期刊、论文、研究的motivation是啥?
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了期刊、论文、研究的motivation是啥?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 1、对于一篇论文来说,它的发布意味着它解决了一个其他人没有解决或者没有发表出来的问题; 问题的motivation会被提炼到一个research question中,这个问题正是这篇文章想要解决的 。 ---- [here] --- 我的理解是往上有people problem(大众问题),往下有technical problem(先前存在的对该问题的解法是不够的,因此这篇论文就会说明 先前有哪些方法以及这些方法为什么不够或者不合理 )2、motivation这部分其实是解释了该研究的重要性,为什么要写这篇文章。 ---- [here]
3、最近学习工作生活都有所懈怠,感觉生活缺少了足够的motivation。 ----- [here]
4、如果要写一篇文章,题目是“在超速测试中提高小时延缺陷的故障覆盖率”。在序言中,你就不要大谈“测试”如何重要,也不必谈“超速测试”如何必要。你要谈的是:在超速测试中, 现有 的检测小时延缺陷 的方法 ,故障覆盖率怎么样的不高, 为什么会不高 。你现在要 提出一个办法 提高覆盖率。然后,在你的实验结果中列出:人家的故障覆盖率是多少,你的覆盖率达到了多少。这就有力地说明了你的工作达到了你预期的目标。
我发现:我们现在的许多论文不是这样,而是从 大帽子谈起 。一写网络方面的论文,就先写信息时代如何如何,网络如何重要。其实你要写你的文章究竟是想解决网络方面一个什么具体问题。有人写信息安全方面的论文,序言里就写信息安全 如何重要。这个还需要你写吗?任何人都承认。问题是你想解决信息安全里什么问题 。最后,你再用数据说明,你的确在某一种程度上解决了你提出的问题,或者是有所进展。人家审查你的文章,首先是你提的问题是不是有意义、是否真是个问题。然后是看你的文章在多大程度上解决或缓解了该问题。
要写好论文,首先就是要有清晰的研究动机。 ----- [here]
怎样写出优秀的的研究计划 (Research Proposal) [here]
JEI期刊论文:通过机器学习和扩散核方法揭示欧亚水獭(Lutra Lutra)与环境因素相关的空间分布模式研究
原文下载链接:
http://jeionline.org/share/202000443.pdf

原文信息

Title: Spatial Distribution Patterns of Eurasian Otter (Lutra Lutra) in Association with Environmental Factors Unravelled by Machine Learning and Diffusion Kernel Method
Authors: S. Hong1, 2, T.-S. Chon2, 3*, and G. J. Joo1*
1. Department of Biological Sciences, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Forest Environment Protection, College of Forest and Environmental Sciences, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 25931, Republic of Korea
3. Ecology and Future Research Association, Busan 46228, Republic of Korea
Abstract
In South Korea, the endangered Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) populations have been recovered throughout the country. To examine the status of otter populations, we monitored spraint densities at 250 ~ 355 sites annually from 2014 to 2017 in the Nakdong River basin. The diffusion kernel method was applied to both binary and continuous spraint data. Two geographical populations were identified: northern and southern populations. The northern population continuously increased over a broad area from north to south during the study period. In contrast, the southern population narrowly dispersed, limited by its location in an industrial area. The spatial self-organizing map (Geo-SOM) revealed associations between spraint densities and environmental factors by correlating the geographic locations of the sampling sites. Both populations were negatively affected by anthropogenic factors, including proximity to factories and human population density. However, cumulative association of all environmental factors, including landscape, food sources, and anthropogenic factors, were noted in 2016 after which otter populations fully recovered. Population development stabilized while exhibiting an overall high association with environmental factors. The results of the diffusion kernel method and data variation according to the Geo-SOM consistently presented substantial change in population dispersal (i.e. the merge of two subpopulations, and complete associations between spraint and environmental factors). The combination of the diffusion kernel method and Geo-SOM was effective in portraying temporal changes in population states in association with environmental factors based on spraint data in the last phase of full recovery.
