稀疏矩阵
Posted guoyujiang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了稀疏矩阵相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SparseMatrix
存储:
使用三元表存储,即结构体数组
struct element
{
int row, col;//元素item在矩阵中的位置
T item;
};
矩阵转置方法:A->B(A按行存储,要求转置得到的矩阵按列存储)
1、直接取,顺序存
从左到右,上到下进行存储
2、顺序取,直接存
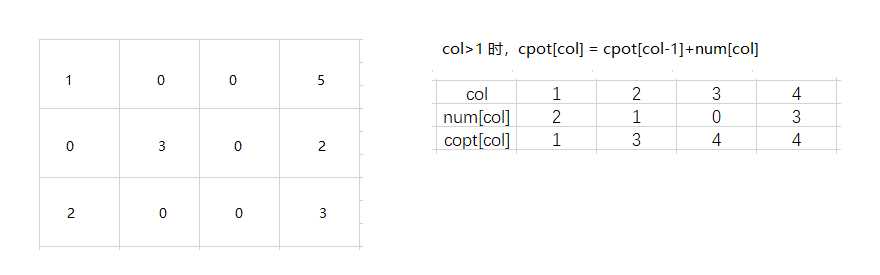
计算每一列的元素数目和每一列非零元素的位置上
1 for (i = 0; i<A.tu; i++) //遍历A的所有元素 2 { 3 j = A.data[i].col;//三元表A的元素i的列号 4 k = cpot[j];//k为待存元素在B中的位置 5 B.data[k].row = A.data[i].col; 6 B.data[k].col = A.data[i].row; 7 B.data[k].item = A.data[i].item; 8 cpot[j]++;//A中记录在cpot中的每一列非零元素改变 9 }
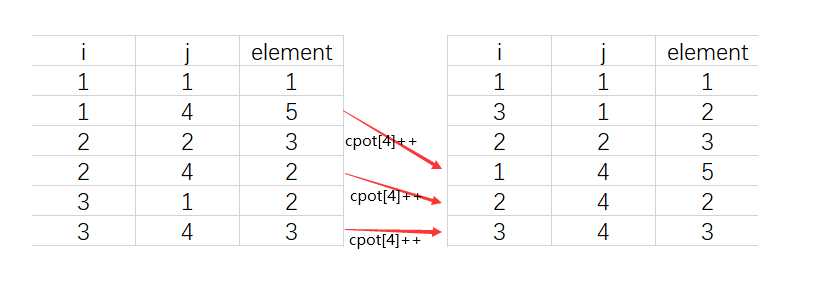
以列号j=4做示范:
当一个元素的列满足要求时,得到k = cpot[j], k为B的三元表中待存位置,然后cpot[j]++,使下一个同列元素存在其下

1 //稀疏矩阵 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 const int MAXTERM = 100;//三元表最长长度 6 7 template<class T> 8 struct element 9 { 10 int row, col;//元素item在矩阵中的位置 11 T item; 12 }; 13 14 template<class T> 15 class SparseMatrix 16 { 17 public: 18 SparseMatrix() {} 19 //有参数的构造函数 20 SparseMatrix(int intmu, int intnu, int inttu, element<T> datatemp[]); 21 ~SparseMatrix() {}//释放空间 22 element<T> GetMatrix(int intnumber);//输出对应下标下的数组元素【索引值】 23 void Prt();//打印三元组顺序表 24 void Trans1(SparseMatrix<T> &B);//矩阵的转置,直接取,顺序存 25 void Trans2(SparseMatrix<T> A, SparseMatrix<T> &B);//矩阵的转置,顺序取,直接存 26 private: 27 element<T>data[MAXTERM]; 28 int mu, nu, tu;//矩阵的行,列,不同元素个数 29 }; 30 31 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 32 { 33 try { 34 element<int> elementtemp1, elementtemp2, elementtemp3; 35 elementtemp1.col = 0, elementtemp1.row = 0, elementtemp1.item = 15; 36 elementtemp2.col = 1, elementtemp2.row = 2, elementtemp2.item = 16; 37 elementtemp3.col = 1, elementtemp3.row = 0, elementtemp3.item = 17; 38 //(0,0),(0,1),(2,1) 39 element<int> A[3]; 40 A[0] = elementtemp1, A[1] = elementtemp2, A[2] = elementtemp3; 41 42 SparseMatrix<int> sparsematrixB; 43 SparseMatrix<int> sparsematrixA(3, 3, 3, A); 44 45 cout << "源三元组顺序表如下:" << endl; 46 sparsematrixA.Prt(); 47 sparsematrixA.Trans1(sparsematrixB); 48 cout << "使用直接取、顺序存转置算法转置后的三元组顺序表如下:" << endl; 49 sparsematrixB.Prt(); 50 