Pytorch如何正确的查看自己定义的网络结构
Posted dlage
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Pytorch如何正确的查看自己定义的网络结构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
今天想看一下gan的网络结构:
原始的gan代码如下。
gan.py
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=200, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=8, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--latent_dim", type=int, default=100, help="dimensionality of the latent space")
parser.add_argument("--img_size", type=int, default=28, help="size of each image dimension")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=1, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=400, help="interval betwen image samples")
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
img_shape = (opt.channels, opt.img_size, opt.img_size)
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
def block(in_feat, out_feat, normalize=True):
layers = [nn.Linear(in_feat, out_feat)]
if normalize:
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_feat, 0.8))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*block(opt.latent_dim, 128, normalize=False),
*block(128, 256),
*block(256, 512),
*block(512, 1024),
nn.Linear(1024, int(np.prod(img_shape))),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, z):
img = self.model(z)
img = img.view(img.size(0), *img_shape)
return img
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(int(np.prod(img_shape)), 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(256, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
def forward(self, img):
img_flat = img.view(img.size(0), -1)
validity = self.model(img_flat)
return validity
# Loss function
adversarial_loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# Initialize generator and discriminator
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
if cuda:
generator.cuda()
discriminator.cuda()
adversarial_loss.cuda()
# Configure data loader
os.makedirs("../../data/mnist", exist_ok=True)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(
"../../data/mnist",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(opt.img_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])]
),
),
batch_size=opt.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
)
# Optimizers
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if cuda else torch.FloatTensor
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
for epoch in range(opt.n_epochs):
for i, (imgs, _) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = Variable(Tensor(imgs.size(0), 1).fill_(1.0), requires_grad=False)
fake = Variable(Tensor(imgs.size(0), 1).fill_(0.0), requires_grad=False)
# Configure input
real_imgs = Variable(imgs.type(Tensor))
# -----------------
# Train Generator
# -----------------
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Sample noise as generator input
z = Variable(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (imgs.shape[0], opt.latent_dim))))
# Generate a batch of images
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# Loss measures generator's ability to fool the discriminator
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs), valid)
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# Measure discriminator's ability to classify real from generated samples
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(real_imgs), valid)
