UVA 1601 双向BFS
Posted hznumqf
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了UVA 1601 双向BFS相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
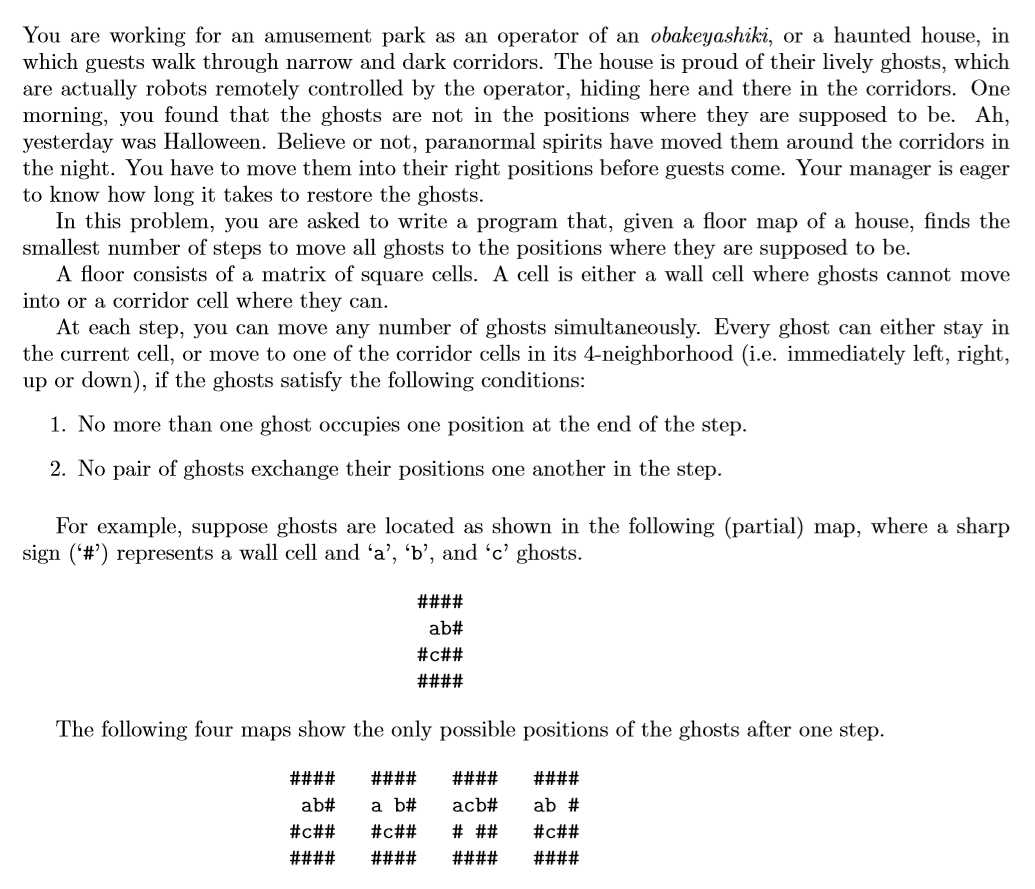


但是我们还不是很清楚每一次的状态怎么储存?我们可以用一个结构体,将每次的位置存起来,但是这个程序中用了一个更好的储存方法:我们知道最大的格数是16*16个,也就是256个,那么我们转换为二进制表示就是8位数,那么我们可以使用24位的二进制表示啊!然后我们再进行解压缩,所以这就是很神奇的地方!
普通BFS

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<set> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<sstream> #include<cstdio> #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f //const int maxn = 1e6 + 5; const double PI = acos(-1.0); typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int maxn = 150; const int maxs = 20; const int dx[] = { 1,-1,0,0,0 }; const int dy[] = { 0,0,1,-1,0 }; inline int ID(int a, int b, int c) { return (a << 16) | (b << 8) | c; } int s[3], t[3]; int deg[maxn]; //记录每个编号为i的空格周围可以走的步数 int G[maxn][5]; inline bool conflict(int a, int b, int a2, int b2) { return a2 == b2 || (a2 == b && b2 == a); } int d[maxn][maxn][maxn]; int bfs() { queue<int> q; memset(d, -1, sizeof d); q.push(ID(s[0], s[1], s[2])); d[s[0]][s[1]][s[2]] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); int a = (u >> 16) & 0xff, b = (u >> 8) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; //解码出三个鬼的位置 if (a == t[0] && b == t[1] && c == t[2]) return d[a][b][c]; for (int i = 0; i < deg[a]; i++) { int a2 = G[a][i]; for (int j = 0; j < deg[b]; j++) { int b2 = G[b][j]; if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue; for (int k = 0; k < deg[c]; k++) { int c2 = G[c][k]; if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2)) continue; if (conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue; if (d[a2][b2][c2] != -1) continue; d[a2][b2][c2] = d[a][b][c] + 1; q.push(ID(a2, b2, c2)); } } } } return -1; } int main() { int w, h, n; while (scanf("%d%d%d", &w, &h, &n) == 3 && n) { char maze[20][20]; for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) fgets(maze[i], 20, stdin); int cnt, x[maxn], y[maxn], id[maxs][maxs]; cnt = 0; for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) { for(int j=0;j<w;j++) if (maze[i][j] != ‘#‘) { x[cnt] = i; y[cnt] = j; id[i][j] = cnt; if (islower(maze[i][j])) s[maze[i][j] - ‘a‘] = cnt; else if (isupper(maze[i][j])) t[maze[i][j] - ‘A‘] = cnt; cnt++; } } for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { deg[i] = 0; for (int dir = 0; dir < 5; dir++) { int xx = x[i] + dx[dir], yy = y[i] + dy[dir]; if (maze[xx][yy] != ‘#‘) G[i][deg[i]++] = id[xx][yy]; } } if (n <= 2) { deg[cnt] = 1; G[cnt][0] = cnt; s[2] = t[2] = cnt++; } if (n <= 1) { deg[cnt] = 1; G[cnt][0] = cnt; s[1] = t[1] = cnt++; } printf("%d ", bfs()); } return 0; }
双向BFS

