flume源码
Posted aidata
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了flume源码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
IDEA查看源码
IDEA快捷键
1 查看接口的实现类:Ctrl+Alt+B
选中按快捷键,然后跳到实现类的地方去
2 切换页面:Alt+<- 和 Alt+->
Alt+->
3 查看Java方法调用树(被调/主调):Ctrl+Alt+H
分为调用当前方法的树、当前方法调用的下级方法
4 查看类继承关系图:Ctrl+Alt+U
5 查看当前类的继承树:Ctrl+H
6 查看定义的变量在哪里被调用:Ctrl+Alt+F7
7 查看一个类中有什么方法:Alt+7 或 点左侧边栏Structure
临时得到的不一定正确的结论,后续需要debug来跟踪研究
启动程序入口是org.apache.flume.node.Application#main
public static void main(String[] args) { try { SSLUtil.initGlobalSSLParameters(); // 用了apache commons-cli的jar包实现的命令行提示 Options options = new Options(); Option option = new Option("n", "name", true, "the name of this agent"); option.setRequired(true); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("f", "conf-file", true, "specify a config file (required if -z missing)"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option(null, "no-reload-conf", false, "do not reload config file if changed"); options.addOption(option); // Options for Zookeeper option = new Option("z", "zkConnString", true, "specify the ZooKeeper connection to use (required if -f missing)"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("p", "zkBasePath", true, "specify the base path in ZooKeeper for agent configs"); option.setRequired(false); options.addOption(option); option = new Option("h", "help", false, "display help text"); options.addOption(option); CommandLineParser parser = new GnuParser(); CommandLine commandLine = parser.parse(options, args); if (commandLine.hasOption(‘h‘)) { new HelpFormatter().printHelp("flume-ng agent", options, true); return; } String agentName = commandLine.getOptionValue(‘n‘); boolean reload = !commandLine.hasOption("no-reload-conf"); // 代码待续
上面的代码是解析命令行参数
下面是使用zookeeper进行配置flume
// 代码接上面 boolean isZkConfigured = false; if (commandLine.hasOption(‘z‘) || commandLine.hasOption("zkConnString")) { isZkConfigured = true; } Application application; if (isZkConfigured) { // get options String zkConnectionStr = commandLine.getOptionValue(‘z‘); String baseZkPath = commandLine.getOptionValue(‘p‘); if (reload) { EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider = new PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider( agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath, eventBus); components.add(zookeeperConfigurationProvider); application = new Application(components); eventBus.register(application); } else { StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider = new StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider( agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath); application = new Application(); application.handleConfigurationEvent(zookeeperConfigurationProvider.getConfiguration()); } } else { // 代码待续
下面使用本地文件配置flume,判断配置文件是否存在
// 代码接上面 // 使用本地配置文件进行配置 File configurationFile = new File(commandLine.getOptionValue(‘f‘)); /* * The following is to ensure that by default the agent will fail on * startup if the file does not exist. */ if (!configurationFile.exists()) { // If command line invocation, then need to fail fast if (System.getProperty(Constants.SYSPROP_CALLED_FROM_SERVICE) == null) { String path = configurationFile.getPath(); try { path = configurationFile.getCanonicalPath(); } catch (IOException ex) { logger.error("Failed to read canonical path for file: " + path, ex); } throw new ParseException( "The specified configuration file does not exist: " + path); } }
// 代码待续
下面代码,如果使用的shell命令中没有no-reload-conf,则每30秒钟会监控配置文件
// 代码接上方
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); if (reload) { EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider( agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30); components.add(configurationProvider); application = new Application(components); eventBus.register(application); } else { ......
