C# UTM坐标和WGS84坐标转换小工具
Posted netlzl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C# UTM坐标和WGS84坐标转换小工具相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
工具根据:http://home.hiwaay.net/~taylorc/toolbox/geography/geoutm.html js代码改编
工具源码github:https://github.com/JeroLong/TUMAndWGS84TransTool.git
效果:
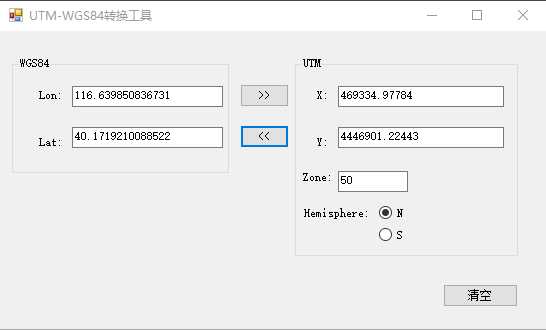
主要代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace UTMAndWGS84TransTool { public class UTMAndWGS84 { static double pi = Math.PI; /* Ellipsoid model constants (actual values here are for WGS84) */ static double sm_a = 6378137.0; static double sm_b = 6356752.314; static double sm_EccSquared = 6.69437999013e-03; static double UTMScaleFactor = 0.9996; /* * DegToRad * * Converts degrees to radians. * */ private static double DegToRad(double deg) { return (deg / 180.0 * pi); } /* * RadToDeg * * Converts radians to degrees. * */ private static double RadToDeg(double rad) { return (rad / pi * 180.0); } /* * ArcLengthOfMeridian * * Computes the ellipsoidal distance from the equator to a point at a * given latitude. * * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. * * Inputs: * phi - Latitude of the point, in radians. * * Globals: * sm_a - Ellipsoid model major axis. * sm_b - Ellipsoid model minor axis. * * Returns: * The ellipsoidal distance of the point from the equator, in meters. * */ private static double ArcLengthOfMeridian(double phi) { double alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, n; double result; /* Precalculate n */ n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); /* Precalculate alpha */ alpha = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * (1.0 + (Math.Pow(n, 2.0) / 4.0) + (Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 64.0)); /* Precalculate beta */ beta = (-3.0 * n / 2.0) + (9.0 * Math.Pow(n, 3.0) / 16.0) + (-3.0 * Math.Pow(n, 5.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate gamma */ gamma = (15.0 * Math.Pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-15.0 * Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate delta */ delta = (-35.0 * Math.Pow(n, 3.0) / 48.0) + (105.0 * Math.Pow(n, 5.0) / 256.0); /* Precalculate epsilon */ epsilon = (315.0 * Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); /* Now calculate the sum of the series and return */ result = alpha * (phi + (beta * Math.Sin(2.0 * phi)) + (gamma * Math.Sin(4.0 * phi)) + (delta * Math.Sin(6.0 * phi)) + (epsilon * Math.Sin(8.0 * phi))); return result; } /* * UTMCentralMeridian * * Determines the central meridian for the given UTM zone. * * Inputs: * zone - An integer value designating the UTM zone, range [1,60]. * * Returns: * The central meridian for the given UTM zone, in radians, or zero * if the UTM zone parameter is outside the range [1,60]. * Range of the central meridian is the radian equivalent of [-177,+177]. * */ private static double UTMCentralMeridian(double zone) { double cmeridian; cmeridian = DegToRad(-183.0 + (zone * 6.0)); return cmeridian; } /* * FootpointLatitude * * Computes the footpoint latitude for use in converting transverse * Mercator coordinates to ellipsoidal coordinates. * * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. * * Inputs: * y - The UTM northing coordinate, in meters. * * Returns: * The footpoint latitude, in radians. * */ private static double FootpointLatitude(double y) { double y_, alpha_, beta_, gamma_, delta_, epsilon_, n; double result; /* Precalculate n (Eq. 10.18) */ n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); /* Precalculate alpha_ (Eq. 10.22) */ /* (Same as alpha in Eq. 10.17) */ alpha_ = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * (1 + (Math.Pow(n, 2.0) / 4) + (Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 64)); /* Precalculate y_ (Eq. 10.23) */ y_ = y / alpha_; /* Precalculate beta_ (Eq. 10.22) */ beta_ = (3.0 * n / 2.0) + (-27.0 * Math.Pow(n, 3.0) / 32.0) + (269.0 * Math.Pow(n, 5.0) / 512.0); /* Precalculate gamma_ (Eq. 10.22) */ gamma_ = (21.0 * Math.Pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-55.0 * Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate delta_ (Eq. 10.22) */ delta_ = (151.0 * Math.Pow(n, 3.0) / 96.0) + (-417.0 * Math.Pow(n, 5.0) / 128.0); /* Precalculate epsilon_ (Eq. 10.22) */ epsilon_ = (1097.0 * Math.Pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); /* Now calculate the sum of the series (Eq. 10.21) */ result = y_ + (beta_ * Math.Sin(2.0 * y_)) + (gamma_ * Math.Sin(4.0 * y_)) + (delta_ * Math.Sin(6.0 * y_)) + (epsilon_ * Math.Sin(8.0 * y_)); return result; } /* * MapLatLonToXY * * Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the * Transverse Mercator projection. Note that Transverse Mercator is not * the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them. * * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. * * Inputs: * phi - Latitude of the point, in radians. * lambda - Longitude of the point, in radians. * lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians. * * Outputs: * xy - A 2-element array containing the x and y coordinates * of the computed point. * * Returns: * The function does not return a value. * */ private static void MapLatLonToXY(double phi, double lambda, double lambda0, out double[] xy) { double N, nu2, ep2, t, t2, l; double l3coef, l4coef, l5coef, l6coef, l7coef, l8coef; double tmp; /* Precalculate ep2 */ ep2 = (Math.Pow(sm_a, 2.0) - Math.Pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / Math.Pow(sm_b, 2.0); /* Precalculate nu2 */ nu2 = ep2 * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 2.0); /* Precalculate N */ N = Math.Pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * Math.Sqrt(1 + nu2)); /* Precalculate t */ t = Math.Tan(phi); t2 = t * t; tmp = (t2 * t2 * t2) - Math.Pow(t, 6.0); /* Precalculate l */ l = lambda - lambda0; /* Precalculate coefficients for l**n in the equations below so a normal human being can read the expressions for easting and northing -- l**1 and l**2 have coefficients of 1.0 */ l3coef = 1.0 - t2 + nu2; l4coef = 5.0 - t2 + 9 * nu2 + 4.0 * (nu2 * nu2); l5coef = 5.0 - 18.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 14.0 * nu2 - 58.0 * t2 * nu2; l6coef = 61.0 - 58.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 270.0 * nu2 - 330.0 * t2 * nu2; l7coef = 61.0 - 479.0 * t2 + 179.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); l8coef = 1385.0 - 3111.0 * t2 + 543.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); xy = new double[2]; /* Calculate easting (x) */ xy[0] = N * Math.Cos(phi) * l + (N / 6.0 * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 3.0) * l3coef * Math.Pow(l, 3.0)) + (N / 120.0 * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 5.0) * l5coef * Math.Pow(l, 5.0)) + (N / 5040.0 * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 7.0) * l7coef * Math.Pow(l, 7.0)); /* Calculate northing (y) */ xy[1] = ArcLengthOfMeridian(phi) + (t / 2.0 * N * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 2.0) * Math.Pow(l, 2.0)) + (t / 24.0 * N * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 4.0) * l4coef * Math.Pow(l, 4.0)) + (t / 720.0 * N * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 6.0) * l6coef * Math.Pow(l, 6.0)) + (t / 40320.0 * N * Math.Pow(Math.Cos(phi), 8.0) * l8coef * Math.Pow(l, 8.0)); return; } /* * MapXYToLatLon * * Converts x and y coordinates in the Transverse Mercator projection to * a latitude/longitude pair. Note that Transverse Mercator is not * the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them. * * Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J., * GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994. * * Inputs: * x - The easting of the point, in meters. * y - The northing of the point, in meters. * lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians. * * Outputs: * philambda - A 2-element containing the latitude and longitude * in radians. * * Returns: * The function does not return a value. * * Remarks: * The local variables Nf, nuf2, tf, and tf2 serve the same purpose as * N, nu2, t, and t2 in MapLatLonToXY, but they are computed with respect * to the footpoint latitude phif. * * x1frac, x2frac, x2poly, x3poly, etc. are to enhance readability and * to optimize computations. * */ private static void MapXYToLatLon(double x, double y, double lambda0, out double[] xy) { double phif, Nf, Nfpow, nuf2, ep2, tf, tf2, tf4, cf; double x1frac, x2frac, x3frac, x4frac, x5frac, x6frac, x7frac, x8frac; double