关于C++默认拷贝构造函数
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于C++默认拷贝构造函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我建了一个工程 ,定义了两个类,分别是Person和Date,如下(注:类的声明和实现分开的),代码如下:
Data的声明:
#ifndef DATE_H
#define DATE_H
class Date
public:
Date(int,int,int);
int getYear();
void setYear(int);
private:
int year;
int month;
int day;
;
#endif
Date的实现:
#include"Date.h"
Date::Date(int newYear,int newMonth,int newDay)
year = newYear;
month = newMonth;
day = newDay;
int Date::getYear()
return year;
void Date::setYear(int newYear)
year = newYear;
;
Person的声明:
#include"Date.h"
class Person
public:
Person(int,int,int,int);
~Person();
int getId();
Date* getBirthDate();
private:
int id;
Date* birthDate;
;
Person的实现:
#include"Person.h"
Person::Person(int id,int year,int month,int day)
this->id = id;
birthDate = new Date(year,month,day);
int Person::getId()
return id;
Date* Person::getBirthDate()
return birthDate;
Person::~Person()
delete birthDate;
;
带有主函数的程序:
#include<iostream>
#include"Person.h"
using namespace std;
void displayPerson(Person &person1,Person &person2)
cout<<"\tPerson1 id:"<<person1.getId()<<endl;
cout<<"\tperson1 birth year:"<<person1.getBirthDate()->getYear()<<endl;
cout<<"\tPerson2 id:"<<person2.getId()<<endl;
cout<<"\tperson2 birth year:"<<person2.getBirthDate()->getYear()<<endl;
int main()
Person person1(111,1970,5,3);
Person person2(222,2000,11,8);
cout<<"After creating person1 and person2"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
person1 = Person(person2);
cout<<"\nAfter copying person2 to person1"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
person2.getBirthDate()->setYear(1963);
cout<<"\nAfter modifying person2's birthDate"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
cout<<"\n"<<(person1.getBirthDate()==person2.getBirthDate())<<endl;
return 0;
编译执行后显示
我用的VC++6.0,程序是照着书给的问题编的,编完执行老出错,后来对照答案检查了好多遍,的确没错 , 不知道是编译器的问题还是怎么,我没办法了,望好心人过来帮帮忙。

//delete birthDate;
不要自己定义析构函数
如果数据成员有new分配的,因为析构函数里面有delete,如果是默认构造函数,那就是浅复制了,那最后2个类对象调用析构函数的时候,同一个内存会释放2次,然后出错啊。
但是默认的析构函数析构就是正确的。。
---------------------------------------
目前解决问题
------------------------------------
我先看看有没有内存泄露。。。一会再答。。。
------------------------
查看了一下,有内存泄露
------------------
如果一个类中有指针成员,使用缺省的复制构造函数初始化对象就会出现问题。
--------------------------------------------
把析构函数删了会有内存泄露。。。。。
------------------------------------
修改如下:
//Date.h
#ifndef DATE_H
#define DATE_H
class Date
public:
Date(int,int,int);
int getYear() const;
void setYear(int);
int getMonth() const;
void setMonth(int);
int getDay() const;
void setDay(int);
private:
int year;
int month;
int day;
;
#endif
----------------------
//Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"
Date::Date(int newYear,int newMonth,int newDay)
year = newYear;
month = newMonth;
day = newDay;
int Date::getYear() const
return year;
void Date::setYear(int newYear)
year = newYear;
int Date::getMonth() const
return month;
void Date::setMonth(int newMonth)
this->month = newMonth;
int Date::getDay() const
return day;
void Date::setDay(int newDay)
this->day = newDay;
-----------------------
//Person.h
#include"Date.h"
class Person
public:
Person(int,int,int,int);
~Person();
int getId();
Date* getBirthDate() const;
Person(const Person &rhs);
Person& operator=(const Person& rhs);
