Java-IO流总结
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java-IO流总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
IO流:
IO流分为两大类:字节流和字符流
IO的作用就是为了读写操作的。
每种流都分为输入流(Input)、输出流(Output);站在java程序的角度来说,java程序进行读取操作时,就是输入流;如果java程序向其他地方(硬盘,其他的设备)写入操作时,就是输出流。
IO流只能操作文件,不能操作文件夹,否则会报错。
字节流:
字节输入流:InputStream
字节输出流:OutputStream
OutputStream:
可以向文件中写入字节,进行写入常用的是OutputStream的子类:FileOutputStream,常用的写入方法是write(byte[]),传入byte数组。
下面将是演示利用FileOutputStream来进行写入文件:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /** * 使用FileOutputStream来写入文件 * @throws IOException * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建FileOutputStream对象 // write.txt 文件在项目的根目录下面 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("write.txt"); // 准备byte数组 byte[] b = "Hello every body!".getBytes(); // 写入整个数组 fos.write(b); // 写入换行符,System.lineSeparator()方法返回一个字符串,表示跨平台的换行符 fos.write(System.lineSeparator().getBytes()); // 写入数组的一部分 fos.write(b, 0, 5);// 应该写入的是Hello // 关闭输出流 fos.close(); // 文件的内容为: /* Hello every body! Hello */ } }
如果写入的文件存在,会被覆盖掉;要想在文件的末尾进行追加内容(保留以前的内容),就需要在创建FileOutputStream对象是,向构造器传入一个true;下面演示向文件中追加内容:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /** * 使用FileOutputStream来写入文件 * 直接在Write.txt文件追加内容 * @throws IOException * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建FileOutputStream对象 // write.txt 文件在项目的根目录下面 File writeFile = new File("write.txt"); // 在创建对象传入一个true FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(writeFile, true); // 准备byte数组 byte[] b = (System.lineSeparator()+"我是追加的内容,哈哈").getBytes(); // 写入文件 fos.write(b); // 关闭输出流 fos.close(); // 文件的内容为: /* Hello every body! Hello 我是追加的内容,哈哈 */ } }
InputStream:
进行文件的读取经常使用的是InputStream的子类,FileInputStream可以读取任何文件,经常用的方法就是直接读入一个byte数组,这样是为了提高读取效率,不是用一个一个字节的读取。
下面演示一个文件的复制,文件的复制,就是利用字节输入流读取文件,然后利用输出流写入文件。下面是复制一个视频文件(同时用了输入流和输出流):
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /** * 将C:\\Users\\Beck\\Desktop\\temp目录下all.avi文件复制到 * 当前文件中,名字为copy.avi */ public static void main(String[] args){ // 创建输入输出流 FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try{ File file = new File("C:/Users/Beck/Desktop/temp"); fis = new FileInputStream(new File(file, "all.avi")); fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(file, "copy.avi")); // 进行读写操作 int len = -1; // 每次读入1M byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024]; while ((len=fis.read(b)) != -1){ // 写入 fos.write(b, 0, len); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("文件复制失败!"); }finally{ // 关闭流对象 try{ if (fos != null){ fos.close(); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("释放资源失败!"); }finally{ try{ if (fis != null){ fis.close(); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("释放资源失败!"); } } } System.out.println("复制文件完毕!"); // 输出结果: /*复制文件完毕!*/ } }
BufferedInputStream&BufferedOutputStream:
字符缓冲输入流和字符缓冲输出流,这两个流的作用的是提高输入输出的效率。BufferedInputStream&BufferedOutputStream,接收的参数分别是InputStream,OutputStream,底层还是利用字节的输入输出流,只是对输入输出流进行了封装。
下面利用BufferedInputStream&BufferedOutputStream进行文件的复制:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /** * 将C:\\Users\\Beck\\Desktop\\temp目录下all.avi文件复制到 * 当前文件中,名字为copy.avi * 这次使用的是BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream来完成 */ public static void main(String[] args){ // 创建缓冲输入输出流 BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try{ File file = new File("C:/Users/Beck/Desktop/temp"); bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(file, "all.avi"))); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(file, "copy.avi"))); // 进行读写操作 int len = -1; // 每次读入1M byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024]; while ((len=bis.read(b)) != -1){ // 写入 bos.write(b, 0, len); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("文件复制失败!"); }finally{ // 关闭流对象 try{ if (bos != null){ bos.close(); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("释放资源失败!"); }finally{ try{ if (bis != null){ bis.close(); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("释放资源失败!"); } } } System.out.println("复制文件完毕!"); // 输出结果: /*复制文件完毕!*/ } }
