VUEVue 源码解析
Posted lilicat
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了VUEVue 源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Vue 源码解析
Vue 的工作机制
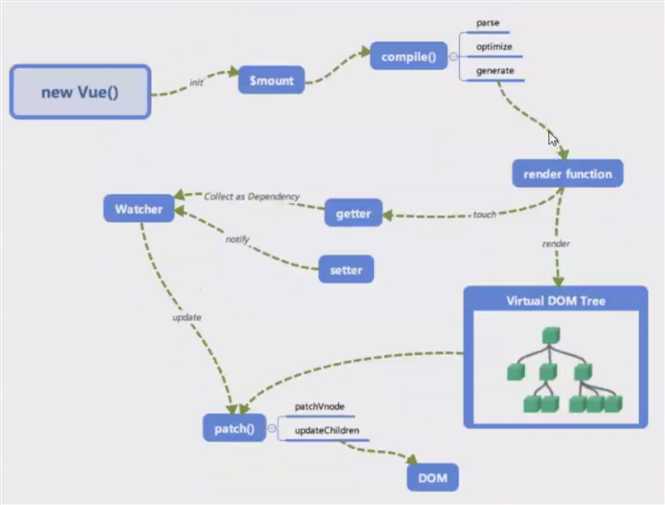
在 new vue() 之后,Vue 会调用进行初始化,会初始化生命周期、事件、props、methods、data、computed和watch等。其中最重要的是通过Object.defineProperty设置setter和getter,用来实现响应式和依赖收集。
初始化之后,调用 $mount 挂载组件。
启动编译器compile(),对template进行扫描,parse、optimize、generate,在这个阶段会生成渲染函数或更新函数,render function,生成虚拟节点数,将来我们改变的数据,并不是真的DOM操作,而是虚拟DOM上的数值。
在更新前,会做一个diff算法的比较,通过新值和老值的比较,计算出最小的DOM更新。执行到patch()来打补丁,做界面更新,目的是用JS计算的时间换DOM操作的时间。因为页面渲染很耗时间,所以vue的目的就是减少页面渲染的次数和数量。
render function除了编译渲染函数以外,还做了一个依赖搜集(界面中做了很多绑定,如何知道和数据模型之间的关系)。当数据变化时,该去界面中更新哪个数据节点。通过观察者watcher()来调用更新函数patch()
编译
编译模块分为三个阶段
- parse 使用正则解析template中vue的指令变量等,形成语法树AST
- optimize 标记一些静态节点,用作后面的性能优化,在diff的时候直接略过
- generate 把第一步生成的AST转化为渲染函数render function
响应式
vue 核心内容
初始化的时候通过defineProverty进行绑定,设置通知机制,当编译生成的渲染函数被实际渲染时,会触发getter进行依赖收集,在数据变化时,通过setter进行更新。
虚拟DOM
virtual DOM 是react首创,Vue2开始支持,用js对象来描述DOM结构,数据修改的时候,先修改虚拟DOM中的数据,然后数组做diff,最后再汇总所有的diff,力求做最少的dom操作,毕竟js里对比很快,而真实的dom操作太慢。
{
tag: ‘div‘,
props: {
name: ‘xx‘,
style: {color: red},
onClick: xx
},
children: [{
tag: ‘a‘,
text: ‘click me‘
}]
}
<div name="xx" style="color: red" @click="xx">
<a>click me</a>
</div>
更新视图
数据修改触发setter,然后监听器会通知进行修改,通过对比两个DOM树,得到改变的地方,就是patch,只需要把这些差异修改即可。
Vue2响应式的原理: defineProperty
<div id="app"><div id="name"></div></div>
<script>
let obj = {}
Object.defineProperty(obj, ‘name‘, {
get: function() {
return document.querySelector(‘#name‘).innerhtml
},
set: function(val) {
document.querySelector(‘#name‘).innerHTML = val
}
})
obj.name=‘adela‘
</script>
描述vue数据绑定的原理
利用了Object.defineProperty这个属性,将data中的每一个属性,都定义了getter和setter,去监听这些属性的变化,当某些属性变化时,我们可以通知需要更新的地方去更新。[数据劫持]
实现数据响应式
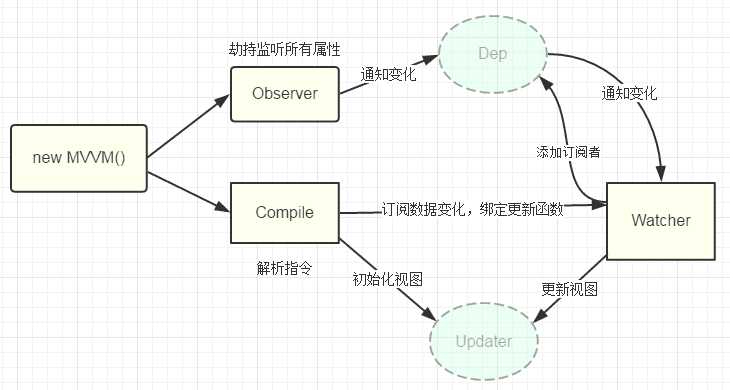
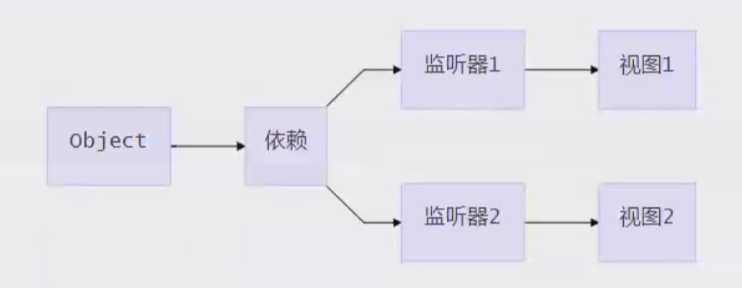
增加了一个Dep类,用来搜集Watcher对象。
读数据的时候,会触发getter函数把当前的Watcher对象(存放在Dep.target中)搜集到Dep类中去。
写数据的时候,则会触发setter方法,通知Dep类调用notify来触发所有watcher对象的update方法更新对应视图。
检查点
- vue编译过程是怎么样的 vue写的模板语句,HTML不识别,通过编译的过程,进行依赖搜集,data中的数据模型和视图进行了绑定,如果模型发生变化,会通知依赖的地方进行更新,这就是执行编译的目的。模型驱动视图。
- 双向绑定的原理是什么 v-model 的指令放在input上,在编译时,可以解析出v-model。操作时做了两件事情,一,在当前v-model所属的元素上加了一个事件监听,v-model指定的事件回调函数当做input事件回调函数去监听,当input发生变化时,就将值更新到vue实例上。二、vue实例已经实现了数据的响应化,setter函数会触发界面中所有依赖的更新。
代码
// kvue.js