private:
int id;
Date* birthDate;
;
----------------
//Person.cpp
#include"Person.h"
Person::Person(int _id,int year,int month,int day):id(_id), birthDate(new Date(year,month,day))
int Person::getId()
return id;
Date* Person::getBirthDate() const
return birthDate;
Person::~Person()
if(birthDate)
delete birthDate;
birthDate = 0;
Person::Person(const Person& rhs)
this->id = rhs.id;
Date *date = rhs.getBirthDate();
this->birthDate = new Date(date->getYear(), date->getMonth(), date->getDay());
Person& Person::operator=(const Person& rhs)
delete birthDate;
this->id = rhs.id;
Date *date = rhs.getBirthDate();
this->birthDate = new Date(date->getYear(), date->getMonth(), date->getDay());
return *this;
-----------------------
//main.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include"Person.h"
using namespace std;
#include <assert.h>
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define DEBUG_CLIENTBLOCK new( _CLIENT_BLOCK, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#else
#define DEBUG_CLIENTBLOCK
#endif
#define _CRTDBG_MAP_ALLOC
#include <crtdbg.h>
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_CLIENTBLOCK
#endif
void Exit()
int i = _CrtDumpMemoryLeaks();
assert( i == 0);
void displayPerson(Person &person1,Person &person2)
cout<<"\tPerson1 id:"<<person1.getId()<<endl;
cout<<"\tperson1 birth year:"<<person1.getBirthDate()->getYear()<<endl;
cout<<"\tPerson2 id:"<<person2.getId()<<endl;
cout<<"\tperson2 birth year:"<<person2.getBirthDate()->getYear()<<endl;
int main()
atexit(Exit);
Person person1(111,1970,5,3);
Person person2(222,2000,11,8);
cout<<"After creating person1 and person2"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
person1 = Person(person2);
cout<<"\nAfter copying person2 to person1"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
person2.getBirthDate()->setYear(1963);
cout<<"\nAfter modifying person2's birthDate"<<endl;
displayPerson(person1,person2);
cout<<"\n"<<(person1.getBirthDate()==person2.getBirthDate())<<endl;
return 0;
-----------------------------
这个main.cpp可以检测内存泄露。。。
--------------
假设不要的就是你原来的。。。 参考技术A person1 = Person(person2);
这里的信息量很大,首先通过person2对象创建了一个临时对象,然后事情并不是想象中的那样,这个临时对象被析构掉了!!也就是person2.birthDate 被delete了!!!!
然后将一个被析构掉的临时对象再次通过默认=复制到person1。。。。
然后结尾再对person2析构的话,就delete 两次,所以报错。追问
谢谢哈,我把那个析构函数删了,果然可以了。然后大侠你能不能再帮我讲一下那个析构函数是怎么回事,析构函数会被自动调用吗 ? 我对你说的临时对象也不是太懂,我看的这本书讲的匿名对象应该就是你说的临时对象吧,你再指点指点我吧,拜托了!
追答Person(person2)就是调用拷贝构造函数创建一个临时对象,然后按理说应该调用operator =()进行复制,但是你这里没有重载,这个临时对象就被析构了,然后再调用默认的operator = () 进行复制,当然结果也就错了。
至于为什么你没有重载等号它就先析构再调用默认等号运算符,这个我也不是很清楚。
反正你记住临时对象就是用完扔的东西。
_____________________________________
对不起上面误导你了,的确是先调用ooerator = () 再析构。
只是因为你没有自定义operator = () 然后复制过去的是临时对象的成员指针,然后紧接着析构后这个指针不复存在,当然,这个指针就是person2.birthDate 。所以。。你懂得。。。
1:person1 = Person(person2); 这句有问题 “=”这个运算符 在Person这个类中没有重载,因此,即使Person(person2); 这样进行强制转换(也不需要强制转换,他们类型一致)也不可以这样使用。
将person1 = Person(person2);这句话注释掉 就不会报错了。
2:cout<<"\n"<<(person1.getBirthDate()==person2.getBirthDate())<<endl;这段代码也是 运算符重载的问题 “==” Date 这个类 没有 对运算符 进行重载 因此 person2.getBirthDate())它会返回一个Date 类型的地址。而且若person2与person1指向的地址不相同,那么这个值永远为0。希望可以帮到你。 参考技术C #include<iostream>是不是少了个.h?我是新手!!求帮忙
C++类的成员函数:构造析构拷贝构造运算符重载
目录
1.类的六个默认成员函数
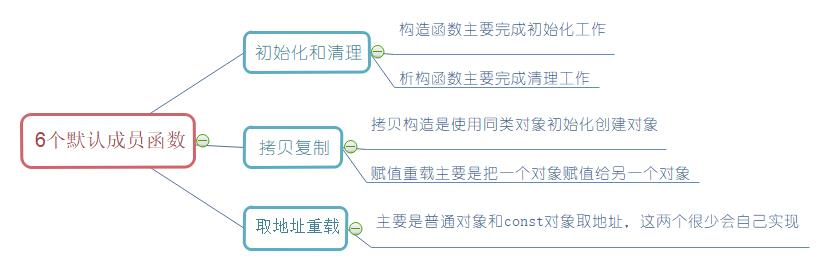
2.构造函数
2.1构造函数是干什么的?