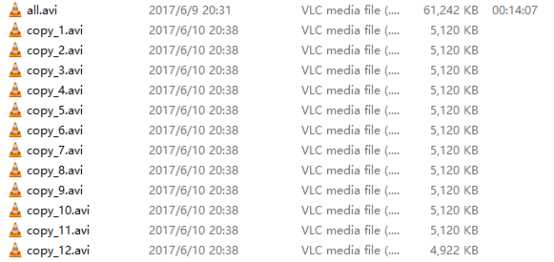
练习:把一个视频文件按照5M的大小切割成多个。
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /** * 将C:\\Users\\Beck\\Desktop\\temp目录下all.avi文件复制到 * 这次是把all.avi视频文件切割成多个文件。按照每个文件5M的大小切割 * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 这次我把IOException直接抛出去了没有捕获 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream("C:/Users/Beck/Desktop/temp/all.avi")); // 读取视频文件 int len = -1; // 每次读入5M byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*5]; int flag = 0; while ((len=bis.read(bytes)) != -1 ){ flag++; // 把读入的文件写入到一个文件中 writeToFile(bytes, len, flag); } // 关闭输入流 bis.close(); System.out.println("切割完成!"); } // 将一个byte数组的内容写入到一个文件中 private static void writeToFile(byte[] bytes, int len, int flag) throws IOException { BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("C:/Users/Beck/Desktop/temp/copy_"+flag+".avi")); bos.write(bytes, 0, len); bos.close(); } }
切割结果:
字符流:
输出流:Writer
输入流:Reader
字符流的底层是字节流+编码表
字符流只能操作文本文件,进行文本文件的读写,如果是为了复制文件的话,最好选择字节流进行复制。
Writer:
Writer下面有两个常用的字符输出流:OutputStreamWriter和FileWriter
OutputStreamWriter:接收的参数是一个OutputStream参数,也可以传一个charset编码字符串,这样就可以按照你设置的编码写入文本文件中。
以utf-8编码形式向文本文件中写入内容:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; public class Test { /* * 以utf8的格式向文件中写入字符串 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 创建 OutputStreamWriter对象 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream("wirter.txt"),"utf-8"); osw.write("我是OutputStreamWriter写入的,"); osw.write("我的编码是UTF-8格式的。"); // 字符流需要自己刷新 osw.flush(); // 关闭流 osw.close(); //输出结果,两句话在一行,因为没有写入换行符 /* 我是OutputStreamWriter写入的,我的编码是UTF-8格式的。 */ } }
FileWriter:可以接收的参数可以是File对象或者是String类型的;它的编码是系统默认的编码,我们的一般编码是使用的是GBK编码。
使用FileWriter向文本文件中写入字符串:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /* * 用FileWriter向文件中写入内容 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 创建 FileWriter对象 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("writer_gbk.txt"); fw.write("我是用FileWriter写的"); // 写入换行符 fw.write(System.lineSeparator()); fw.write("我的编码是用的是默认的,GBK"); fw.flush(); // 关闭流 fw.close(); // 输出结果 /* 我是用FileWriter写的 我的编码是用的是默认的,GBK */ } }
Reader:
Reader下面有两个常用的字符流:InputStreamReader,FileReader
InputStreamReader:可以按照指定的编码去读取文本文件,接收的参数是InputStream和一个编码字符串。
以utf-8的编码去读取一个文本文件:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class Test { /* * 以UTF-8去读取writer.txt * 这个文件是刚才用utf-8的格式写入的, * 也只能以utf8的格式去读取,否则会出现乱码 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 创建InputStreamReader对象 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("wirter.txt"), "utf-8"); int len = -1; // 一次可以读取1024个字符,2*1024个字节,2KB char[] ch = new char[1024]; while ((len=isr.read(ch)) != -1){ System.out.print(new String(ch, 0, len)); } // 关闭流 isr.close(); // 输出结果: /* 我是OutputStreamWriter写入的,我的编码是UTF-8格式的。 */ } }
FileReader:以系统默认的编码去读取一个文本文件。接收的参数可以是一个File或者String。
用FileReader去读取GBK的文件,系统默认的编码是GBK
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /* * 用FileReader来读取文件writer_gbk.txt * FileReader默认是用的是系统的默认编码 * 本机的默认编码是GBK */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 创建FileReader对象 FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("writer_gbk.txt")); int len = -1; char[] ch = new char[1024]; while ((len=fr.read(ch)) != -1){ System.out.println(new String(ch,0,len)); } // 关闭流 fr.close(); // 输出结果 /* 我是用FileWriter写的 我的编码是用的是默认的,GBK */ } }
乱码:
乱码产生的原因:用一个A编码表将字符转成字节, 又用B编码表将字节转回字符. 两个编码表对应的关系不同,因此查到的结果就不同.
保证不乱码的方式 : 编码与解码保持相同.
