前端基础常识
Posted peace1
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了前端基础常识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
触发BFC
- body 根元素
- 浮动元素:float 除 none 以外的值
- 绝对定位元素:position (absolute、fixed)
- display 为 inline-block、table-cells、flex
- overflow 除了 visible 以外的值 (hidden、auto、scroll)
BFC特性
1. 同一个 BFC 下外边距会发生折叠
2. BFC 可以包含浮动的元素(清除浮动)
3. BFC 可以阻止元素被浮动元素覆盖
CSRF预防
1..设置随机token
2.验证referrer
3.ajax添加自定义header
xss预防
1.用户输入信息转义html tag
2.开启https
自定义new
function newObj(obj,...args) { let newObj = new Object(); newObj.__proto__ == obj.prototype; let result = obj.apply(newObj,args); return typeof result === ‘object‘?ret:newObj; }
自定义call
Function.prototype.myCall = function(obj) { let object = obj || window; let args = [...arguments].slice(1); object[fun] = this; let result = object[fun](args); delete object.fun; return result };
防抖:短时间触发事件会覆盖上一次事件,直到阈值时间未触发才调用
节流:高频率触发的事件,每隔一段时间只会触发一次
树遍历
数据

let classList = [ { id: 2, content: "分类2", children: [{ id: 21, content: "分类2.1", children: null }] }, { id: 1, content: "分类1", children: [{ id: 11, content: "分类1.1", children: null }, { id: 12, content: "分类1.2", children: [{ id: 121, content: "分类1.2.1", children: null }] }] }, ]
递归遍历
function getContentsById(list, id, parentContents) { for (var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { const item = list[i]; if (item.id == id) { return `${parentContents}-${item.content}`.substr(1) } if (item.children !== null) { const itemContents = `${parentContents}-${item.content}`; return getContentsById(item.children, id, itemContents); } } }
栈遍历
function getContentsById(list,id) { let array = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(list)); let item,cacheItem=[]; let pContent = ‘‘; do{ item = array.shift(); if (cacheItem.children&&cacheItem.children.indexOf(item)>=0) { item.content = cacheItem.content+‘-‘+item.content; } if (item.id!==id&&item.children !== null) { cacheItem = item; array = item.children.concat(array); } }while(array.length!=0&&item.id!=id); if (item.id==id) { return item.content; } }
栈遍历好处:在数据层级较大时候,避免内存泄露
柯里化(不知有何卵用的东西)
const currying = fn => { const len = fn.length return function curr(...args1) { if (args1.length >= len) { return fn(...args1) } return (...args2) => curr(...args1, ...args2) } }
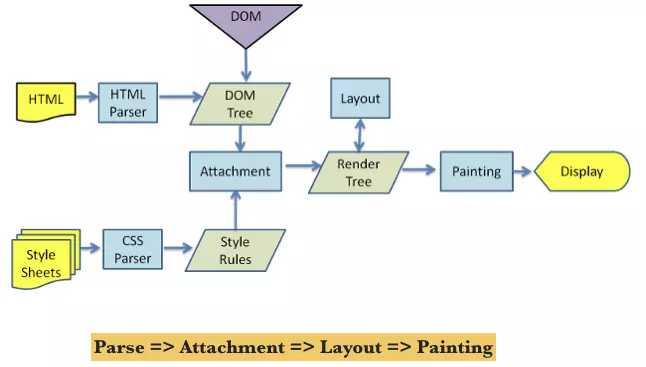
浏览器渲染
GPU Process:
renderProcess : mian: DOM->Style->Layout->compositiing update -> paint->
impl: commit->tiling->raster->active-draw
borwser parse:dispay
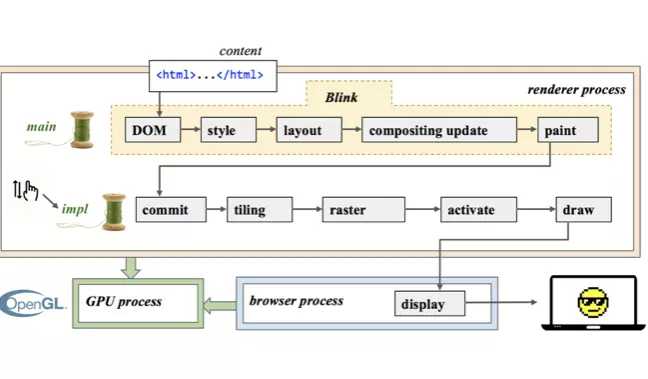
参考地址 https://www.jianshu.com/p/125c5e9159b5
fixed:相对于视口定位,如果祖先元素有设置transform非none时候,相对祖先定位
GPU加速(合成):
- 3D 或者 CSS transform
- <video> 和 <canvas> 标签
- CSS filters
- 元素覆盖时,比如使用了 z-index 属性
使用硬件减速的问题
1. 内存。如果CPU加载了大量的纹理,那么很容易就会发生内容问题,这一点在移动端浏览器上尤为明显,所以,一定要牢记不要让页面的每个元素都使用硬件加速
2. 使用GPU渲染会影响字体的抗锯齿效果,这是因为GPU和CPU的具有不同的渲染机制。即使最终硬件加速停止了,文本还是会在动画期间显示得很模糊。
以上是关于前端基础常识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