// else块中代码在下方 } } application.start();
// 代码待续
eventbus
动态配置使用了PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,其中中有FileWatcherRunnable来具体实现监控配置文件 变化,如果改动时间晚于文件最后修改时间,会eventBus.post(),该方法会激活带有@Subscribe的handleConfigurationEvent()方法
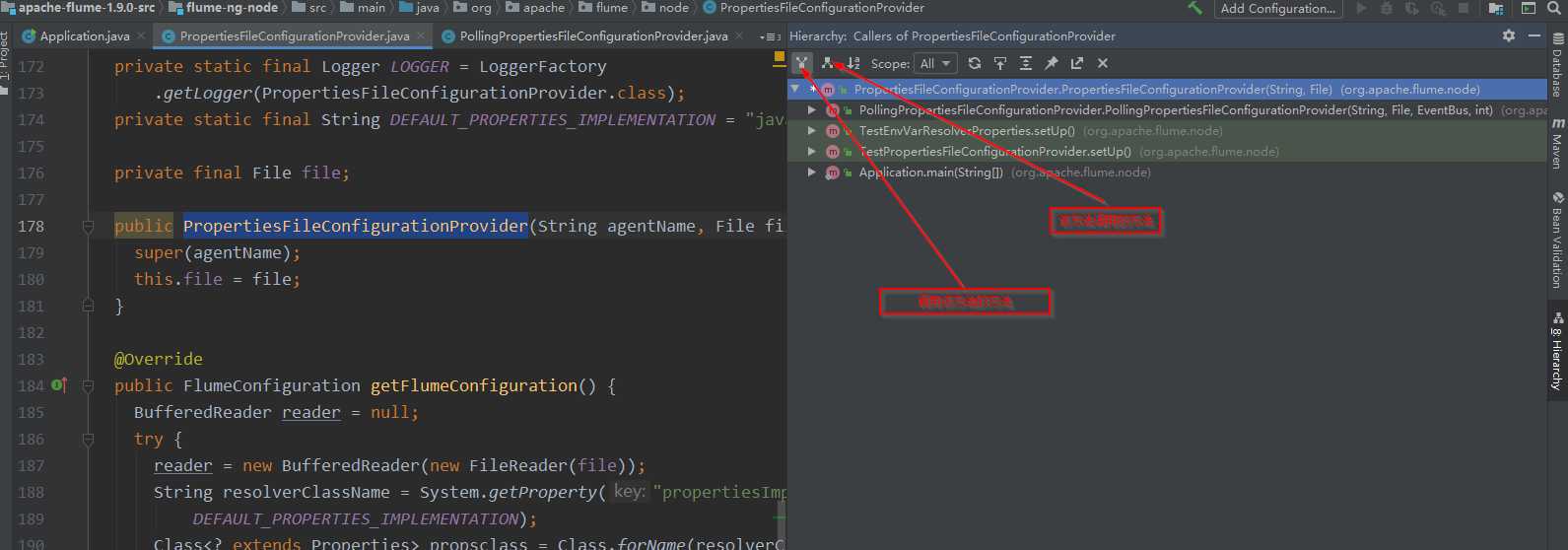
由components.add(configurationProvider),我们发现components是PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider
public PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(String agentName, File file, EventBus eventBus, int interval) { super(agentName, file); this.eventBus = eventBus; this.file = file; this.interval = interval; counterGroup = new CounterGroup(); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.IDLE; } @Override public void start() { LOGGER.info("Configuration provider starting"); Preconditions.checkState(file != null, "The parameter file must not be null"); executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor( new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("conf-file-poller-%d") .build()); FileWatcherRunnable fileWatcherRunnable = new FileWatcherRunnable(file, counterGroup); executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(fileWatcherRunnable, 0, interval, TimeUnit.SECONDS); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START; LOGGER.debug("Configuration provider started"); } @Override public void stop() { LOGGER.info("Configuration provider stopping"); executorService.shutdown(); try { if (!executorService.awaitTermination(500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { LOGGER.debug("File watcher has not terminated. Forcing shutdown of executor."); executorService.shutdownNow(); while (!executorService.awaitTermination(500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { LOGGER.debug("Waiting for file watcher to terminate"); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { LOGGER.debug("Interrupted while waiting for file watcher to terminate"); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } lifecycleState = LifecycleState.STOP; LOGGER.debug("Configuration provider stopped"); } @Override public synchronized LifecycleState getLifecycleState() { return lifecycleState; } @Override public String toString() { return "{ file:" + file + " counterGroup:" + counterGroup + " provider:" + getClass().getCanonicalName() + " agentName:" + getAgentName() + " }"; } public class FileWatcherRunnable implements Runnable { private final File file; private final CounterGroup counterGroup; private long lastChange; public FileWatcherRunnable(File file, CounterGroup counterGroup) { super(); this.file = file; this.counterGroup = counterGroup; this.lastChange = 0L; } @Override public void run() { LOGGER.debug("Checking file:{} for changes", file); counterGroup.incrementAndGet("file.checks"); long lastModified = file.lastModified(); if (lastModified > lastChange) { LOGGER.info("Reloading configuration file:{}", file); counterGroup.incrementAndGet("file.loads"); lastChange = lastModified; try { eventBus.post(getConfiguration()); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Failed to load configuration data. Exception follows.", e); } catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) { LOGGER.error("Failed to start agent because dependencies were not " + "found in classpath. Error follows.", e); } catch (Throwable t) { // caught because the caller does not handle or log Throwables LOGGER.error("Unhandled error", t); } } } } }
org.apache.flume.node.Application#handleConfigurationEvent方法,会调用先终止所有components,再启动components
@Subscribe public void handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf) { try { lifecycleLock.lockInterruptibly(); stopAllComponents(); startAllComponents(conf); } catch (InterruptedException e) { logger.info("Interrupted while trying to handle configuration event"); return; } finally { // If interrupted while trying to lock, we don‘t own the lock, so must not attempt to unlock if (lifecycleLock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { lifecycleLock.unlock(); } } }
application.start();会将component传入supervise方法
public void start() { lifecycleLock.lock(); try { for (LifecycleAware component : components) { supervisor.supervise(component, new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START); } } finally { lifecycleLock.unlock(); } }
supervise方法对组件进行监督
该方法中对每一个component会通过线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor monitorService起一个MonitorRunnable线程执行,在monitorRunnable中的run()方法中,是每一个component的执行逻辑,根据desiredState的不同,选择不同的状态执行方法去执行
