eclipse的工程项目太多了,怎么隐藏工程
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了eclipse的工程项目太多了,怎么隐藏工程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
方法1:按键盘 Delete 键删除。这样的话只是在eclipse上的工程没了,源文件还是在存放的那个文件夹而不会被删除。方法2:在项目下点击右键,选择 Close Project。 参考技术A 只能关闭哦,要么就像上面的一样删除工程,但不删除磁盘文件 参考技术B 建立工作集 就行了
分分类 然后再包资源管理器里 点那个倒三角,选顶层元素--工作集
就行了 参考技术C 你可以关闭工程。
或者删除Eclipse中的工程(不删除磁盘文件) 参考技术D 你点右键Delete掉,不要Delete磁盘文件即可。
项目中的if else太多了,该怎么重构?
一. 项目中的if else太多了,该怎么重构?
环境:SpringBoot,JDK1.8
在实际开发中,有一部分业务逻辑是这样的
if (msgType = "文本") {
// dosomething
} else if(msgType = "图片") {
// doshomething
} else if(msgType = "视频") {
// doshomething
} else {
// doshomething
}
就是根据消息的不同类型有不同的处理策略,每种消息的处理策略代码都很长,如果都放在这种if else代码快中,代码很难维护也很丑,所以我们一开始就用了策略模式来处理这种情况。
策略模式还挺简单的,就是定义一个接口,然后有多个实现类,每种实现类封装了一种行为。然后根据条件的不同选择不同的实现类。
1. 实现过程
消息对象,当然真实的对象没有这么简单,省略了很多属性
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MessageInfo {
// 消息类型
private Integer type;
// 消息内容
private String content;
}
定义一个消息处理接口
public interface MessageService {
void handleMessage(MessageInfo messageInfo);
}
有2个消息处理接口,分别处理不同的消息
处理文本消息
@Service
@MsgTypeHandler(value = MSG_TYPE.TEXT)
public class TextMessageService implements MessageService {
@Override
public void handleMessage(MessageInfo messageInfo) {
System.out.println("处理文本消息 " + messageInfo.getContent());
}
}
处理图片消息
@Service
@MsgTypeHandler(value = MSG_TYPE.IMAGE)
public class ImageMessageService implements MessageService {
@Override
public void handleMessage(MessageInfo messageInfo) {
System.out.println("处理图片消息 " + messageInfo.getContent());
}
}
文章写到这,可能大多数人可能会想到要需要如下一个Map, Map<消息类型,消息处理对象>,这样直接根据消息类型就能拿到消息处理对象,调用消息处理对象的方法即可。我们就是这样做的,但是我们不想手动维护这个Map对象,因为每次增加新的消息处理类,Map的初始化过程就得修改。
我们使用了注解+ApplicationListener来保存这种映射关系,来看看怎么做的吧。
定义一个消息类型的枚举类
public enum MSG_TYPE {
TEXT(1, "文本"),
IMAGE(2, "图片"),
VIDEO(3, "视频");
public final int code;
public final String name;
MSG_TYPE(int code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
}
定义一个注解
@Documented
@Inherited
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MsgTypeHandler {
MSG_TYPE value();
}
不知道你注意到了没,前面的代码中,每种消息处理类上面都有一个@MsgTypeHandler注解,表明了这个处理类处理哪种类型的消息
@Service
@MsgTypeHandler(value = MSG_TYPE.TEXT)
public class TextMessageService implements MessageService {
@Override
public void handleMessage(MessageInfo messageInfo) {
System.out.println("处理文本消息 " + messageInfo.getContent());
}
}
用一个context对象保存了消息类型->消息处理对象的映射关系
@Component
public class MessageServiceContext {
private final Map<Integer, MessageService> handlerMap = new HashMap<>();
public MessageService getMessageService(Integer type) {
return handlerMap.get(type);
}
public void putMessageService(Integer code, MessageService messageService) {
handlerMap.put(code, messageService);
}
}
最精彩的部分到了
@Component
public class MessageServiceListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
Map<String, Object> beans = event.getApplicationContext().getBeansWithAnnotation(MsgTypeHandler.class);
MessageServiceContext messageServiceContext = event.getApplicationContext().getBean(MessageServiceContext.class);
beans.forEach((name, bean) -> {
MsgTypeHandler typeHandler = bean.getClass().getAnnotation(MsgTypeHandler.class);
messageServiceContext.putMessageService(typeHandler.value().code, (MessageService) bean);
});
}
}
在spring的启动过程中,通过解析注解,将消息类型->消息处理对象的映射关系保存到MessageServiceContext对象中
@Autowired
MessageServiceContext messageServiceContext;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
// 构建一个文本消息
MessageInfo messageInfo = new MessageInfo(MSG_TYPE.TEXT.code, "消息内容");
MessageService messageService = messageServiceContext.getMessageService(messageInfo.getType());
// 处理文本消息 消息内容
// 可以看到文本消息被文本处理类所处理
messageService.handleMessage(messageInfo);
}
测试类正常工作,通过策略模式避免了写大量的if else代码,也更容易维护
二. SpringBoot集成Shiro与Swagger-Bootstrap-UI极简教程
1. 前言
Apache Shiro是一个功能强大且易于使用的Java安全框架,提供了认证,授权,加密,和会话管理。
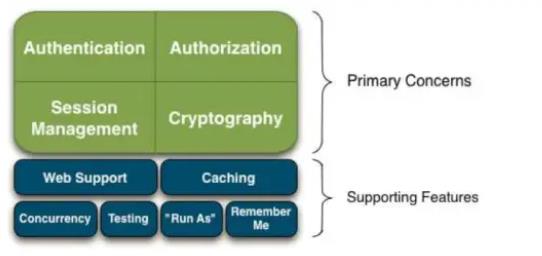
Shiro有三大核心组件:
- Subject: 即当前用户,在权限管理的应用程序里往往需要知道谁能够操作什么,谁拥有操作该程序的权利,shiro中则需要通过Subject来提供基础的当前用户信息,Subject 不仅仅代表某个用户,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject,如网络爬虫等。所有的Subject都要绑定到SecurityManager上,与Subject的交互实际上是被转换为与SecurityManager的交互。
- SecurityManager: 即所有Subject的管理者,这是Shiro框架的核心组件,可以把他看做是一个Shiro框架的全局管理组件,用于调度各种Shiro框架的服务。作用类似于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet,用于拦截所有请求并进行处理。
