数组pta总结
Posted fetterslove
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数组pta总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本题要求编写程序,从给定字符串中查找某指定的字符。
输入格式:
输入的第一行是一个待查找的字符。第二行是一个以回车结束的非空字符串(不超过80个字符)。
输出格式:
如果找到,在一行内按照格式“index = 下标”输出该字符在字符串中所对应的最大下标(下标从0开始);否则输出"Not Found"。
输入样例1:
m
programming
输出样例1:
index = 7
输入样例2:
a
1234
输出样例2:
Not Found

1 #include<stdio.h>
2 void search(char strsource[],char c)//设成void输出就不用在主函数设成int就要交给主函数或其他函数
3 {
4 int i=0;
5 int indexpos=-1;//
6 while(strsource[i]!=‘�‘)//次数未知
7 {
8 //看当前的字符是不是要找的字符
9 if(strsource[i]==c)
10 {
11 indexpos=i;
12 }
13 i++;
14 }
15 //字符是存在,不存在
16 if(indexpos==-1)
17 {
18 printf("Not Found
");
19 }
20 else
21 {
22 printf("index = %d
",indexpos);
23 }
24 }
25 int main()
26 {
27 char c;
28 char strsource[81];//空字符
29 c=getchar();
30 getchar();
31 gets(strsource);//gets和scanf(%s)放的字符串,最后一个元素都是自动填上斜杠0。但最好用gets(钉钉老师所讲)
32 search(strsource,c); //传递的数组名首地址
33 }
总结:循环字符数组时一般用while
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出一个不超过80个字符且以回车结束的字符串。
输出格式:
在一行中输出转换后的整数。题目保证输出不超过长整型范围。
输入样例:
free82jeep5
输出样例:
825
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 int getnumber(char strsource[])
3 {
4 int i=0;
5 int sum=0;
6 while(strsource[i]!=‘�‘)//字符数组一般都是while
7 {
8 //取数字
9 if(strsource[i]>=‘0‘&&strsource[i]<=‘9‘)
10 {
11 sum=sum*10+(strsource[i]-‘0‘);
12 }
13 i++;
14 }
15 return sum;
16 }
17 int main()
18 {
19 char strsource[81];//留一个位置存放斜杠0字符(联想钉钉上老师的演示)
20 int strnumber;//定义一个变量接收函数返回值
21 gets(strsource);
22 strnumber=getnumber(strsource);
23 printf("%d",strnumber);
24 return 0;
25 }
03 删除重复字符
输入格式:
输入是一个以回车结束的非空字符串(少于80个字符)。
输出格式:
输出去重排序后的结果字符串。
输入样例:
ad2f3adjfeainzzzv
输出样例:
23adefijnvz

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 //用空代表删除
4 void delRepeatLetter(char strSource[],int n)
5 {
6 int i;
7 int j;
8 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
9 {
10 if(strSource[i]==‘�‘)
11 {
12 continue;
13 }
14 for(j=i+1; j<n; j++)
15 {
16 if(strSource[i]==strSource[j])
17 {
18 strSource[j]=‘�‘;
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
23
24 void selectionSort(char strSource[],int n)
25 {
26 int i,j,t;
27 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
28 {
29 for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
30 {
31 if(strSource[i]>strSource[j])
32 {
33 t=strSource[i];
34 strSource[i]=strSource[j];
35 strSource[j]=t;
36 }
37 }
38 }
39 }
40 void show(char strSource[],int n)
41 {
42 int i;
43 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
44 {
45 if(strSource[i]!=‘�‘)
46 {
47 printf("%c",strSource[i]);
48 }
49 }
50 }
51 int main()
52 {
53 char strSource[81];
54 int strLen;
55 gets(strSource);
56 strLen=strlen(strSource);
57 delRepeatLetter(strSource,strLen);
58 selectionSort(strSource,strLen);
59 show(strSource,strLen);
60 }
总结:删除字符的方法斜杠0,而且这里有两个功能函数,不可能在其中一个进行输出,所以还要再定义一个功能函数做输出
一般有两个及其以上的功能函数则要设计一个输出函数。
本题目要求编写程序统计一行字符中单词的个数。所谓“单词”是指连续不含空格的字符串,各单词之间用空格分隔,空格数可以是多个。
输入格式:
输入给出一行字符。
输出格式:
在一行中输出单词个数。
输入样例:
Let‘s go to room 209.