public synchronized void supervise(LifecycleAware lifecycleAware, SupervisorPolicy policy, LifecycleState desiredState) { if (this.monitorService.isShutdown() || this.monitorService.isTerminated() || this.monitorService.isTerminating()) { throw new FlumeException("Supervise called on " + lifecycleAware + " " + "after shutdown has been initiated. " + lifecycleAware + " will not" + " be started"); } Preconditions.checkState(!supervisedProcesses.containsKey(lifecycleAware), "Refusing to supervise " + lifecycleAware + " more than once"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Supervising service:{} policy:{} desiredState:{}", new Object[] { lifecycleAware, policy, desiredState }); } Supervisoree process = new Supervisoree(); process.status = new Status(); process.policy = policy; process.status.desiredState = desiredState; process.status.error = false; MonitorRunnable monitorRunnable = new MonitorRunnable(); monitorRunnable.lifecycleAware = lifecycleAware; monitorRunnable.supervisoree = process; monitorRunnable.monitorService = monitorService; supervisedProcesses.put(lifecycleAware, process); ScheduledFuture<?> future = monitorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay( monitorRunnable, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); monitorFutures.put(lifecycleAware, future); }
monitorService 是一个线程池,在对象创建的时候初始化用,该线程池,来启动 Channels Sources , Sinks 的Runner 实例
monitorRunnable中的run()方法
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider是实现了LifecycleAware接口的,component是PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,因此run()方法会调用PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider的start()方法,
也就是application.start()最终调用了PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start(),组件启动了
同时,启动了后,我们设置了要持续监控配置文件,因此要保证周期性监控配置文件。恰好,PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start()会新建FileWatcherRunnable,该runnable会监控文件的变化,如果配置文件发生变化,会调用里面的eventBus.post(),从而激活了handleConfigurationEvent(),进而会stopAllComponents然后startAllComponents
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start()中使用了executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(fileWatcherRunnable, 0, interval, TimeUnit.SECONDS)来使用上面提到的runnable,每隔30秒监控变化
@Override public void run() { logger.debug("checking process:{} supervisoree:{}", lifecycleAware, supervisoree); long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { if (supervisoree.status.firstSeen == null) { logger.debug("first time seeing {}", lifecycleAware); supervisoree.status.firstSeen = now; } supervisoree.status.lastSeen = now; synchronized (lifecycleAware) { if (supervisoree.status.discard) { // Unsupervise has already been called on this. logger.info("Component has already been stopped {}", lifecycleAware); return; } else if (supervisoree.status.error) { logger.info("Component {} is in error state, and Flume will not" + "attempt to change its state", lifecycleAware); return; } supervisoree.status.lastSeenState = lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState(); if (!lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState().equals( supervisoree.status.desiredState)) { logger.debug("Want to transition {} from {} to {} (failures:{})", new Object[] { lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status.lastSeenState, supervisoree.status.desiredState, supervisoree.status.failures }); switch (supervisoree.status.desiredState) { case START: try { lifecycleAware.start(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Unable to start " + lifecycleAware + " - Exception follows.", e); if (e instanceof Error) { // This component can never recover, shut it down. supervisoree.status.desiredState = LifecycleState.STOP; try { lifecycleAware.stop(); logger.warn("Component {} stopped, since it could not be" + "successfully started due to missing dependencies", lifecycleAware); } catch (Throwable e1) { logger.error("Unsuccessful attempt to " + "shutdown component: {} due to missing dependencies." + " Please shutdown the agent" + "or disable this component, or the agent will be" + "in an undefined state.", e1); supervisoree.status.error = true; if (e1 instanceof Error) { throw (Error) e1; } // Set the state to stop, so that the conf poller can // proceed. } } supervisoree.status.failures++; } break; case STOP: try { lifecycleAware.stop(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Unable to stop " + lifecycleAware + " - Exception follows.", e); if (e instanceof Error) { throw (Error) e; } supervisoree.status.failures++; } break; default: logger.warn("I refuse to acknowledge {} as a desired state", supervisoree.status.desiredState); } if (!supervisoree.policy.isValid(lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status)) { logger.error( "Policy {} of {} has been violated - supervisor should exit!", supervisoree.policy, lifecycleAware); } } } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Unexpected error", t); } logger.debug("Status check complete"); }
