ES6基础-ES6 class
Posted dashucoding
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ES6基础-ES6 class相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

作者 | Jeskson
来源 | 达达前端小酒馆
ES - Class
类和面向对象:
面向对象,即万物皆对象,面向对象是我们做开发一种的方式,开发思维,面向对象的思维中万物皆对象,以人作为例子,它的特性有哪些。比如有姓名,性别,出生年月,身高等,还有人的行为,为吃饭,睡觉。特性和行为组合起来就成为人类,特性和行为都是人都有的,通过这些不同的特性和行为给不同的值,构成不同的人。
使用类进行编程,是可以降低维护成本,类的封装性是非常强的,很多情况下,类和业务是低耦合,使用类可以让代码高度复用,类是具有继承的特性的,所以类需要扩充,是不需要修改自身的,就可进行扩展,类的使用降低了设计成本,使用简单。
那么什么是类与对象,讲解ES6中类的特性,类的继承,Babel,基于流程控制的形变类实现。
什么是类与对象以及它们之间的关系
封装的思想
(function() {
let snake = []; // 存放
let food = { x: 0, y: 0 }; // 食物
function move() {
// 移动
}
function getFood() {
// 是否吃到食物
}
function putFood() {
// 放置食物
}
function gameover() {
// 判断游戏结束
}
function init() {
// 入口函数
// 初始化
}
start();
})();class Car {
// 构造函数
constructor(...args) {
console.log(args);
}
}
new Car('蓝色', 2)class Car {
constructor(wheel, color, length, width) {
this.whell = wheel;
this.color = color;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.speed = 0; // 实速
}
// 加速
speedUp() {
this.speed += 1;
}
}
const car = new Car(2, '#000', 23, 45);
console.log(car.color);
console.log(car.spedd);
car.speedUp(); // 加速
console.log(car);三大基本特性:多态,继承,封装。
多态,同一个接口,有不同的表现。
音乐播放器类
class AudioPlayer {
constructor(container) {
this.container = document.querySelector(container);
this.songsList = []; // 歌单列表
this.dom = null; // 用于存放dom
this.audio = new Audio();
this.status = 0;
this.getSongs();
this.createElement();
this.bindEvents();
this.render();
}
getSongs() {
this.songsList = [
{
cover: '',
url: .mp3,
singer: {},
name: ''
}
];
}
createElement() {
const div = document.createElement('div');
div.innerhtml = `
<div>播放按钮</div>
<div>进度条</div>
`
this.dom = div;
}
bindEvents() {
this.div.querySelector('.btn').addEventListener('click',()=>{
console.log('开始播放');
})
}
render() {
this.container.appendChild(this.dom);
}
}静态方法与静态属性
静态属性和静态方法,getter与setter,类的表达式,name属性与New.target属性,es5中模拟类。
类中的静态属性与静态方法,有两个特点:
不会被类的实例所拥有的属性和方法,只有类自身拥有;只能通过类调用。
用static关键字去声明一个静态方法
class Car {
static totalCar = 0;
constructor() {
this.speed = 0;
this.errors = 0;
}
speedUp() {
this.speed += 1;
}
// 自检
check() {
console.log('开始');
if(this.errors === 0){
console.log('this');
}
}
// 工厂
static checker() {
console.log('haha');
}
static repair(car) {
console.log('da');
}
}
const car = new Car();
car.checker();
Car.repair(car);
Car.repair('1号车');Car.属性名 = 属性值;class Person {
}
Person.format = programmer => {
programmer.haveGirlFriend = true;
programmer.hair = true;
};
class Programmer {
constructor() {
this.haveGirlFriend = false;
this.hair = false;
}
}
const programmer = new Programmer();
console.log(programmer);类表达式:
const Person = class P {
constructor() {
console.log('dada');
}
}
new Person();函数表达式:
const a = function() {
}函数声明:
function a() {
}getter与setter
getter,setter
类似于给属性提供钩子
在获取属性值和设置属性值的时候做一些额外的事情
ES5 getter/setter
在对象字面量中书写get/set方法
Object.definedProperty
const obj = {
_name: '',
get name() {
return this._name;
},
set name(val) {
this._name = val;
}
}
obj.name = 3;Object.definedProperty
var obj = {
_name: ''
};
Object.definedProperty(obj, 'age', {
value: 12,
enumerable: true
});
var i;
for(i in obj) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log(obj);var obj = {