输出样例:
5
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 void wordCounter(char sentence[])
4 {
5 char newSentece[1000]=" ";
6 int counter=0;
7 int i=0;
8 strcat(newSentece,sentence);
9 while(newSentece[i]!=‘�‘)
10 {
11 if(newSentece[i-1]==‘ ‘&&newSentece[i]!=‘ ‘)
12 {
13 counter++;
14 }
15 i++;
16 }
17 printf("%d",counter);
18 }
19 int main()
20 {
21 char sentence[1000];
22 gets(sentence);
23 wordCounter(sentence);
24 }
05 字符串字母大小写转换
输入格式:
输入为一个以“#”结束的字符串(不超过30个字符)。
输出格式:
在一行中输出大小写转换后的结果字符串。
输入样例:
Hello World! 123#
输出样例:
hELLO wORLD! 123
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 void chageUpLower(char strSource[])
4 {
5 int i=0;
6 while(strSource[i]!=‘#‘)
7 {
8 if(strSource[i]>=‘a‘ && strSource[i]<=‘z‘)
9 {
10 strSource[i]=strSource[i]-(‘a‘-‘A‘);
11 }
12 else if(strSource[i]>=‘A‘ && strSource[i]<=‘Z‘)
13 {
14 strSource[i]=strSource[i]+(‘a‘-‘A‘);
15 }
16 i++;
17 }
18 }
19 void show(char strSource[])
20 {
21 int i=0;
22 while(strSource[i]!=‘#‘)
23 {
24 printf("%c",strSource[i]);
25 i++;
26 }
27 }
28 int main()
29 {
30 char strSource[32];//# ‘�‘一定要注意这里pta有要求
31 gets(strSource);
32 chageUpLower(strSource);
33 show(strSource);
34 }
总结:这里如果把show函数写到第一功能函数会冗杂;所以再设一个输出函数,看上去美观
06 交换最小值和最大值
本题要求编写程序,先将输入的一系列整数中的最小值与第一个数交换,然后将最大值与最后一个数交换,最后输出交换后的序列。
注意:题目保证最大和最小值都是唯一的。
输入格式:
输入在第一行中给出一个正整数N(≤10),第二行给出N个整数,数字间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中顺序输出交换后的序列,每个整数后跟一个空格。
输入样例:
5
8 2 5 1 4
输出样例:
1 2 5 4 8 1 #include <stdio.h>
2 void changePos(int listArray[],int n)
3 {
4 int minPos=0;
5 int maxPos=0;
6 int i;
7 int temp;
8 for(i=1; i<n; i++)
9 {
10 if(listArray[i]<listArray[minPos])
11 {
12 minPos=i;把最小值的下标存到minpos里
13 }
14 if(listArray[i]>listArray[maxPos])
15 {
16 maxPos=i;//把最大值的下标存到maxpos里
17 }
18 }
19 temp=listArray[minPos];
20 listArray[minPos]=listArray[0];
21 listArray[0]=temp;
22 if(maxPos!=0)
23 {
24 temp=listArray[maxPos];
25 listArray[maxPos]=listArray[n-1];
26 listArray[n-1]=temp;
27 }
28 else
29 {
30 temp=listArray[minPos];
31 listArray[minPos]=listArray[n-1];
32 listArray[n-1]=temp;
33 }
34 }
35 void printArray(int listArray[],int n)
36 {
37 int i;
38 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
39 {
40 printf("%d ",listArray[i]);
41 }
42 }
43 void main()
44 {
45 int N;
46 int listArray[10];
47 int i;
48 scanf("%d",&N);
49 for(i=0; i<N; i++)
50 {
51 scanf("%d",&listArray[i]);
52 }
53 changePos(listArray,N);
54 printArray(listArray,N);
55 }
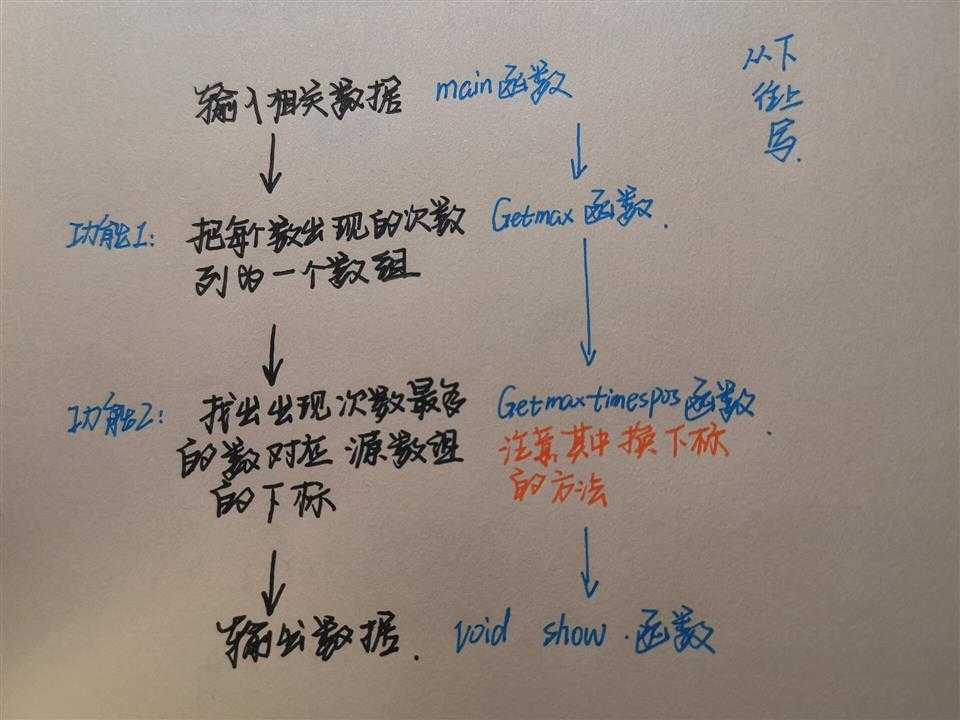
07 求整数序列中出现次数最多的数
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出序列中整数个数N(0<N≤1000),以及N个整数。数字间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中输出出现次数最多的整数及其出现次数,数字间以空格分隔。题目保证这样的数字是唯一的。
输入样例:
10 3 2 -1 5 3 4 3 0 3 2
输出样例:
3 4
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 void show(int sourceArray[],int n,int data)
3 {
4 int i=0;
5 int counter=0;
6 printf("%d ",data);
7 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
8 {
9 if(sourceArray[i]==data)
