策略模式
Posted shareandstudy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了策略模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
策略模式简述
策略模式作为一种软件设计模式,指对象有某个行为,但是在不同的场景中,该行为有不同的实现算法。策略模式属于对象的行为模式。其用意是针对一组算法,将每一个算法封装到具有共同接口的独立的类中,从而使得它们可以相互替换。最直接的例子就是我们java api使用的Comparator接口,类如我现在想对自定义Student类型数据进行排序。我们需要自定义一个比较策略才能进行排序,每种比较策略就是就是一种算法,把每种比较策略封装在特定策略类方法中,然后根据需要调用相应的策略类的策略方法进行排序就行了。
策略模式结构
已自定义的Comparator接口为例,对自定义的Student类型的数据进行排序,uml图如下:
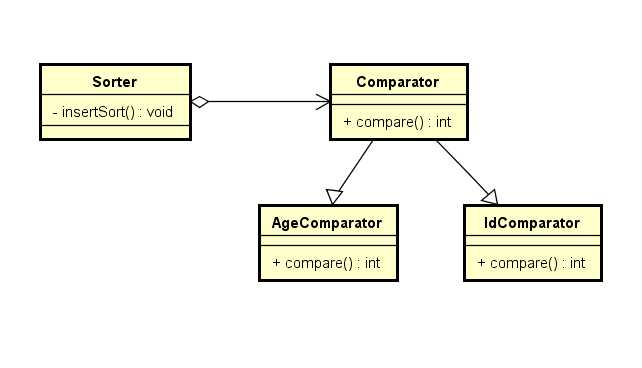
这个模式涉及到三个角色:
● 环境(Context)角色:持有一个策略接口型引用。在本例子就是Sorter类
● 抽象策略(Strategy)角色:这是一个抽象角色,通常由一个接口或抽象类实现。此角色给出所有的具体策略类所需的接口。在本例子中就是自定义的Comparator接口。
● 具体策略(ConcreteStrategy)角色:在本例子就是AgeComparator跟IdComparator。
策略模式案例
现在以自定义一个Comparator为例来解释策略模式。还是以自定义的Student类型数据排序为例,现在需要实现按age排序,id排序,代码如下:
定义一个Student
public class Student { private String stuName; private int stuId; private int stuAge; public String getStuName() { return stuName; } public void setStuName(String stuName) { this.stuName = stuName; } public int getStuAge() { return stuAge; } public void setStuAge(int stuAge) { this.stuAge = stuAge; } public int getStuId() { return stuId; } public void setStuId(int stuId) { this.stuId = stuId; } public Student(String stuName, int stuId, int stuAge) { this.stuName = stuName; this.stuId = stuId; this.stuAge = stuAge; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "stuName=‘" + stuName + ‘‘‘ + ", stuId=" + stuId + ", stuAge=" + stuAge + ‘}‘; } }
定义一个比较器接口Comparator
public interface Comparator<T> { int compare(T o1, T o2); }
定义一个具体比较器AgeComparator
public class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student> { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.getStuAge()-o2.getStuAge(); } }
定义一个具体比较器IdComparator
public class IdComparator implements Comparator<Student> { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.getStuId()-o2.getStuId(); } }
定义环境角色Sorter排序类
public class Sorter <T>{ Comparator<T> comparator; public Sorter(Comparator<T> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } public void insertSort(T [] ary ) { for (int i = 1; i < ary.length; i++) { int j=i;//j为要插入元素下标 T temp=ary[i];//暂存要插入的元素 while(j>0&&comparator.compare(ary[j-1],temp)>0) {//将要插入元素与已排序的数组元素进行比较,找到要插入的位置 ary[j]=ary[j-1]; j--; } ary[j]=temp;//插入要插入的元素 } } }
客户端测试类
public class StrategyClient { public static void main(String[] args) { Student [] students=new Student[]{new Student("jack",23,34),new Student("mary",22,20), new Student("jerk",25,33)}; cn.ck.strategy.Comparator ageComparater=new AgeComparator(); cn.ck.strategy.Comparator idComparater=new IdComparator(); //按照age排序 //Sorter<Student> sorter=new Sorter<Student>(ageComparater); //sorter.insertSort(students); //按照id排序 Sorter<Student> sorter1=new Sorter<Student>(idComparater); sorter1.insertSort(students); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(students)); }
策略模式的优点
(1)策略模式用继承(实现)的方式合理管理算法族。通过继承可以把公共的代码移到父类里面,从而避免代码重复。
(2)使用策略模式可以避免使用多重条件(if-else)语句。多重条件语句不易维护,它把采取哪一种算法或采取哪一种行为的逻辑与算法或行为的逻辑混合在一起,统统列在一个多重条件语句里面,比使用继承的办法还要原始和落后。
策略模式的缺点
(1)客户端必须知道所有的策略类,并自行决定使用哪一个策略类。这就意味着客户端必须理解这些算法的区别,以便适时选择恰当的算法类。换言之,策略模式只适用于客户端知道算法或行为的情况。
(2)由于策略模式把每个具体的策略实现都单独封装成为类,如果备选的策略很多的话,那么对象的数目就会很多
以上是关于策略模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章