x2poly, x3poly, x4poly, x5poly, x6poly, x7poly, x8poly; /* Get the value of phif, the footpoint latitude. */ phif = FootpointLatitude(y); /* Precalculate ep2 */ ep2 = (Math.Pow(sm_a, 2.0) - Math.Pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / Math.Pow(sm_b, 2.0); /* Precalculate cos (phif) */ cf = Math.Cos(phif); /* Precalculate nuf2 */ nuf2 = ep2 * Math.Pow(cf, 2.0); /* Precalculate Nf and initialize Nfpow */ Nf = Math.Pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * Math.Sqrt(1 + nuf2)); Nfpow = Nf; /* Precalculate tf */ tf = Math.Tan(phif); tf2 = tf * tf; tf4 = tf2 * tf2; /* Precalculate fractional coefficients for x**n in the equations below to simplify the expressions for latitude and longitude. */ x1frac = 1.0 / (Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**2) */ x2frac = tf / (2.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**3) */ x3frac = 1.0 / (6.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**4) */ x4frac = tf / (24.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**5) */ x5frac = 1.0 / (120.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**6) */ x6frac = tf / (720.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**7) */ x7frac = 1.0 / (5040.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**8) */ x8frac = tf / (40320.0 * Nfpow); /* Precalculate polynomial coefficients for x**n. -- x**1 does not have a polynomial coefficient. */ x2poly = -1.0 - nuf2; x3poly = -1.0 - 2 * tf2 - nuf2; x4poly = 5.0 + 3.0 * tf2 + 6.0 * nuf2 - 6.0 * tf2 * nuf2 - 3.0 * (nuf2 * nuf2) - 9.0 * tf2 * (nuf2 * nuf2); x5poly = 5.0 + 28.0 * tf2 + 24.0 * tf4 + 6.0 * nuf2 + 8.0 * tf2 * nuf2; x6poly = -61.0 - 90.0 * tf2 - 45.0 * tf4 - 107.0 * nuf2 + 162.0 * tf2 * nuf2; x7poly = -61.0 - 662.0 * tf2 - 1320.0 * tf4 - 720.0 * (tf4 * tf2); x8poly = 1385.0 + 3633.0 * tf2 + 4095.0 * tf4 + 1575 * (tf4 * tf2); xy = new double[2]; /* Calculate latitude */ xy[0] = phif + x2frac * x2poly * (x * x) + x4frac * x4poly * Math.Pow(x, 4.0) + x6frac * x6poly * Math.Pow(x, 6.0) + x8frac * x8poly * Math.Pow(x, 8.0); /* Calculate longitude */ xy[1] = lambda0 + x1frac * x + x3frac * x3poly * Math.Pow(x, 3.0) + x5frac * x5poly * Math.Pow(x, 5.0) + x7frac * x7poly * Math.Pow(x, 7.0); return; } /* * LatLonToUTMXY * * Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the * Universal Transverse Mercator projection. * * Inputs: * lat - Latitude of the point, in radians. * lon - Longitude of the point, in radians. * zone - UTM zone to be used for calculating values for x and y. * If zone is less than 1 or greater than 60, the routine * will determine the appropriate zone from the value of lon. * * Outputs: * xy - A 2-element array where the UTM x and y values will be stored. * * Returns: * The UTM zone used for calculating the values of x and y. * */ public static double[] LatLonToUTMXY(double lat, double lon) { double zone = Math.Floor((lon + 180.0) / 6) + 1; double[] xy = new double[2]; MapLatLonToXY(DegToRad(lat),DegToRad (lon), UTMCentralMeridian(zone), out xy); /* Adjust easting and northing for UTM system. */ xy[0] = xy[0] * UTMScaleFactor + 500000.0; xy[1] = xy[1] * UTMScaleFactor; if (xy[1] < 0.0) xy[1] = xy[1] + 10000000.0; return new double[] { xy[0], xy[1], zone }; } /* * UTMXYToLatLon * * Converts x and y coordinates in the Universal Transverse Mercator * projection to a latitude/longitude pair. * * Inputs: * x - The easting of the point, in meters. * y - The northing of the point, in meters. * zone - The UTM zone in which the point lies. * southhemi - True if the point is in the southern hemisphere; * false otherwise. * * Outputs: * latlon - A 2-element array containing the latitude and * longitude of the point, in radians. * * Returns: * The function does not return a value. * */ public static double[] UTMXYToLatLon(double x, double y, double zone, bool southhemi) { double cmeridian; x -= 500000.0; x /= UTMScaleFactor; /* If in southern hemisphere, adjust y accordingly. */ if (southhemi) y -= 10000000.0; y /= UTMScaleFactor; cmeridian = UTMCentralMeridian(zone); double[] xy = new double[2]; MapXYToLatLon(x, y, cmeridian, out xy); xy[0] = RadToDeg(xy[0]); xy[1] = RadToDeg(xy[1]); return xy; } } }
以上是关于C# UTM坐标和WGS84坐标转换小工具的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章