pthread_create的函数简介
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了pthread_create的函数简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 若线程创建成功,则返回0。若线程创建失败,则返回出错编号,并且*thread中的内容是未定义的。
返回成功时,由tidp指向的内存单元被设置为新创建线程的线程ID。attr参数用于指定各种不同的线程属性。新创建的线程从start_rtn函数的地址开始运行,该函数只有一个万能指针参数arg,如果需要向start_rtn函数传递的参数不止一个,那么需要把这些参数放到一个结构中,然后把这个结构的地址作为arg的参数传入。
linux下用C语言开发多线程程序,Linux系统下的多线程遵循POSIX线程接口,称为pthread。
由 restrict 修饰的指针是最初唯一对指针所指向的对象进行存取的方法,仅当第二个指针基于第一个时,才能对对象进行存取。对对象的存取都限定于基于由 restrict 修饰的指针表达式中。 由 restrict 修饰的指针主要用于函数形参,或指向由 malloc() 分配的内存空间。restrict 数据类型不改变程序的语义。 编译器能通过作出 restrict 修饰的指针是存取对象的唯一方法的假设,更好地优化某些类型的例程。 第一个参数为指向线程标识符的指针。
第二个参数用来设置线程属性。
第三个参数是线程运行函数的起始地址。
最后一个参数是运行函数的参数。 #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <string.h>void printids(const char *s) pid_t pid; pthread_t tid; pid = getpid(); tid = pthread_self(); printf(%s pid %u tid %u (0x%x)\\n, s, (unsigned int) pid, (unsigned int) tid, (unsigned int) tid);void *thr_fn(void *arg) printids(new thread: ); return NULL;int main(void) int err; pthread_t ntid; err = pthread_create(&ntid, NULL, thr_fn, NULL); if (err != 0) printf(can't create thread: %s\\n, strerror(err)); printids(main thread:); pthread_join(ntid,NULL); return EXIT_SUCCESS;$ gcc main.c -o main -std=c99 -pthread
$ ./main
main thread: pid 13073 tid 3077572816 (0xb77008d0)
new thread: pid 13073 tid 3077569392 (0xb76ffb70) #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#define NUM_THREADS 8void *PrintHello(void *args) int thread_arg; sleep(1); thread_arg = (int)(*((int*)args)); printf(Hello from thread %d\\n, thread_arg); return NULL;int main(void) int rc,t; pthread_t thread[NUM_THREADS]; for( t = 0; t < NUM_THREADS; t++) printf(Creating thread %d\\n, t); rc = pthread_create(&thread[t], NULL, PrintHello, &t); if (rc) printf(ERROR; return code is %d\\n, rc); return EXIT_FAILURE; sleep(5); for( t = 0; t < NUM_THREADS; t++) pthread_join(thread[t], NULL); return EXIT_SUCCESS;$ gcc thread_test.c -o thread_test -std=c99 -pthread
$ ./thread_test
Creating thread 0
Creating thread 1
Creating thread 2
Creating thread 3
Creating thread 4
Creating thread 5
Creating thread 6
Creating thread 7
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
Hello from thread 8
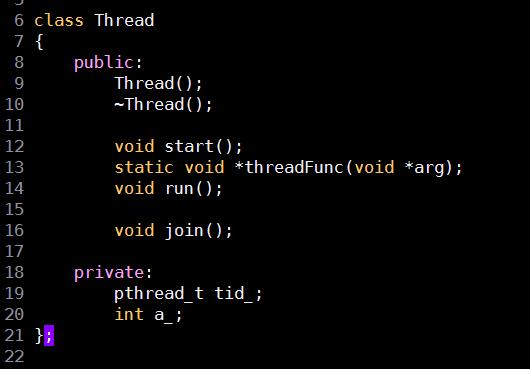
linux创建线程之pthread_create
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/amanlikethis/p/5537175.html
函数简介
pthread_create是UNIX环境创建线程函数
头文件
#include<pthread.h>
函数声明
int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp,const pthread_attr_t *restrict_attr,void*(*start_rtn)(void*),void *restrict arg);
返回值
若成功则返回0,否则返回出错编号
参数
第一个参数为指向线程标识符的指针。
第二个参数用来设置线程属性。
第三个参数是线程运行函数的地址。
最后一个参数是运行函数的参数。
注意
在编译时注意加上-lpthread参数,以调用静态链接库。因为pthread并非Linux系统的默认库。
pthread_join函数
函数简介
函数pthread_join用来等待一个线程的结束。
函数原型为:
extern int pthread_join __P (pthread_t __th, void **__thread_return);
参数:
第一个参数为被等待的线程标识符
第二个参数为一个用户定义的指针,它可以用来存储被等待线程的返回值。
注意
这个函数是一个线程阻塞的函数,调用它的函数将一直等待到被等待的线程结束为止,当函数返回时,被等待线程的资源被收回。如果执行成功,将返回0,如果失败则返回一个错误号。
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<pthread.h>
4
5 /* 声明结构体 */
6 struct member
7
8 int num;
9 char *name;
10 ;
11
12 /* 定义线程pthread */
13 static void * pthread(void *arg)
14
15 struct member *temp;
16
17 /* 线程pthread开始运行 */
18 printf("pthread start!\\n");
19
20 /* 令主线程继续执行 */
21 sleep(2);
22
23 /* 打印传入参数 */
24 temp = (struct member *)arg;
25 printf("member->num:%d\\n",temp->num);
26 printf("member->name:%s\\n",temp->name);
27
28 return NULL;
29
30
31 /* main函数 */
32 int main(int agrc,char* argv[])
33
34 pthread_t tidp;
35 struct member *b;
36
37 /* 为结构体变量b赋值 */
38 b = (struct member *)malloc(sizeof(struct member));
39 b->num=1;
40 b->name="mlq";
41
42 /* 创建线程pthread */
43 if ((pthread_create(&tidp, NULL, pthread, (void*)b)) == -1)
44
45 printf("create error!\\n");
46 return 1;
47
48
49 /* 令线程pthread先运行 */
50 sleep(1);
51
52 /* 线程pthread睡眠2s,此时main可以先执行 */
53 printf("mian continue!\\n");
54
55 /* 等待线程pthread释放 */
56 if (pthread_join(tidp, NULL))
57
58 printf("thread is not exit...\\n");
59 return -2;
60
61
62 return 0;
63
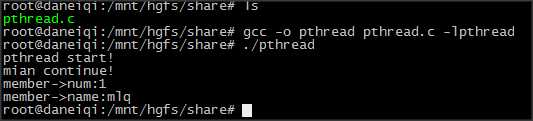
编译与执行结果
编译与执行结果如下图所示,可以看到主线程main和线程pthread交替执行。也就是说是当我们创建了线程pthread之后,两个线程都在执行,证明创建成功。另外,可以看到创建线程pthread时候,传入的参数被正确打印。
以上是关于pthread_create的函数简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章