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()), fake)
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
print(
"[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]"
% (epoch, opt.n_epochs, i, len(dataloader), d_loss.item(), g_loss.item())
)
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
save_image(gen_imgs.data[:25], "images/%d.png" % batches_done, nrow=5, normalize=True)
安装torchsummary包
sudo pip3 install torchsummary
如果是查看pytorch直接给的模型:下面代码就可以查看常用的网络结构了
import torchvision.models as models
from torchsummary import summary
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
vgg = models.vgg19().to(device)
summary(vgg, (3, 224, 224))
但是我们的网络是自己定义的,并且还有一定的限制。
这里先给出正确的方法:将网络的定义代码copy到这个文件(network_show.py)。然后加上查看网络结构的代码。
network_show.py
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
from torchsummary import summary
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=200, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=8, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--latent_dim", type=int, default=100, help="dimensionality of the latent space")
parser.add_argument("--img_size", type=int, default=28, help="size of each image dimension")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=1, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=400, help="interval betwen image samples")
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
img_shape = (opt.channels, opt.img_size, opt.img_size)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
def block(in_feat, out_feat, normalize=True):
layers = [nn.Linear(in_feat, out_feat)]
if normalize:
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_feat, 0.8))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*block(opt.latent_dim, 128, normalize=False),
*block(128, 256),
*block(256, 512),
*block(512, 1024),
nn.Linear(1024, int(np.prod(img_shape))),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, z):
img = self.model(z)
img = img.view(img.size(0), *img_shape)
return img
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(int(np.prod(img_shape)), 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(256, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
def forward(self, img):
img_flat = img.view(img.size(0), -1)
validity = self.model(img_flat)
return validity
G = Generator().to(device)
D = Discriminator().to(device)
summary(G)
为什么要单独建一个文件才能查看它的网络结构,不可以直接使用命令行吗。
答案:不可以
第一:首先我是准备直接在命令行import文件,然后接可以直接查看网络结构了。
但是出现了一个问题:import gan 这行命令会直接让它跑起来,gan.py文件在最上面给出了。
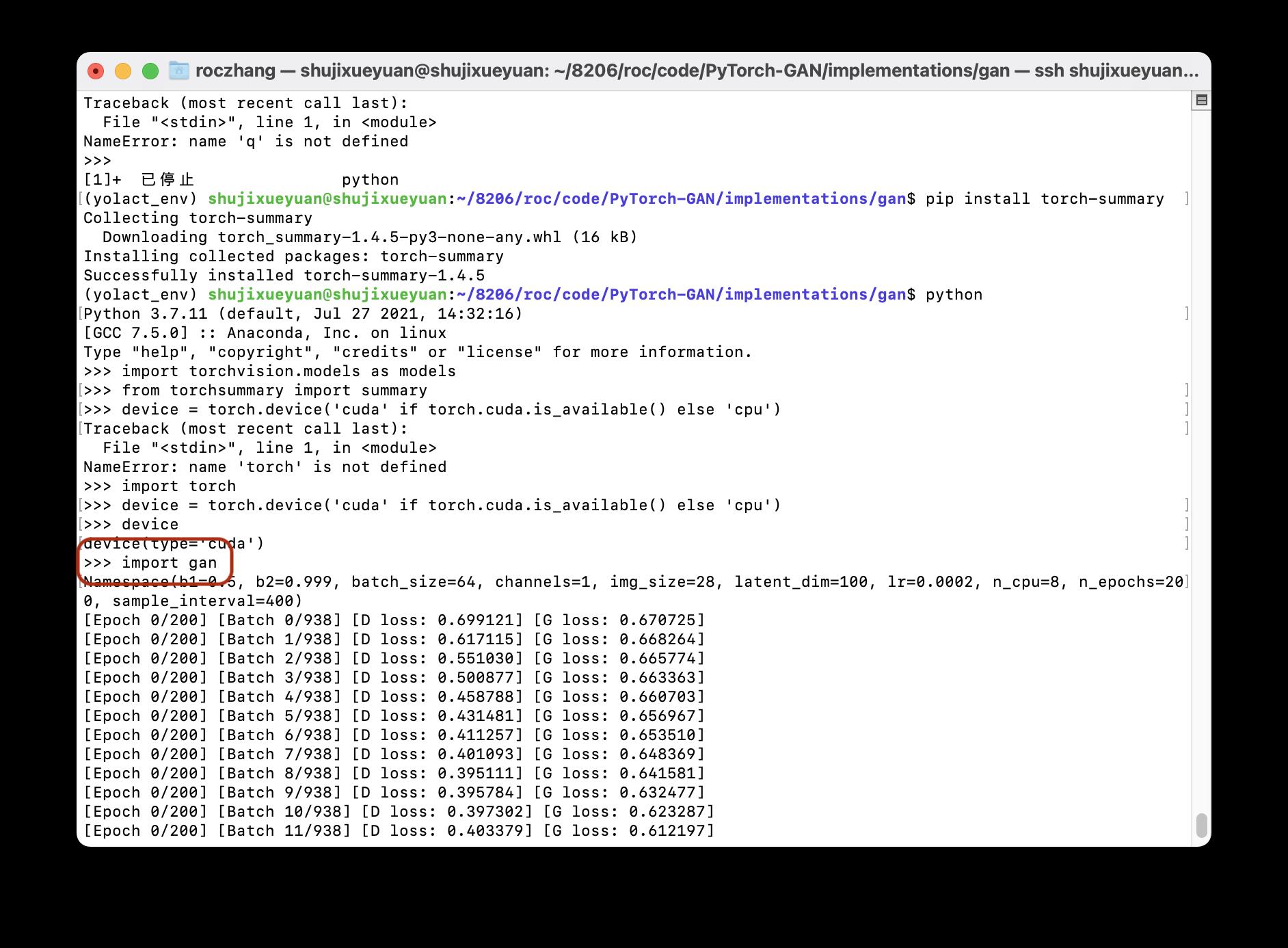
第二:看一下它的生成器代码:
很明显,在生成器中使用了opt.latent_dim, 128, normalize=False这个参数,这个参数需要结合python ***.py 参数 这样的命令来使用。所以我们不能直接用命令行来import这个py文件。 所以它并不能直接import。
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
def block(in_feat, out_feat, normalize=True):
layers = [nn.Linear(in_feat, out_feat)]
if normalize:
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_feat, 0.8))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*block(opt.latent_dim, 128, normalize=False),
*block(128, 256),
*block(256, 512),
*block(512, 1024),
nn.Linear(1024, int(np.prod(img_shape))),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, z):
img = self.model(z)
img = img.view(img.size(0), *img_shape)
return img
以上是关于Pytorch如何正确的查看自己定义的网络结构的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章