Keywords: dispersal; recovery; spraints; habitat preference; conservation; Republic of Korea


文中重要图表信息


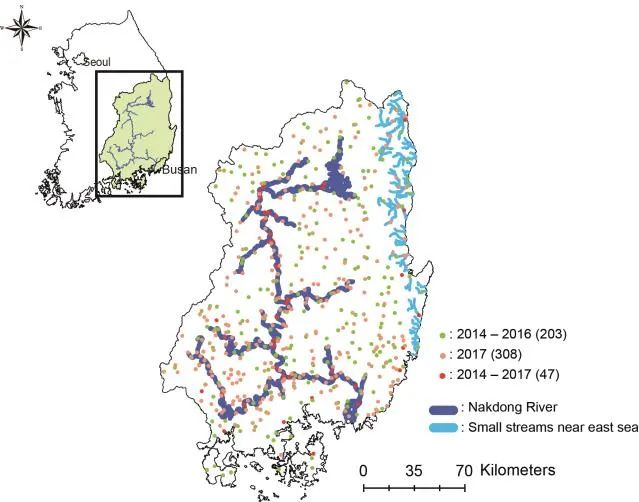
Figure 1. Study area. 250 sites between 2014 and 2016, and 355 sites during 2017 in the Nakdong River basin. Red circles (47 sample sites) represent the consistent sites throughout survey periods (2014 ~ 2017). Light green (203 sample sites) and light red circles (308 sample sites) represent the survey sites from 2014 to 2016 and 2017, respectively. Dark and light blue lines show the main river and tributaries of local rivers near the east coast, respectively. The upper left panel shows South Korea, and the light green area in the rectangle represent the Nakdong River basin.
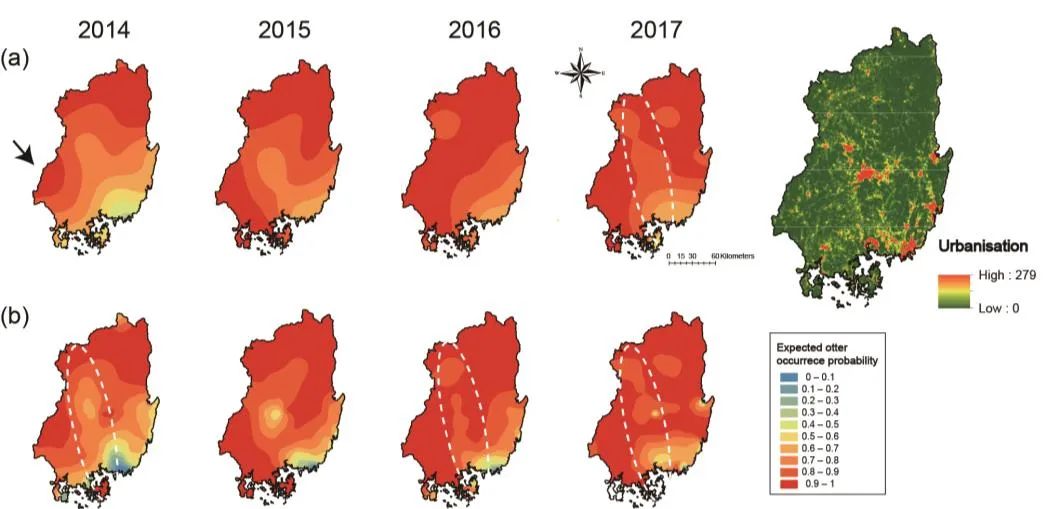
Figure 2. (a) Four maps of binary data using diffusion kernel estimations. Arrows indicate origin of S population. (b) Four maps using diffusion kernel estimations with additive barriers (urban area densities). (c) Urban area densities. Red and green colours represent high and low levels of urbanisation, respectively. White dotted circles in the fourth map of panel (a), first, third, and fourth maps of panel (b), and map (c) indicate the industrial belts (Gumi, Daegu, and Changwon).