该类对象被创建的时候,编译系统给对象分配内存空间,并自动调用该构造函数,由构造函数完成成员的初始化工作,故:构造函数的作用:初始化对象的数据成员
2.2概念
构造函数是一个特殊的成员函数,名字与类名相同,创建类类型对象时由编译器自动调用,保证每个数据成员都有一个合适的初始值,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次。
2.3特性
构造函数的主要任务并不是开辟空间创建对象,而是初始化对象。
- 函数名与类名相同。
- 无返回值。
- 对象实例化时编译器自动调用对应的构造函数。
- 构造函数可以重载。
class Date
public :
// 1.无参构造函数
Date ()
// 2.带参构造函数
Date (int year, int month , int day )
_year = year ;
_month = month ;
_day = day ;
private :
int _year ;
int _month ;
int _day ;
;
void TestDate()
Date d1; // 调用无参构造函数,后面没有()
Date d2 (2015, 1, 1); // 调用带参的构造函数
// 注意:如果通过无参构造函数创建对象时,对象后面不用跟括号,否则就成了函数声明
// 以下代码的函数:声明了d3函数,该函数无参,返回一个日期类型的对象
Date d3();
- 如果类中没有显式定义构造函数,则C++编译器会自动生成一个无参的默认构造函数,一旦用户显式定义编译器将不再生成。
- 无参的构造函数和全缺省的构造函数都称为默认构造函数,并且默认构造函数只能有一个。注意:无参构造函数、全缺省构造函数、我们没写编译器默认生成的构造函数,都可以认为是默认成员函数。
- C++把类型分成内置类型(基本类型)和自定义类型。内置类型就是语法已经定义好的类型:如int/char…,自定义类型就是我们使用class/struct/union自己定义的类型,看看下面的程序,就会发现编译器生成默认的构造函数会对自定类型成员_t调用的它的默认成员函数
class Time
public:
Time()
cout << "Time()" << endl;
_hour = 0;
_minute = 0;
_second = 0;
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
;
class Date
private:
// 基本类型(内置类型)
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
// 自定义类型
Time _t;
;
int main()
Date d;
return 0;
- 成员变量的命名风格
// 我们看看这个函数,是不是很僵硬?
class Date
public:
Date(int year)
// 这里的year到底是成员变量,还是函数形参?