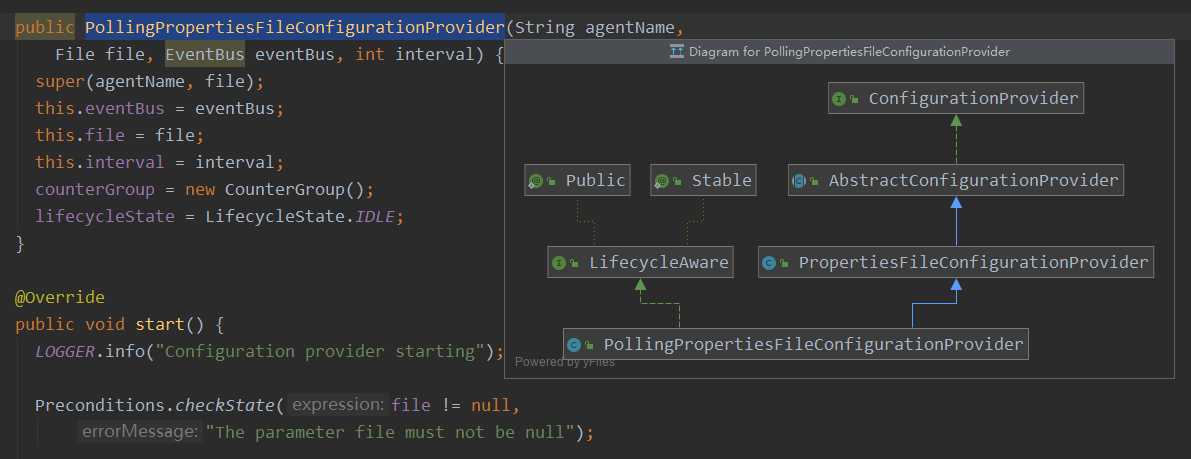
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider 继承了 PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider 继承了 :AbstractConfigurationProvider,在抽象类:AbstractConfigurationProvider
启动不是瞎启动,而是根据配置文件
eventBus.post(getConfiguration());
激活
handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf)
里面
startAllComponents(conf);
org.apache.flume.node.AbstractConfigurationProvider#getConfiguration 方法.
这个方法分两步.
1.读取配置文件. 使用的是 FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration();
2.生成 source、channel、sink 对应的 runner . 加入到 MaterializedConfiguration 中
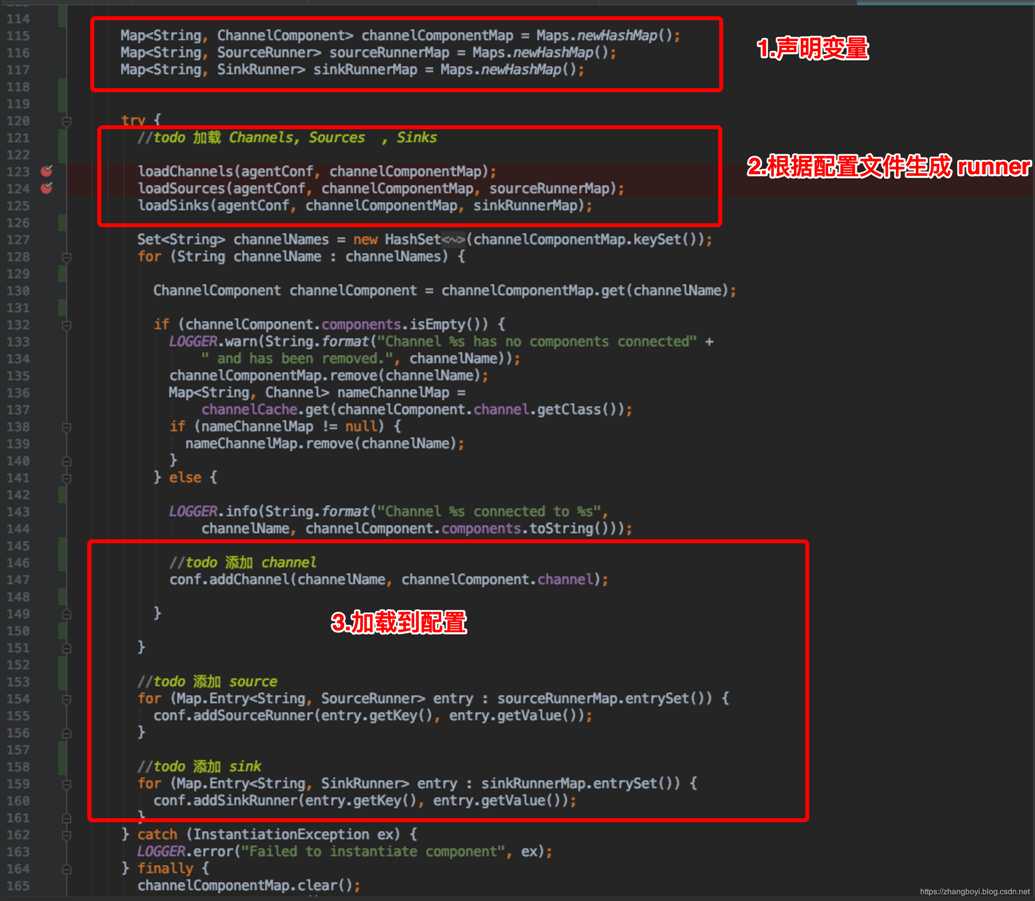
public MaterializedConfiguration getConfiguration() { MaterializedConfiguration conf = new SimpleMaterializedConfiguration(); FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration(); AgentConfiguration agentConf = fconfig.getConfigurationFor(getAgentName()); if (agentConf != null) { Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap = Maps.newHashMap(); Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); try { loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap); loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap); loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap); Set<String> channelNames = new HashSet<String>(channelComponentMap.keySet()); for (String channelName : channelNames) { ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(channelName); if (channelComponent.components.isEmpty()) { LOGGER.warn(String.format("Channel %s has no components connected" + " and has been removed.", channelName)); channelComponentMap.remove(channelName); Map<String, Channel> nameChannelMap = channelCache.get(channelComponent.channel.getClass()); if (nameChannelMap != null) { nameChannelMap.remove(channelName); } } else { LOGGER.info(String.format("Channel %s connected to %s", channelName, channelComponent.components.toString())); conf.addChannel(channelName, channelComponent.channel); } } for (Map.Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry : sourceRunnerMap.entrySet()) { conf.addSourceRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } for (Map.Entry<String, SinkRunner> entry : sinkRunnerMap.entrySet()) { conf.addSinkRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } } catch (InstantiationException ex) { LOGGER.error("Failed to instantiate component", ex); } finally { channelComponentMap.clear(); sourceRunnerMap.clear(); sinkRunnerMap.clear(); } } else { LOGGER.warn("No configuration found for this host:{}", getAgentName()); } return conf; }
loadChannels( agentConf , channelComponentMap );//创建channel,并存入channelComponentMap中
loadSources( agentConf , channelComponentMap , sourceRunnerMap );//创建source,并存入sourceRunnerMap中。在source中,读取创建的多个channel,并根据多个channel创建ChannelSelector,根据selector,创建ChannelProcessor。选择器和拦截器会传入ChannelProcessor。
loadSinks( agentConf , channelComponentMap , sinkRunnerMap );//创建sink,并存入sinkRunnerMap中
loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap);
这个方法主要干了四件事件事.
1.将缓存的 channel 加入到一个 ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String>集合中
2. 创建具有ComponentConfiguration 对象的Channel 实例
3. 创建没有ComponentConfiguration 对象, 但是配置 context 的Channel 实例
4.将缓存中的 channel 与新生成的 channel 做匹配, 去掉配置项中没有的 channel
private void loadChannels(AgentConfiguration agentConf, Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap) throws InstantiationException { LOGGER.info("Creating channels"); //todo 缓存中的 channel ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused = ArrayListMultimap.create(); // assume all channels will not be re-used for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Channel>, Map<String, Channel>> entry : channelCache.entrySet()) { Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass = entry.getKey(); Set<String> channelNames = entry.getValue().keySet(); channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass).addAll(channelNames); } Set<String> channelNames = agentConf.getChannelSet(); Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getChannelConfigMap(); for (String chName : channelNames) { ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(chName); if (comp != null) { // todo 使用工厂类创建Channel Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused, comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); try { //todo 更新配置 , 因为 channelComponentMap 刚开始传进来的时候是空值 Configurables.configure(channel, comp); channelComponentMap.put(comp.getComponentName(), new ChannelComponent(channel)); LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", chName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } //todo 