]; 11 //创建无名管道 12 int p=pipe(pfd);//pfd[0] read; pfd[1] write 13 if(p==-1){ 14 perror("pipe"); 15 return -1; 16 } 17 //创建子进程 18 pid_t pid=fork(); 19 if(pid==-1){ 20 perror("fork"); 21 return -1; 22 } 23 if(pid==0){//son 24 close(pfd[0]);//关闭读 25 write(pfd[1],msg,strlen(msg)); 26 close(pfd[1]); 27 exit(0); 28 } 29 else{//father 30 close(pfd[1]); 31 int r=read(pfd[0],buf,128); 32 write(1,buf,r); 33 close(pfd[0]); 34 wait(NULL); 35 } 36 return 0; 37 }
有名管道:其实就是一个文件,这个文件没有内容,只是起到一个桥梁的作用
mkfifo(3)
1 //mkfifo.c 2 //创建管道文件 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 7 int main(int argc,char* argv[]){ 8 int mk=mkfifo(argv[1],0644); 9 if(mk==-1){ 10 perror("mkfifo"); 11 return -1; 12 } 13 return 0; 14 }
//fifo_w.c #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main(int argc,char* argv[]){ char* msg="hello.read\\n"; //打开管道文件 int fd=open(argv[1],O_WRONLY); if(fd==-1){ perror("open"); return -1; } //向管道文件中写 write(fd,msg,strlen(msg)); close(fd); return 0; }
1 //fifo_r.c 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <sys/stat.h> 5 #include <fcntl.h> 6 7 int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ 8 char buf[128]; 9 int fd=open(argv[1],O_RDONLY); 10 if(fd==-1){ 11 perror("open"); 12 return -1; 13 } 14 int r=read(fd,buf,128); 15 write(1,buf,r); 16 close(fd); 17 return 0; 18 }
以上是关于进程间的通信----管道的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章