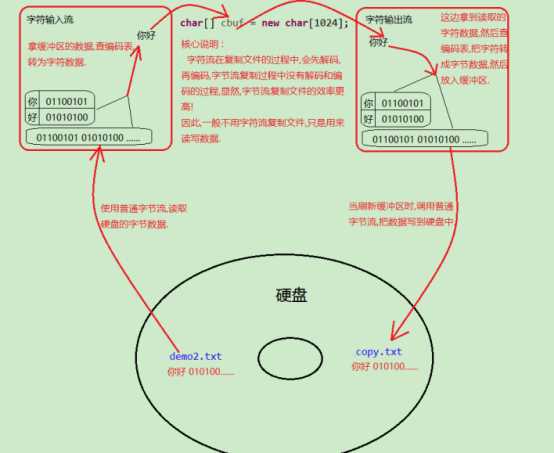
字符流复制文件原理:
BufferedReader&BufferedWriter:
BufferedReader&BufferedWriter:字符缓冲输入输出流,接收的参数分别是:Reader,Writer;作用是提高读写的速度,读写时字符的编码是系统默认的编码:
BufferedReader特有的一个方式读取一行readLine(),不会读取换行符
BufferedWrter特有的一个方法时,newLine()写入一个换行符
在写入的数据之后,需要手动flush。
利用BufferedReader&BufferedWriter进行文本文件的读写:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { /* * 利用BufferedReader&BufferedWriter进行文本文件的读写: * 复制文件:test.properties */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.properties")); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("test_copy.properties")); // 进行读写,缓冲流特有的方法就是可以按照行来读取,如果读取结束返回null String line = null; while ((line=br.readLine()) != null){ bw.write(line); // 写入换行 bw.newLine(); // 刷新 bw.flush(); } // 关闭流 bw.close(); br.close(); } }
字节流和字符流的总结:

IO流只能操作文件”文件”,不能操作文件夹(目录),否则会出现异常。
打印流:
PrintStream,PrintWriter:字节打印流,字符打印流;打印流只有输出流,没有输入流;输出的目的可以是文件,也可以是其他流。PrintStream自带刷新功能,PrintWriter需要手动开启。
PrintStream:打印出来的字符的编码使用的是系统默认编码。
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintStream; public class Test { /* * 使用打印流:PrintStream */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("print.txt"); ps.println("旺旺"); ps.println("欢欢"); ps.println("乐乐"); ps.close(); // 结果: /* 旺旺 欢欢 乐乐 */ } }
PrintWriter:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class Test { /* * 使用打印流:PrintWriter */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 创建PrintWriter对象时,开启自动刷新功能 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("print.txt"), true); pw.println("我是PrintWriter"); pw.println("出来的"); pw.close(); // 结果: /* 我是PrintWriter 出来的 */ } }
序列化&反序列化:
序列化:就是将对象写入文件的过程
反序列化:从文件读入对象的过程
ObjectOutputStream&ObjectInputStream:需要序列化的对象必须去实现Serializable接口,否则在序列化的时候会出错。
序列化的注意点:
1、static修饰的成员不能被序列化
2、要想成员变量不被序列化,可以用transient关键字修饰
3、为了不发生序列号冲突,设置:serialVersionUID
下面就进行序列化和反序列化:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.Serializable; public class Student implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = -5214244848175027425L; private String name; private String id; private transient String phone; public Student(String name, String id, String phone) { super(); this.name = name; this.id = id; this.phone = phone; } public Student() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", id=" + id + ", phone=" + phone + "]"; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } } package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class Test { /* * 进行序列化和反序列化 * 对Student对象序列化 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ // 创建ObjectOutputStream对象,绑定目的地 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("tmp.txt")); // 创建Student对象 Student stu = new Student("张三", "T001", "15522223333"); // 写入对象 oos.writeObject(stu); // 关闭流 oos.close(); System.out.println("序列化成功!"); System.out.println("==============分割=============="); // 进行反序列化 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("tmp.txt")); // 读取对象 Object obj = ois.readObject(); if (obj instanceof Student){ Student s = (Student)obj; System.out.println(s); } // 关闭流 ois.close(); System.out.println("反序列化成功!"); // 结果:phone是transient关键字修饰的,所以没有被序列化 /* 序列化成功! ==============分割============== Student [name=张三, id=T001, phone=null] 反序列化成功! */ } }
Properties:
Properties类是HashTable的一个子类,实现了Map接口,所以里面保存的是键值对,元素的存取是无序的,这个类经常被用来处理配置文件。
利用Properties来读写文件:
package com.xiaoshitou_io; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Properties; public class Test { /* * 利用Properties来读写文件 */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ // 读取Properties文件:pro.properties Properties pro = new Properties(); // 加载文件 pro.load(new FileReader("pro.properties")); // 根据key来读取值 String key = pro.getProperty("key"); System.out.println(key); String value = pro.getProperty("匿名"); System.out.println(value); System.out.println("============================="); // 修改Properties内的值,或者添加新的值 pro.setProperty("key", "我是修改的值"); pro.setProperty("add", "我是新添加的值"); // 保存进文件 pro.store(new FileWriter("pro.properties"),""); System.out.println("修改完成"); // 控制台打印结果: /* 姥姥阿里 娇娇 ============================= 修改完成 */ // pro.properties 文件中的内容: /* # #Sun Jun 11 08:53:22 CST 2017 key=我是修改的值 张嘴=监控 匿名=娇娇 add=我是新添加的值 */ } }
以上是关于Java-IO流总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章