year = year;
private:
int year;
;
// 所以我们一般都建议这样
class Date
public:
Date(int year)
_year = year;
private:
int _year;
;
// 或者这样。
class Date
public:
Date(int year)
m_year = year;
private:
int m_year;
;
// 其他方式也可以的,主要看公司要求。一般都是加个前缀或者后缀标识区分就行。
3.析构函数
3.1概念
析构函数:与构造函数功能相反,析构函数不是完成对象的销毁,局部对象销毁工作是由编译器完成的。而对象在销毁时会自动调用析构函数,完成类的一些资源清理工作。
3.2特性
- 析构函数名是在类名前加上字符 ~。
- 无参数无返回值。
- 一个类有且只有一个析构函数。若未显式定义,系统会自动生成默认的析构函数。
- 对象生命周期结束时,C++编译系统系统自动调用析构函数。
4.拷贝构造函数
4.1概念
拷贝构造函数:只有单个形参,该形参是对本类类型对象的引用(一般常用const修饰),在用已存在的类类型对象创建新对象时由编译器自动调用。
4.2特性
- 拷贝构造函数是构造函数的一个重载形式。
- 拷贝构造函数的参数只有一个且必须使用引用传参,使用传值方式会引发无穷递归调用。
class Date
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1) //构造函数
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
Date(const Date& d) //拷贝构造函数,形参只有一个,引用传参
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
;
int main()
Date d1;
Date d2(d1);
return 0;
- 若未显示定义,系统生成默认的拷贝构造函数。 默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝我们叫做浅拷贝,或者值拷贝。
class Date
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
;
int main()
Date d1;
// 这里d2调用的默认拷贝构造完成拷贝,d2和d1的值也是一样的。
Date d2(d1);
return 0;
4.3浅拷贝与深拷贝
- 浅拷贝
浅拷贝只是拷贝一个指针,并没有新开辟一个地址,拷贝的指针和原来的指针指向同一块地址,如果原来的指针指向的资源释放了,那么再释放浅拷贝的指针的资源就会出现错误。 - 深拷贝
深拷贝不仅拷贝值,还开辟出一块新的空间用来存放新的值,即使原先的对象被析构掉,释放内存了也不会影响深拷贝得到的值。在自己实现拷贝赋值的时候,如果有指针变量的话需要自己实现深拷贝。
5.运算符重载
5.1什么是C++的运算符重载?
对对象进行运算操作
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
注意:
- 不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
- 重载操作符必须有一个类类型或者枚举类型的操作数
- 用于内置类型的操作符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不能改变其含义
- 作为类成员的重载函数时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1成员函数的操作符有一个默认的形参this,限定为第一个形参
- .* 、:: 、sizeof 、?: 、. 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。这个经常在笔试选择题中出现。
什么情况下要用到运算符重载?
为了解释上面的问题我们先来看看这样一个简单地例子:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
cout << a + b << endl;
return 0;
我们很容易实现对两个基本数据类型int 或double 类型对象的加减操作
如果我们要进行加减操作的对象不是基本的数据类型而是两个对象,那我们该使用什么办法呢?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CBook
private:
int m_iPage;//这是看书的页数
public:
//有参构造函数
CBook(int page)
m_iPage = page;
//定义成员函数实现将你我看书的页数相加
int add(CBook a)
return m_iPage + a.m_iPage;
//当前的m_iPage+我们传入的参数a.m_iPage
;
int main()
CBook you(100);
CBook me(100);
cout << you.add(me) << endl;
return 0;
从上面的代码中可以看出我们可以通过成员函数的方式来对两个对象进行相加,但是成员函数的方式来实现这个对象相加的功能太单一,并且不利于代码的重复利用,我们定义多少个类型的相加就要定义多少个成员函数,因此我们用重载运算符的方法来解决这个问题
重载运算符的声明与规则:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CBook
private:
int m_iPage;
public:
CBook(int page)
m_iPage = page;
CBook operator+(CBook b)
return CBook(m_iPage + b.m_iPage);
//写完对对象的重载运算符之后我们的对象就可以像整数一样相加了