_name: ''
};
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {
get: function() {
console.log('正在访问name');
},
set: function(val) {
console.log('正在修改');
this._name = val;
}
});class Person {
constructor() {
this._name = '';
}
get name() {
console.log('getname);
return `名字${this._name}`;
}
set name(val) {
console.log('name');
this._name = val;
}
}
const person = new Person();
person.name = '炸';
console.log(person.name);class AudioPlayer {
constructor() {
this._status = 0;
this.status = 0;
}
get status() {
return this._status;
}
set status(val) {
const StatusMap = {
0: '暂停',
1: '播放',
2: '加载中'
};
document.querySelector('#app. play-btn').innerText = StatusMap[val];
this._status = val;
}
}name属性与new.target属性
class Person {
}
console.log(Person.name);
const da = class d {
}
console.log(da.name);
class Car {
constructor() {
console.log(new.target);
}
}
new Car();function Car() {
if(new target !== Car) {
throw Error('使用new调用car');
}
}
new Car();function Car() {
if(!(this instanceof Car)) {
throw Error('new');
}
}
new Car();使用ES5模拟类
// 构造函数
class Car {
constructor() {
}
}
function Car() {
}
new Car();function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
new Person('张三', 12);创建一个空的对象,把构造函数的prototype属性作为空对象的原型,this赋值为这个空对象,执行函数,如果函数没有返回值,则返回this
function Constructor(fn, args) {
var _this = Object.create(fn.prototype);
fn.apply(_this, args);
}function Constructor(fn, args) {
var _this = Object.create(fn.prototype);
var res = fn.apply(_this, args);
return res ? res : _this;
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.say = function() {
console.log('dada' + this.name);
}
var person = Constructor(Person, ['da', 12]);
console.log(person);// 重载
class SimpleCalc {
addCalc(...args) {
if(args.length === 0) {
return this.zero();
}
if(args.length === 1){
return this.onlyOneArgument(args);
}
return this.add(args);
}
zero() {
return 0;
}
onlyOneArgument() {
return args[0];
}
add(args) {
return args.reduce((a,b) => a+b,0);
}
}
function post(url, header, params) {
if(!params) {
params = header;
header = null; // undefined
}
}
post('http:...' , {
a:1,
b:2
});ES5中的继承
// 利用构造函数
function P() {
this.name = 'parent';
this.gender = 2;
this.say = function() {
console.log('ddd');
}
}
P.prototype.test = function() {
console.log('da');
}
function C() {
P.call(this);
this.name = 'child',
this.age = 11;
}
C.prototype = new P();
var child = new C();
child.say();Babel是一个javascript编译器
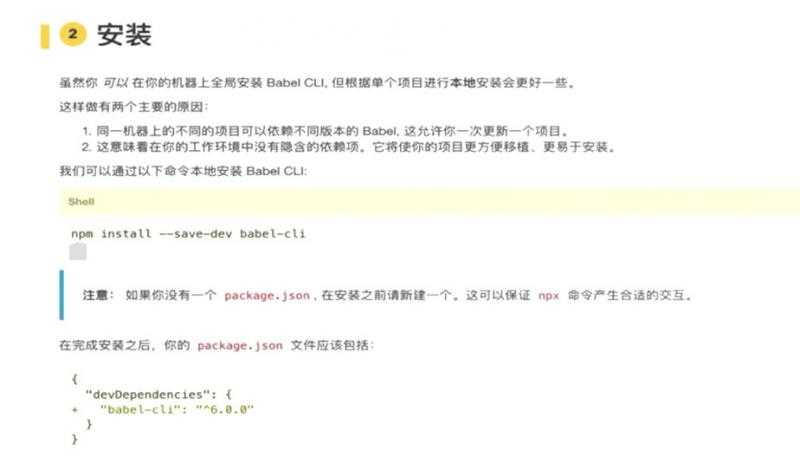
const add = (a,b) => a+b;
alert(add(1,2));
alert(add(3,4));
class Person {
static aa = 1;
bb = 2;
static A() {
alert('b');
}
constructor() {
}
}class Car {
static total_car = 0;
color='#000';
constructor(color) {
Car.total_car += 1;
this.color = color;
}
}
new Car();
new Car();
new Car();
console.log(Car.total_car);?? 不要忘记留下你学习的脚印 [点赞 收藏 评论]
作者Info:
【作者】:Jeskson
【原创公众号】:达达前端小酒馆。
【转载说明】:转载请说明出处,谢谢合作!~
关于目前文章内容即涉及前端,php知识点,如果有兴趣即可关注,很荣幸,能被您发现,真是慧眼识英!也感谢您的关注,在未来的日子里,希望能够一直默默的支持我,我也会努力写出更多优秀的作品。我们一起成长,从零基础学编程,将 Web前端领域、数据结构与算法、网络原理等通俗易懂的呈现给小伙伴。分享 Web 前端相关的技术文章、工具资源、精选课程、热点资讯。
若本号内容有做得不到位的地方(比如:涉及版权或其他问题),请及时联系我们进行整改即可,会在第一时间进行处理。
请点赞!因为你们的赞同/鼓励是我写作的最大动力!
欢迎关注达达的CSDN!
这是一个有质量,有态度的博客

以上是关于ES6基础-ES6 class的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章