组合没有 ComponentConfiguration配置, 仅仅使用Context的对象. for (String chName : channelNames) { Context context = agentConf.getChannelContext().get(chName); if (context != null) { // todo 使用工厂类创建Channel Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused, chName, context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); try { // todo 更新配置 , 因为 channelComponentMap 刚开始传进来的时候是空值 Configurables.configure(channel, context); channelComponentMap.put(chName, new ChannelComponent(channel)); LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", chName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } for (Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass : channelsNotReused.keySet()) { Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelKlass); if (channelMap != null) { for (String channelName : channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass)) { if (channelMap.remove(channelName) != null) { LOGGER.info("Removed {} of type {}", channelName, channelKlass); } } if (channelMap.isEmpty()) { //todo 有一些 channel 在配置中没有重新使用, 将会将其从缓存中移除. channelCache.remove(channelKlass); } } } }
private Channel getOrCreateChannel( ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused, String name, String type) throws FlumeException { // todo 根据传入的类型, 获取对应的类 Class<? extends Channel> channelClass = channelFactory.getClass(type); /* * Channel has requested a new instance on each re-configuration * todo 根据新的配置, 实例化对象. */ //todo 如何类的注解 Disposable 存在, 则直接进行实例化,并返回 只有 jdbc 和 file 模式用到了 if (channelClass.isAnnotationPresent(Disposable.class)) { Channel channel = channelFactory.create(name, type); channel.setName(name); return channel; } Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelClass); //todo 如果缓存中不存在 channel 的话, 那么直接加入缓存. if (channelMap == null) { channelMap = new HashMap<String, Channel>(); channelCache.put(channelClass, channelMap); } //todo 如果channelMap 中的 channel 为 null ,使用工厂类创建. Channel channel = channelMap.get(name); if (channel == null) { channel = channelFactory.create(name, type); channel.setName(name); channelMap.put(name, channel); } //todo 如果缓存中已经存在对应的 channel 的话,那么移除它, 后续的方法会更新它 . channelsNotReused.get(channelClass).remove(name); return channel; }
loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap);
读取配置文件生成 source , 然后创建 sourceRunner, 并注册到 channel
private void loadSources(AgentConfiguration agentConf, Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap, Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap) throws InstantiationException { Set<String> sourceNames = agentConf.getSourceSet(); Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getSourceConfigMap(); /* * Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object */ for (String sourceName : sourceNames) { ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sourceName); if (comp != null) { SourceConfiguration config = (SourceConfiguration) comp; Source source = sourceFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); try { Configurables.configure(source, config); //配置source Set<String> channelNames = config.getChannels(); List<Channel> sourceChannels = getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, channelNames); if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) { String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " + "channel", sourceName); throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } ChannelSelectorConfiguration selectorConfig = config.getSelectorConfiguration(); ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create( sourceChannels, selectorConfig); //创建channel 选择器 ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector); Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, config); // 这里实际是调用ChannelProcessor的configure()方法,设置拦截器链 source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor); sourceRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(), SourceRunner.forSource(source)); for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) { ChannelComponent channelComponent = Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()), String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName())); channelComponent.components.add(sourceName); } } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", sourceName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } /* * Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object * and use only Context */ Map<String, Context> sourceContexts = agentConf.getSourceContext(); for (String sourceName : sourceNames) { Context context = sourceContexts.get(sourceName); if (context != null) { Source source = sourceFactory.create(sourceName, context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); try { Configurables.configure(source, context); String[] channelNames = context.getString( BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNELS).split("\\s+"); List<Channel> sourceChannels = getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, Arrays.asList(channelNames)); if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) { String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " + "channel", sourceName); throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } Map<String, String> selectorConfig = context.getSubProperties( BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_SOURCE_CHANNELSELECTOR_PREFIX); ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create( sourceChannels, selectorConfig); ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector); Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, context); source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor); sourceRunnerMap.put(sourceName, SourceRunner.forSource(source)); for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) { ChannelComponent channelComponent = Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()), String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName())); channelComponent.components.add(sourceName); } } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", sourceName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } }
在loadSources()方法中,把source封装进SourceRunner类中,再把sourceRunner存入sourceRunnerMap中。
SourceRunner是一个抽象类,有两个类继承它。
从名字可以看出,一个是事件驱动,一个是主动拉取。
通过抽象类中的forSource()方法执行是哪个类。forSource()方法在loadSources()方法中被调用
public static SourceRunner forSource(Source source) { SourceRunner runner = null; if (source instanceof PollableSource) { runner = new PollableSourceRunner(); ((PollableSourceRunner) runner).setSource((PollableSource) source); } else if (source instanceof EventDrivenSource) { runner = new EventDrivenSourceRunner(); ((EventDrivenSourceRunner) runner).setSource((EventDrivenSource) source); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("No known runner type for source " + source); } return runner; }
loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap);
读取配置文件生成 sink , 并注册到 channel , 然后根据分组情况 sinkRunner, 未设置分组的,单独创建sinkRunner
private void loadSinks(AgentConfiguration agentConf, Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap) throws InstantiationException { Set<String> sinkNames = agentConf.getSinkSet(); Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getSinkConfigMap(); Map<String, Sink> sinks = new HashMap<String, Sink>(); /* * Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object * todo 组合配置ComponentConfiguration 的对象 */ for (String sinkName : sinkNames) { ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sinkName); if (comp != null) { //todo 使用SinkFactory 直接采用根据类型,采用反射方式 实例化 Sink SinkConfiguration config = (SinkConfiguration) comp; Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); try { //todo 为 Sink 匹配对应的 channel Configurables.configure(sink, config); ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(config.getChannel()); if (channelComponent == null) { String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " + "channel", sinkName); throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } //todo 检查 channel 是否可用 : sink 的 batch size 要小于 channel 的 transaction capacity checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel); sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel); sinks.put(comp.getComponentName(), sink); //todo Sink 向 channel 反向注册 SinkName channelComponent.components.add(sinkName); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", sinkName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } /* * Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object * and use only Context * todo 组合没有配置 ComponentConfiguration 但是使用 context 的对象 */ Map<String, Context> sinkContexts = agentConf.getSinkContext(); for (String sinkName : sinkNames) { Context context = sinkContexts.get(sinkName); if (context != null) { //todo 直接采用根据类型,采用反射方式 实例化 Sink Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(sinkName, context.getString( BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); try { //todo 为 Sink 匹配对应的 channel Configurables.configure(sink, context); ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get( context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNEL)); if (channelComponent == null) { String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " + "channel", sinkName); throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } //todo 检查 channel 是否可用 : sink 的 batch size 要大于 channel 的 transaction capacity checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel); sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel); sinks.put(sinkName, sink); channelComponent.components.add(sinkName); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " + "error during configuration", sinkName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } //todo 对 sink 进行分组 loadSinkGroups(agentConf, sinks, sinkRunnerMap); }