- Realm: Realm是用户的信息认证器和用户的权限人证器,我们需要自己来实现Realm来自定义的管理我们自己系统内部的权限规则。SecurityManager要验证用户,需要从Realm中获取用户。可以把Realm看做是数据源。
2. 数据库设计
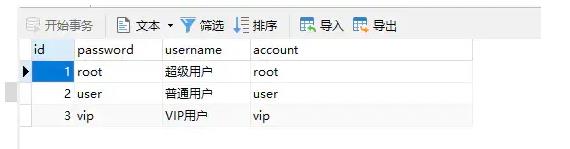
2.1 User(用户)
account:表示账号
username:用户名
password:密码
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`password` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`username` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`account` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (1, 'root', '超级用户', 'root');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (2, 'user', '普通用户', 'user');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (3, 'vip', 'VIP用户', 'vip');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
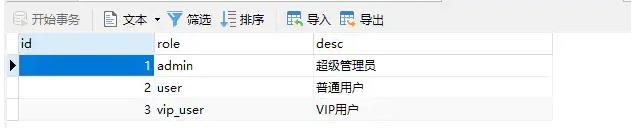
2.2 Role(角色)
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES (1, 'admin', '超级管理员');
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES (2, 'user', '普通用户');
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES (3, 'vip_user', 'VIP用户');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
2.3 Permission(权限)

SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `permission`;
CREATE TABLE `permission` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`permission` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限名称',
`desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限描述',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT = 5 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `permission` VALUES (1, 'add', '增加');
INSERT INTO `permission` VALUES (2, 'update', '更新');
INSERT INTO `permission` VALUES (3, 'select', '查看');
INSERT INTO `permission` VALUES (4, 'delete', '删除');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
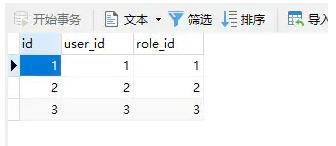
2.4 User_Role(用户-角色)
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `user_role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`role_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Fixed;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user_role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES (2, 2, 2);
INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES (3, 3, 3);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
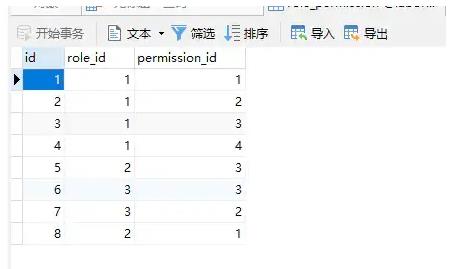
2.5 Role_Permission(角色-权限)
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for role_permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `role_permission` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`permission_id` int(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT = 9 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Fixed;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of role_permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (2, 1, 2);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (3, 1, 3);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (4, 1, 4);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (5, 2, 3);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (6, 3, 3);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (7, 3, 2);
INSERT INTO `role_permission` VALUES (8, 2, 1);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
3. 项目结构
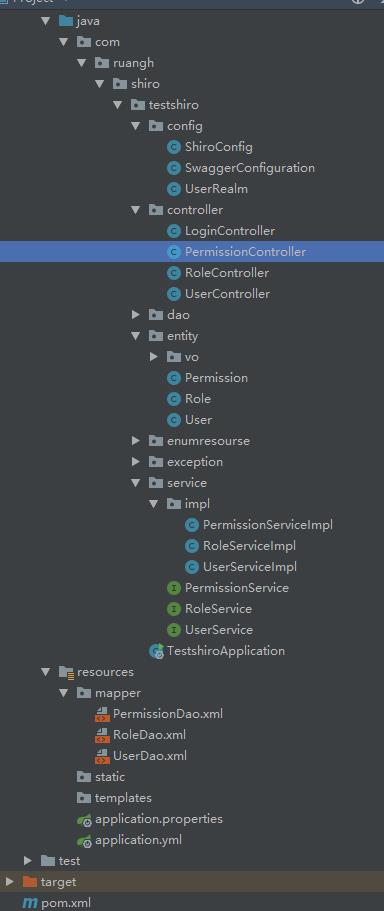
4. 前期准备
4.1 导入Pom
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger-bootstrap-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
4.2 application.yml
server:
port: 8903
spring:
application:
name: lab-user
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/shiro?charset=utf8
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.ruangh.shiro.testshiro.entity
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
4.3 实体类
4.3.1 User.java
@Data
@ToString
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6056125703075132981L;
private Integer id;
private String account;
private String password;
private String username;
}
4.3.2 Role.java
@Data
@ToString
public class Role implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1767327914553823741L;
private Integer id;
private String role;
private String desc;
}
4.4 Dao层
4.4.1 PermissionMapper.java
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface PermissionMapper {
List<String> findByRoleId(@以上是关于eclipse的工程项目太多了,怎么隐藏工程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章