sparsematrixA.Trans2(sparsematrixA, sparsematrixB); 51 cout << "使用顺序取、直接存转置算法后的三元组顺序表如下:" << endl; 52 sparsematrixB.Prt(); 53 } 54 catch (char *s) 55 { 56 cout << s << endl; 57 } 58 system("pause"); 59 return 0; 60 } 61 62 template<class T> 63 SparseMatrix<T>::SparseMatrix(int intmu, int intnu, int inttu, element<T> datatemp[]) 64 { 65 if (inttu>MAXTERM) 66 throw"构造函数的初始化参数不正确"; 67 mu = intmu, nu = intnu, tu = inttu; 68 for (int i = 0; i<inttu; i++) 69 data[i] = datatemp[i]; 70 } 71 72 template<class T> 73 element<T> SparseMatrix<T>::GetMatrix(int intnumber) 74 { 75 if (intnumber<0 || intnumber >= tu) 76 throw"输入位置不正确"; 77 return data[i]; 78 } 79 80 template<class T> 81 void SparseMatrix<T>::Prt() 82 { 83 for (int i = 0; i<tu; i++) 84 cout << "row:" << data[i].row << ",col:" << data[i].col << ",item:" << data[i].item << endl; 85 } 86 87 88 89 template<class T>//待转置的源三元组顺序表A和目标三元顺序表B的引用 90 void SparseMatrix<T>::Trans1(SparseMatrix<T> &B) 91 { 92 int pb; 93 B.mu = nu, B.nu = mu, B.tu = tu; 94 95 if (B.tu>0) 96 { 97 pb = 0; 98 for (int col = 0; col < nu; col++) 99 for (int i = 0; i < tu; i++) 100 if (data[i].col == col) 101 { 102 B.data[pb].row = data[i].col; 103 B.data[pb].col = data[i].row; 104 B.data[pb++].item = data[i].item; 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 109 template<class T> 110 void SparseMatrix<T>::Trans2(SparseMatrix<T> A, SparseMatrix<T> &B) 111 { 112 B.mu = A.nu, B.nu = A.mu, B.tu = A.tu; 113 int i, j, k, num[MAXTERM], cpot[MAXTERM]; 114 if (B.tu > 0) 115 { 116 for (i = 0; i<A.nu; i++) 117 num[i] = 0;//A中每一列的非零个数,初始化为0 118 for (i = 0; i<A.tu; i++) 119 { 120 j = A.data[i].col; 121 num[j]++;//得到A每一列的元素数,得到num[i] 122 } 123 cpot[0] = 0;//A中第0列中第一个元素在B的三元表中位置为0 124 for (i = 1; i<A.nu; i++) 125 cpot[i] = cpot[i - 1] + num[i - 1];//求A中第i列第一个非零元素在B的三元表中的下标 126 127 for (i = 0; i<A.tu; i++) 128 { 129 j = A.data[i].col;//三元组元素i的列号 130 k = cpot[j];//A中第j列的非零元素的下标【行号】 131 B.data[k].row = A.data[i].col; 132 B.data[k].col = A.data[i].row; 133 B.data[k].item = A.data[i].item; 134 cpot[j]++;//A中第j列的非零元素下标【行号】下移 135 } 136 } 137 }
以上是关于稀疏矩阵的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