private void loadSinkGroups(AgentConfiguration agentConf, Map<String, Sink> sinks, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap) throws InstantiationException { // todo 获取配置中的 group 分组 Set<String> sinkGroupNames = agentConf.getSinkgroupSet(); Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getSinkGroupConfigMap(); Map<String, String> usedSinks = new HashMap<String, String>(); for (String groupName: sinkGroupNames) { ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(groupName); if (comp != null) { SinkGroupConfiguration groupConf = (SinkGroupConfiguration) comp; List<Sink> groupSinks = new ArrayList<Sink>(); for (String sink : groupConf.getSinks()) { Sink s = sinks.remove(sink); if (s == null) { String sinkUser = usedSinks.get(sink); if (sinkUser != null) { throw new InstantiationException(String.format( "Sink %s of group %s already " + "in use by group %s", sink, groupName, sinkUser)); } else { throw new InstantiationException(String.format( "Sink %s of group %s does " + "not exist or is not properly configured", sink, groupName)); } } groupSinks.add(s); usedSinks.put(sink, groupName); } try { SinkGroup group = new SinkGroup(groupSinks); Configurables.configure(group, groupConf); //todo 创建 sinkRunner sinkRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(), new SinkRunner(group.getProcessor())); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " + "an error during configuration", groupName); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } // add any unassigned sinks to solo collectors // todo 对未分组的 sink 进行处理 for (Entry<String, Sink> entry : sinks.entrySet()) { if (!usedSinks.containsValue(entry.getKey())) { try { SinkProcessor pr = new DefaultSinkProcessor(); List<Sink> sinkMap = new ArrayList<Sink>(); sinkMap.add(entry.getValue()); pr.setSinks(sinkMap); Configurables.configure(pr, new Context()); //todo 创建 SinkRunner sinkRunnerMap.put(entry.getKey(), new SinkRunner(pr)); } catch (Exception e) { String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " + "an error during configuration", entry.getKey()); LOGGER.error(msg, e); } } } }
else块中的内容
PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(agentName, configurationFile); application = new Application(); application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider.getConfiguration());
静态获取配置文件,由于静态所以不需要eventBus和PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,只要PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider
也是用handleConfigurationEvent(),根据配置文件重启components
钩子函数Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook,主要是用来进行内存清理、对象销毁等操作
// 代码接上方
final Application appReference = application; Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread("agent-shutdown-hook") { @Override public void run() { appReference.stop(); } }); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("A fatal error occurred while running. Exception follows.", e); } } }
Flume 1.9.0 源码解析 : 一篇文章弄清Flume 程序启动流程
channel的主要功能就是put和take
@InterfaceAudience.Public @InterfaceStability.Stable public interface Channel extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent { public void put(Event event) throws ChannelException; public Event take() throws ChannelException; public Transaction getTransaction(); }
Channel中还有两个重要的类ChannelProcessor和ChannelSelector
ChannelProcessor 的作用就是执行put操作,将数据放到channel里面。每个ChannelProcessor实例都会配备一个ChannelSelector来决定event要put到那个channl当中,这个selector是作为参数传入的,从中获取对应的channel来执行event的put操作
public class ChannelProcessor implements Configurable { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChannelProcessor.class); private final ChannelSelector selector; private final InterceptorChain interceptorChain; public ChannelProcessor(ChannelSelector selector) { this.selector = selector; this.interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain(); } ...... public ChannelSelector getSelector() { return this.selector; } public void processEventBatch(List<Event> events) { ... while(i$.hasNext()) { Event optChannel = (Event)i$.next(); List tx = this.selector.getRequiredChannels(optChannel); ...//将event放到Required队列 t1 = this.selector.getOptionalChannels(optChannel); Object eventQueue; ...//将event放到Optional队列 } ...//event的分配操作 } public void processEvent(Event event) { event = this.interceptorChain.intercept(event); if(event != null) { List requiredChannels = this.selector.getRequiredChannels(event); Iterator optionalChannels = requiredChannels.iterator(); ...//event的分配操作 List optionalChannels1 = this.selector.getOptionalChannels(event); Iterator i$1 = optionalChannels1.iterator(); ...//event的分配操作 } } }
