2.3 循环结构与跳出
Posted wlyperfect
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2.3 循环结构与跳出相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
使用while循环
只要表达式的值为true,那么while循环就可以重复执行部分代码。
一般形式:
while (expression) statement;
如果expression的值为false,则程序转到循环后面的语句。如果为true,则执行statement。整个过程一直持续到expression的值为false,然后循环结束。
1 // Play Again 2 // Demonstrates while loops 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 char again = ‘y‘; 10 while (again == ‘y‘) 11 { 12 cout << " **Played an exciting game**"; 13 cout << " Do you want to play again? (y/n): "; 14 cin >> again; 15 } 16 17 cout << " Okay, bye."; 18 19 return 0; 20 }

注意:必须在循环之前初始化again,因为它用在了循环表达式中。
使用do循环
do循环在每次循环迭代之后验证表达式。这意味着循环体总是至少要执行一次。
do statement; while(expression)
一旦验证expression为false,则循环终止。
1 // Play Again 2.0 2 // Demonstrates do loops 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 char again; 10 do 11 { 12 cout << " **Played an exciting game**"; 13 cout << " Do you want to play again? (y/n): "; 14 cin >> again; 15 } while (again == ‘y‘); 16 17 cout << " Okay, bye."; 18 19 return 0; 20 }

使用break和continue语句
循环的行为是能够改变的,比如使用break语句立即退出循环,或使用continue语句直接跳转到循环开始。
尽管应当少用这些语句,但它们有时确实很有用。
1 // Finicky Counter 2 // Demonstrates break and continue statements 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 int count = 0; 10 while (true) 11 { 12 count += 1; 13 14 //end loop if count is greater than 10 15 if (count > 10) 16 { 17 break; 18 } 19 20 //skip the number 5 21 if (count == 5) 22 { 23 continue; 24 } 25 26 cout << count << endl; 27 } 28 29 return 0; 30 }
通过while循环从1数到10,但要跳过5这个数。
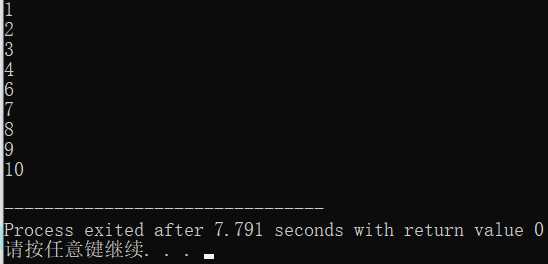
提示:尽管while(true)循环有时能比传统循环更清晰,但也应当尽可能少使用这种循环。
以上是关于2.3 循环结构与跳出的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章