class KVue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options
this.$data = options.data
this.observe(this.$data)
new Compile(options.el, this)
if (options.created) {
options.created.call(this)
}
}
observe(value) {
if (!value || typeof value !== ‘object‘) {
return
}
Object.keys(value).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(value, key, value[key])
// 代理data中的属性到vue实例上
this.proxyData(key)
})
}
defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
this.observe(val) // 递归解决数据嵌套
const dep = new Dep() // 初始化dependence
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target)
return val
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal == val)
return
val = newVal
console.log(`${key}属性更新了:${val}`)
dep.notify()
}
})
}
proxyData(key) {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
return this.$data[key]
},
set(newVal) {
this.$data[key] = newVal
}
})
}
}
// Dep: 用来管理watcher对象。
// 读数据的时候,会触发getter函数,把当前的Watcher对象(存放在Dep.target中)搜集到Dep类中去。
// 写数据的时候,会触发setter方法,通知Dep类调用notify来触发所有watcher对象的update方法更新对应视图。
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 这里存放若干依赖(watcheer)
this.deps = []
}
addDep(dep) {
this.deps.push(dep)
}
notify() {
// 通知所有的依赖去做更新
this.deps.forEach(dep => dep.update())
}
}
// Wathcer
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, cb) {
this.vm = vm
this.key = key
this.cb = cb
// 将当前watcher实例制定到Dep静态属性target
Dep.target = this
this.vm[this.key] // 触发getter, 添加依赖
Dep.target = null
}
update() {
console.log(`属性更新了`)
this.cb.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key])
}
}
// compile.js
class Compile {
constructor(el, vm) {
// 要遍历的宿主节点
this.$el = document.querySelector(el)
this.$vm = vm
// 编译
if (this.$el) {
// 转换内部内容为片段fragment
this.$fragment = this.node2fragment(this.$el)
// 执行编译
this.compile(this.$fragment)
// 将编译完的HTML结果追加至$el
this.$el.appendChild(this.$fragment)
}
}
// 将宿主元素中代码片段拿出来遍历,比较高效
node2fragment(el) {
const frag = document.createDocumentFragment()
// 将el中的所有子元素搬家至frag中
let child
while ((child = el.firstChild)) {
frag.appendChild(child)
}
return frag
}
// 编译过程
compile(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
// 判断类型
if (this.isElement(node)) {
// 元素
// console.log(‘编译元素‘ + node.nodeName)
const nodeAttrs = node.attributes
Array.from(nodeAttrs).forEach(attr => {
const attrName = attr.name // 属性名
const exp = attr.value // 属性值