ChannelSelector是一个接口,我们可以通过ChannelSelectorFactory来创建它的子类,Flume提供了两个实现类MultiplexingChannelSelector和ReplicatingChannelSelector。
public interface ChannelSelector extends NamedComponent, Configurable { void setChannels(List<Channel> var1); List<Channel> getRequiredChannels(Event var1); List<Channel> getOptionalChannels(Event var1); List<Channel> getAllChannels(); }
通过ChannelSelectorFactory 的create来创建,create中调用getSelectorForType来获得一个selector,通过配置文件中的type来创建相应的子类
public static ChannelSelector create(List<Channel> channels, ChannelSelectorConfiguration conf) { String type = ChannelSelectorType.REPLICATING.toString(); if (conf != null) { type = conf.getType(); } ChannelSelector selector = getSelectorForType(type); selector.setChannels(channels); Configurables.configure(selector, conf); return selector; }
Sink是一个接口,里面最主要的方法是process(),用来处理从Channel中获取的数据。Sink的实例是由SinkFactory.create()生成的。
@InterfaceAudience.Public @InterfaceStability.Stable public interface Sink extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent { public void setChannel(Channel channel); public Channel getChannel(); /* 用来处理channel中取来的event*/ public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException; public static enum Status { READY, BACKOFF } }
sink由一个sink运行器管理,sink运行器只是一个负责运行该sink的线程
public class SinkRunner implements LifecycleAware { ... @Override public void start() { SinkProcessor policy = getPolicy(); policy.start(); runner = new PollingRunner(); runner.policy = policy; runner.counterGroup = counterGroup; runner.shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); runnerThread = new Thread(runner); runnerThread.setName("SinkRunner-PollingRunner-" + policy.getClass().getSimpleName()); runnerThread.start(); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START; } ... }
启动SinkRunner实际上就是调用它的start(),而在start()中可以看到主要是启动了一个SinkProcessor
public interface SinkProcessor extends LifecycleAware, Configurable { Status process() throws EventDeliveryException; void setSinks(List<Sink> sinks); }
SinkProcesor是一个接口,他的实现类由SinkProcessorFactory的getProcessor()生成,在AbstractConfigurationProvider中的loadSinkGroup()调用SinkGroup中的configure()生成。
public class SinkGroup implements Configurable, ConfigurableComponent { List<Sink> sinks; SinkProcessor processor; SinkGroupConfiguration conf; public SinkGroup(List<Sink> groupSinks) { sinks = groupSinks; } public SinkProcessor getProcessor() { return processor; } @Override public void configure(ComponentConfiguration conf) { this.conf = (SinkGroupConfiguration) conf; processor = SinkProcessorFactory.getProcessor(this.conf.getProcessorContext(), sinks); } }
sink groups使多个不同的sink组成一个整体,而sink processor提供了组内负载均衡和故障转移的功能。
有三种sink processor :default sink processor,failover sink processor,Load balancing Sink Processor。
default sink processor
一般的单独的sink
public class DefaultSinkProcessor implements SinkProcessor, ConfigurableComponent { private Sink sink; private LifecycleState lifecycleState; @Override public void start() { Preconditions.checkNotNull(sink, "DefaultSinkProcessor sink not set"); sink.start(); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START; } @Override public void stop() { Preconditions.checkNotNull(sink, "DefaultSinkProcessor sink not set"); sink.stop(); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.STOP; } @Override public LifecycleState getLifecycleState() { return lifecycleState; } @Override public void configure(Context context) { } @Override public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { return sink.process(); } @Override public void setSinks(List<Sink> sinks) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(sinks); Preconditions.checkArgument(sinks.size() == 1, "DefaultSinkPolicy can " + "only handle one sink, " + "try using a policy that supports multiple sinks"); sink = sinks.get(0); } @Override public void configure(ComponentConfiguration conf) { } }
default sink processor执行的就是sink的start、stop和process方法
failover sink processor
维护了一个sinks的优先级列表,保证只要有一个sink事件就可以被处理(即故障转移)。
sink优先级高的会被优先激活,若没有设置优先级则按照snk被声明的顺序来决定优先级。
Load balancing Sink Processor
提供了多个sinks负载均衡的能力。它维护了一个active sinks的索引列表,列表中fenb的sinks的负载必须是分布式的。
通过round_robin (轮询)或 random(随机)选择机制实现了分布式负载。选择机制默认为round_robin ,也可通过设置重载。自定义选举类须继承AbstractSinkSelector。
当被调用时,选择器根据配置文件的选择机制挑选下一个sink,并且调用该sink。如果所选的Sink传递Event失败,则通过选择机制挑选下一个可用的Sink,以此类推。失效的sink不会被加入到黑名单里,选择器会继续尝试所有可用的sink。所有的被调用的sink都失败后,选择器才会把失败发送给sink runner。
以上是关于flume源码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章