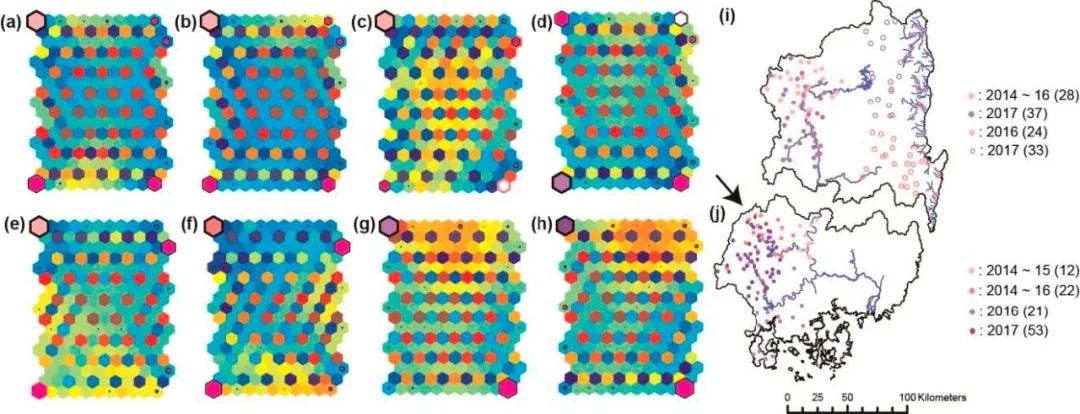
Figure 3. U matrices for N population in (a) 2014, (b) 2015, (c) 2016, and (d) 2017; and S population in (e) 2014, (f) 2015, (g) 2016, and (h) 2017. Sites clustered with high abundance of spraint densities in (i) N population and (j) S population. Hexagons ranging from light to deep purple and outlined in black indicate the strongest spatial clusters from earlier (2014) to later (2017) survey years, corresponding to study sites with the same-coloured circles in legend labels (i and j). Open white circles outlined in corresponding colours for each year indicate highest regional spraint density clusters (c, d) and sites (i). The arrow indicates the origin of the S population.
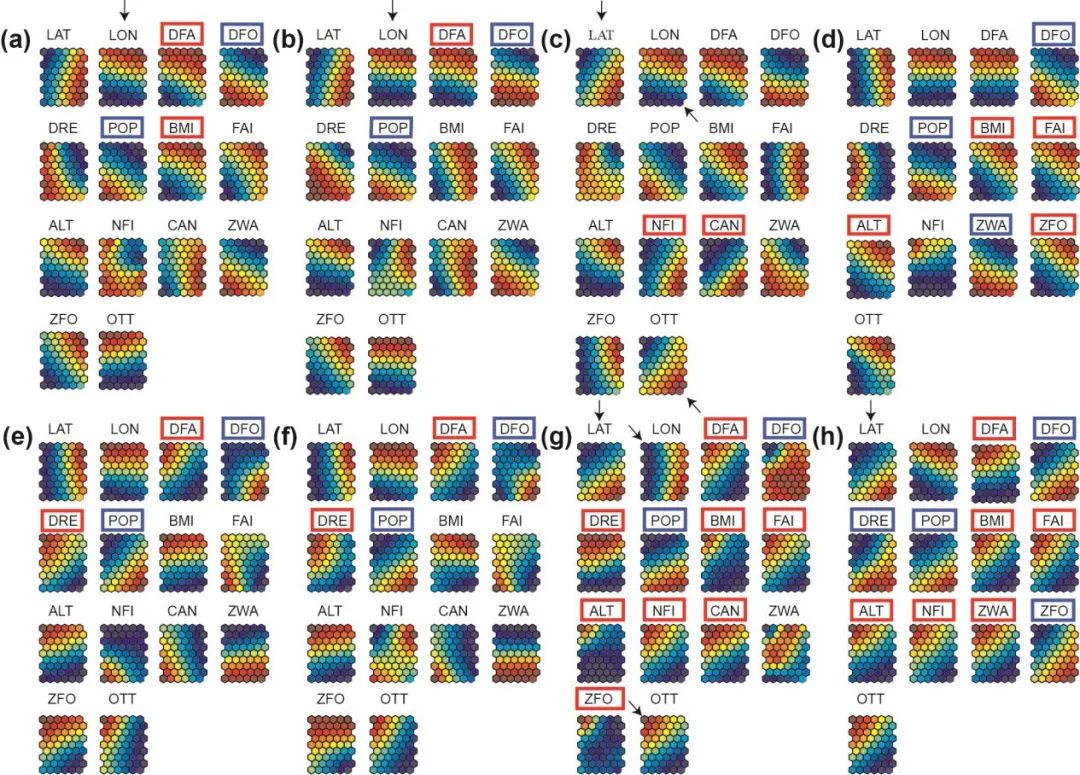
Figure 4. Component maps for N population in (a) 2014, (b) 2015, (c) 2016, and (d) 2017; and S population in (e) 2014, (f) 2015, (g) 2016, and (h) 2017. Red and blue rectangles outside of the abbreviated environmental factors indicate positive and negative relationships with spraint densities, respectively. All arrows correspond to the coordinate information, latitude (LAT) and longitude (LON), with higher spraint density areas. The values of all variables on the component planes were normalized between 0 (blue) and 1 (red).