10 {
11 counter++;
12 }
13 }
14 printf("%d",counter);
15 }
16 int getMaxTimesPos(int counterArray[],int n)
17 {
18 int maxPos=0;
19 int i;
20 for(i=0; i<n; i++) //找出重复次数最多的那个数对应的下标;
21 {
22 if(counterArray[i]>counterArray[maxPos])
23 {
24 maxPos=i;
25 }
26 }
27 return maxPos;
28 }
29 int getMax(int sourceArray[],int n)
30 {
31 int i,j;
32 int counterArray[1000]= {0};
33 int copyArray[1000];
34 int maxCounterPos;
35 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
36 {
37 copyArray[i]=sourceArray[i];
38 }
39 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
40 {
41 counterArray[i]=0;
42 for(j=0; j<n; j++)
43 {
44 if(copyArray[i]==sourceArray[j])
45 {
46 counterArray[i]++;
47 }
48 }
49 }
50 maxCounterPos=getMaxTimesPos(counterArray,n);//这里因为所传的参数不在主函数里,所以在这个函数执行才行,先定义在调用
51 show(sourceArray,n,sourceArray[maxCounterPos]);
52 }
53 int main()
54 {
55 int N;
56 int i;
57 int sourceArray[1000];
58 scanf("%d",&N);
59 for(i=0; i<N; i++)
60 {
61 scanf("%d",&sourceArray[i]);
62 }
63 getMax(sourceArray,N);
64 return 0;
65 }
总结:设一个新的数组变量存放一些所要的值,注意有些功能函数在功能函数里,因为其所传的参数在其中。
本题要求编写程序,针对输入的N个字符串,输出其中最长的字符串。
输入格式:
输入第一行给出正整数N;随后N行,每行给出一个长度小于80的非空字符串,其中不会出现换行符,空格,制表符。
输出格式:
在一行中用以下格式输出最长的字符串:
The longest is: 最长的字符串
如果字符串的长度相同,则输出先输入的字符串。
输入样例:
5
li
wang
zhang
jin
xiang
输出样例:
The longest is: zhang
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 int main()
4 {
5 char strSource[1000][80];
6 int i,j;
7 int N;
8 int longestIndex=-1;
9 int maxlenth=-1;
10 int strLenth;
11 scanf("%d",&N);
12 getchar();
13 for(i=0;i<N;i++)
14 {
15 gets(strSource[i]);
16 strLenth=strlen(strSource[i]);
17 if(strLenth>maxlenth)
18 {
19 longestIndex=i;//一个变量放最长字符串对应的下标
20 maxlenth=strLenth;//一个变量放当前比它长的字符串的值
21 }
22 }
23 printf("The longest is: %s",strSource[longestIndex]);
24 }
总结:找出最长字符串对应的下标见上文
将N个整数按从小到大排序的冒泡排序法是这样工作的:从头到尾比较相邻两个元素,如果前面的元素大于其紧随的后面元素,则交换它们。通过一遍扫描,则最后一个元素必定是最大的元素。然后用同样的方法对前N−1个元素进行第二遍扫描。依此类推,最后只需处理两个元素,就完成了对N个数的排序。
本题要求对任意给定的K(<),输出扫描完第K遍后的中间结果数列。
输入格式:
输入在第1行中给出N和K(1),在第2行中给出N个待排序的整数,数字间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中输出冒泡排序法扫描完第K遍后的中间结果数列,数字间以空格分隔,但末尾不得有多余空格。
输入样例:
6 2
2 3 5 1 6 4
输出样例:
2 1 3 4 5 6
#include<stdio.h>
void bubble(int arr[],int len)
{
int i;
int temp;
for(i=0; i<len-1; i++) //len是传进来值,不能再对其改变
{
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1])
{
temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[i+1];
arr[i+1]=temp;
}
}
}
void bubble_sort(int arr[],int len,int K)
{
int i;
int bullbleTimes=K;
for(i=1; i<=bullbleTimes; i++)
{
bubble(arr,len--);
}
}
void show(int arr[],int len)
{
int i ;
for (i = 0; i <len; i++)
{
if(i==len-1)
{
printf("%d",arr[i]);
}
else
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
}
printf("
");
}
int main()
{
int N,K;
int arr[100];
int i;
scanf("%d%d",&N,&K);
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
bubble_sort(arr,N,K);//排序
show(arr,N);//排序后
return 0;
}
以上是关于数组pta总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章