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<set> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<sstream> #include<cstdio> #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f //const int maxn = 1e6 + 5; const double PI = acos(-1.0); typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int maxn = 150; const int maxs = 20; const int dx[] = { 1,-1,0,0,0 }; const int dy[] = { 0,0,1,-1,0 }; inline int ID(int a, int b, int c) { return (a << 16) | (b << 8) | c; } int s[3], t[3]; int deg[maxn]; //记录每个编号为i的空格周围可以走的步数 int G[maxn][5]; char maze[maxn][maxn]; int color[maxn][maxn][maxn]; inline bool conflict(int a, int b, int a2, int b2) { //两个鬼是exchange位置(违反第2条) //两个鬼移动到同一个格子(违反第1条) return a2 == b2 || (a2 == b && b2 == a); } int d1[maxn][maxn][maxn]; int bfs() { queue<int> qf; queue<int> qb; d1[s[0]][s[1]][s[2]] = 0; d1[t[0]][t[1]][t[2]] = 1; qf.push(ID(s[0], s[1], s[2])); qb.push(ID(t[0], t[1], t[2])); while (!qf.empty() || !qb.empty()) { int fnum = qf.size(), bnum = qb.size(); while (fnum--) { int u = qf.front(); qf.pop(); int a = (u >> 16) & 0xff, b = (u >> 8) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; for (int i = 0; i < deg[a]; i++) { int a2 = G[a][i]; for (int j = 0; j < deg[b]; j++) { int b2 = G[b][j]; if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue; for (int k = 0; k < deg[c]; k++) { int c2 = G[c][k]; if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2) || conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue; if (color[a2][b2][c2] == 0) { d1[a2][b2][c2] = d1[a][b][c] + 1; color[a2][b2][c2] = 1; qf.push(ID(a2, b2, c2)); } else if (color[a2][b2][c2] == 2) { return d1[a][b][c] + d1[a2][b2][c2]; } } } } } while (bnum--) { int u = qb.front(); qb.pop(); int a = (u >> 16) & 0xff, b = (u >> 8) & 0xff, c = u & 0xff; for (int i = 0; i < deg[a]; i++) { int a2 = G[a][i]; for (int j = 0; j < deg[b]; j++) { int b2 = G[b][j]; if (conflict(a, b, a2, b2)) continue; for (int k = 0; k < deg[c]; k++) { int c2 = G[c][k]; if (conflict(a, c, a2, c2) || conflict(b, c, b2, c2)) continue; if (color[a2][b2][c2] == 0) { d1[a2][b2][c2] = d1[a][b][c] + 1; color[a2][b2][c2] = 2; qb.push(ID(a2, b2, c2)); } else if (color[a2][b2][c2] == 1) { return d1[a][b][c] + d1[a2][b2][c2]; } } } } } } return -1; } int main() { int w, h, n; while (scanf("%d%d%d", &w, &h, &n) == 3, n) { for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) fgets(maze[i], 20, stdin); int cnt = 0; int x[maxn], y[maxn]; int id[maxs][maxs]; for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) { if (maze[i][j] != ‘#‘) { x[cnt] = i, y[cnt] = j, id[i][j] = cnt; if (islower(maze[i][j])) s[maze[i][j] - ‘a‘] = cnt; else if (isupper(maze[i][j])) t[maze[i][j] - ‘A‘] = cnt; cnt++; } } } for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { int xx = x[i] + dx[j], yy = y[i] + dy[j]; if (maze[xx][yy] != ‘#‘) G[i][deg[i]++] = id[xx][yy]; } } if (n <= 2) { deg[cnt] = 1; G[cnt][0] = cnt; s[2] = t[2] = cnt++; } if (n <= 1) { deg[cnt] = 1; G[cnt][0] = cnt; s[1] = t[1] = cnt++; } memset(d1, 0, sizeof d1); memset(color, 0, sizeof color); if (s[0] == t[0] && s[1] == t[1] && s[2] == t[2]) printf("0 "); else printf("%d ", bfs()); } return 0; }
以上是关于UVA 1601 双向BFS的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