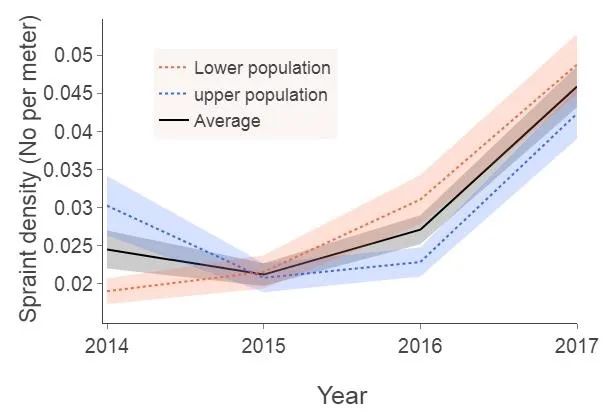
Figure 5. Spraint densities comparing the average (black line), S population (dotted red line), and N population (dotted blue line). Lightly coloured areas represent the standard error of each line.
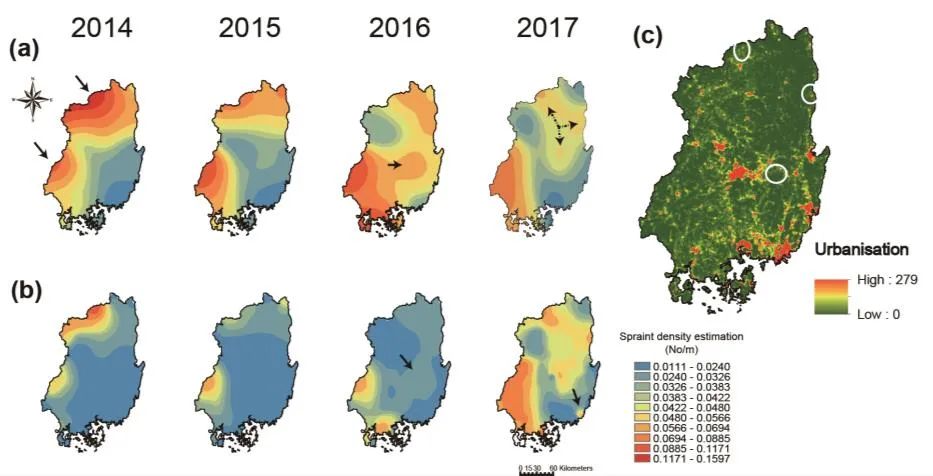
Figure 6. (a) Four maps using spraint densities data applying diffusion kernel estimations. (b) Four maps using diffusion kernel estimations with additive barriers (urban area densities). (c) Urban area densities. Red and green colours represent high and low levels of urbanisation, respectively. Arrows in the first map of upper panel (a) indicate the origin of each population, and third map of panel (a, b) indicate the combined area between the two populations. Dotted arrows in the fourth map of (a, b) suggest small regional populations. White circles in land cover map (c) represent the areas corresponding to all arrows of the third and fourth maps (a, b).

以上是关于期刊、论文、研究的motivation是啥?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章