FM/FFM算法
Posted blowinginthewind
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FM/FFM算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、数据格式
1.1 libffm数据格式定义
为了使用FM/FFM方法,所有的特征必须转换成“field_id:feat_id:value”类型的libffm格式,field_id代表特征所属field的编号,feat_id是特征编号,value是特征的值。注意第一列插入为target值。
数值型的特征比较容易处理,只需分配单独的field和feat编号。
类别型特征需要经过One-Hot编码成数值型,编码产生的所有特征同属于一个field,而特征的值只能是0或1,注意类别特征编码时忽略0值(同一个类别field一般对应一个fea,但也可能对应多个fea);
特别地,如用户浏览/购买品类,有多个品类id且用一个数值衡量用户浏览或购买每个品类商品的数量。这类特征按照categorical特征处理,不同的只是特征的值不是0或1,而是代表用户浏览或购买数量的数值。按前述方法得到field_id之后,再对转换后特征顺序编号,得到feat_id,特征的值也可以按照之前的方法获得。
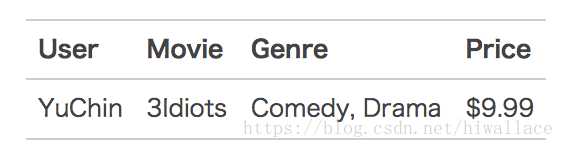
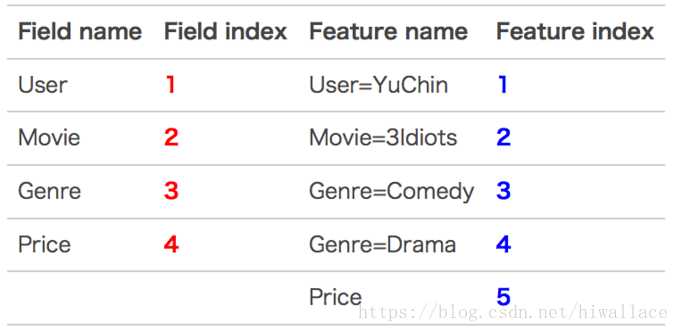
【举例说明】
可编码为
1.2 libffm数据格式转换
核心类:
class df2libffm: def __init__(self, feas_n, feas_c, feas_oh): self.catdict = {} for x in feas_n: self.catdict[x] = 0 #数值型特征 for x in feas_c: self.catdict[x] = 1 #类别单值型特征 for x in feas_oh: self.catdict[x] = 2 #one-hot后的类别多值型特征 self.field_ids = {} self.feat_ids = {} self.fieldcode = 0 self.featcode = 0 #初始化 def build(self, train, test): df = pd.concat([train[feas_n+feas_c],test[feas_n+feas_c]],axis=0) for n, r in enumerate(range(len(df))): datarow = df.iloc[r].to_dict() for i, x in enumerate(self.catdict.keys()): #数值型特征 if(self.catdict[x]==0): if(x not in self.field_ids): self.field_ids[x] = self.fieldcode self.fieldcode +=1 self.feat_ids[x] = self.featcode self.featcode +=1 #类别单值型特征 if(self.catdict[x]==1): if(x not in self.field_ids): self.field_ids[x] = self.fieldcode self.fieldcode +=1 self.feat_ids[x] = {} self.feat_ids[x][datarow[x]] = self.featcode self.featcode +=1 elif(datarow[x] not in self.feat_ids[x]): self.feat_ids[x][datarow[x]] = self.featcode self.featcode +=1 #类别多值型特征 if(self.catdict[x]==2): if(x.split(‘_‘)[0] not in self.field_ids): self.field_ids[x.split(‘_‘)[0]] = self.fieldcode self.fieldcode +=1 self.feat_ids[x] = self.featcode self.featcode +=1 #转换 def gen(self, df, path, dtype): with open(path, "w") as text_file: for n, r in enumerate(range(len(df))): datastring = "" datarow = df.iloc[r].to_dict() #第一列:target if dtype==‘train‘: datastring += str(int(datarow[0])) if dtype==‘valid‘: datastring += str(int(datarow[0])) if dtype==‘test‘: datastring += str(int(0)) #第二列开始:特征编码 for i, x in enumerate(self.catdict.keys()): if(self.catdict[x]==0): datastring = datastring + " "+str(self.field_ids[x])+":"+ str(self.feat_ids[x])+":"+ str(str(datarow[x])) if(self.catdict[x]==1): datastring = datastring + " "+str(self.field_ids[x])+":"+ str(self.feat_ids[x][datarow[x]])+":1" if(self.catdict[x]==2): if datarow[x]==1: datastring = datastring + " "+str(self.field_ids[x.split(‘_‘)[0]])+":"+ str(self.feat_ids[x])+":1" datastring += ‘ ‘ text_file.write(datastring)
【举例说明】
https://github.com/KeenDuang/Duang-Feature-Engineering/blob/master/df2libffm.ipynb
Reference:
https://blog.csdn.net/john_xyz/article/details/78933253#%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0
https://blog.csdn.net/hiwallace/article/details/81333604
https://www.kaggle.com/scirpus/libffm-generator-lb-280
以上是关于FM/FFM算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章