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// k-text
const dir = attrName .substring(2)
this[dir] && this[dir](node, this.$vm, exp)
} else if (this.isEvent(attrName)) {
let dir = attrName.substring(1)
this.eventHandler(node, this.$vm, exp, dir)
}
})
} else if (this.isInterpolation(node)) {
// 文本
// console.log(‘编译文本‘ + node.textContent)
this.compileText(node)
}
// 递归子节点
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
// console.log(RegExp.$1)
this.update(node, this.$vm, RegExp.$1, ‘text‘)
}
// 更新函数
update(node, vm, exp, dir) {
const updaterFn = this[dir + ‘Updater‘]
// 初始化
updaterFn && updaterFn(node, vm[exp])
// 依赖收集
new Watcher(vm, exp, function(value) {
updaterFn && updaterFn(node, value)
})
}
text(node, vm, exp) {
this.update(node, vm, exp, ‘text‘)
}
// 事件处理器
eventHandler(node, vm, exp, dir) {
let fn = vm.$options.methods && vm.$options.methods[exp]
if (dir && fn) {
node.addEventListener(dir, fn.bind(vm))
}
}
html(node, vm, exp) {
this.update(node, vm, exp, ‘html‘)
}
// 双向绑定
model(node, vm, exp) {
// 指定input的value属性
this.update(node, vm, exp, ‘model‘)
// 视图对模型响应
node.addEventListener(‘input‘, e => {
vm[exp] = e.target.value
})
}
modelUpdater(node, value) {
node.value = value
}
textUpdater(node, value) {
node.textContent = value
}
htmlUpdater(node, value) {
node.innerHTML = value
}
isDirective(attr) {
return attr.indexOf(‘k-‘) == 0
}
isEvent(attr) {
return attr.indexOf(‘@‘) == 0
}
isElement(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
isInterpolation(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3 && /{{(.*)}}/.test(node.textContent)
}
}
<!-- index.html -->
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{name}}</p>
<p k-text="name"></p>
<p>{{age}}</p>
<p> {{doubleAge}} </p>
<input type="text" k-model="name">
<button @click="changeName">click me</button>
<div k-html="html"></div>
</div>
<script src=‘./compile.js‘></script>
<script src=‘./kvue.js‘></script>
<script>
let xx = new KVue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
name: "I am test.",
age: 12,
html: ‘<button>这是一个按钮</button>‘
},
created() {
console.log(‘开始啦‘)
setTimeout(() => {
this.name = ‘我是测试‘
}, 1500)
}, methods: {
changeName() {
this.name = ‘哈喽,嘻嘻嘻‘
this.age = 1
this.id = ‘xx‘
console.log(1, this)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>以上是关于VUEVue 源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章