void display()
cout << m_iPage << endl;
//定义一个输出函数
;
int main()
CBook you(100);
CBook me(200);
CBook sum = you + me;
sum.display();
return 0;
下面我们来实现用运算符重载实现对象与整形数据相加:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CBook
public:
int m_pages;
void print()
cout << m_pages << endl;
CBook operator+(const int a)
CBook b;
b.m_pages = m_pages + a;
return b;
//注意这里要返回的是一个对象
;
int main()
CBook one;
one.m_pages = 100;
CBook two;
two = one + 20;
two.print();
return 0;
5.2赋值运算符重载
特点:
- 参数类型
- 返回值
- 检测是否自己给自己赋值
- 返回*this
- 一个类如果没有显式定义赋值运算符重载,编译器也会生成一个,完成对象按字节序的值拷贝。
class Date
public :
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
Date (const Date& d)
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
if(this != &d)
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
private:
int _year ;
int _month ;
int _day ;
;
5.2.1指针悬挂问题
在某些特殊情况下,如类中有指针类型时,使用默认的赋值运算符函数会产生错误。例如,
关于浅层赋值的例子
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
class STRING
private:
char *ptr;
public:
STRING(char *s) //构造函数
cout<<"Constructor called."<<endl;
ptr=new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(ptr,s);
~STRING()
cout<<"Destructor called.---"<<ptr<<endl;
delete ptr;
;
int main()
STRING p1("book");
STRING p2("jeep");
p2=p1;
return 0;
(1)程序开始运行,创建对象 p1 和 p2 ,分别调用构造函数,通过运算符 new 分别从内存中动态分配一块空间,字符指针 ptr 指向内存空间,这时两个动态空间中的字符串分别为 “book”和“jeep”。
(2)执行语句p2=p1时,因为没有用户自定义的赋值运算符函数,于是调用默认的赋值运算符函数,使两个对象 p1 和 p2 的指针 ptr 都指向 new 开辟的同一个空间,这个动态空间中字符串为“book”。
(3)主程序结束,对象逐个撤销。先撤销对象 p2,第 1 次调用析构函数,尽管这时 p1 的指针 ptr 存在,但是其所指向的空间却无法访问了,出现了所谓的 “指针悬挂”,输出出现异常。由于第 2 次执行析构函数中语句“ delete ptr; ”时,企图释放同一空间,从而导致了对同一内存空间的两次释放,这必然引起运行错误。
执行 p2=p1 之前:

执行 p2=p1 之后:
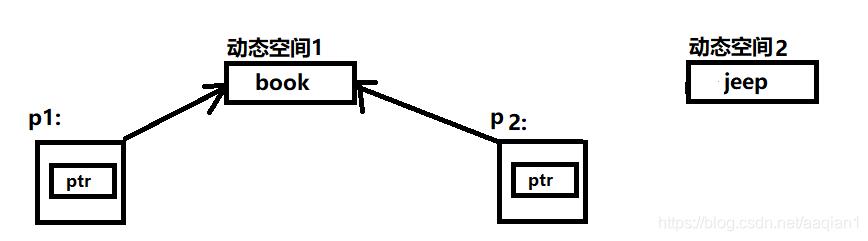
撤销对象 p2 后:

5.2.2用深层复制解决指针悬挂问题
为了解决浅层复制出现的错误,必须显式地定义一个自己的赋值运算符,使之不但赋值数据成员,而且为对象 p1 和 p2 分配了各自的内存空间,这就是深层复制。
关于深层复制的例子,增加了一个自定义的赋值运算符重载函数。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
class STRING
private:
char *ptr;
public:
STRING(char *s) //构造函数
cout<<"Constructor called."<<endl;
ptr=new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(ptr,s);
~STRING()
cout<<"Destructor called.---"<<ptr<<endl;
delete ptr;
STRING &operator=(const STRING &); //声明赋值运算符重载函数 属于成员运算符重载函数
//STRING &operator属于使用引用返回函数值,返回函数的值类型为 STRING
//const STRING & 属于使用常引用作为函数参数 学习笔记30
;
STRING &STRING::operator=(const STRING &s) //定义赋值运算符重载函数
if(this==&s) return *this; //这里的 &s 表示 s 的地址
delete ptr;
ptr=new char[strlen(s.ptr)+1];
strcpy(ptr,s.ptr);
return *this;
int main()
STRING p1("book");
STRING p2("jeep");
p2=p1;
return 0;
(1)创建对象 p1 和 p2,分别调用构造函数,通过运算符 new 分别从内存中动态分配一块空间,字符指针 ptr 指向内存空间,这两个动态空间中的字符串分别为“book”和“jeep”。
(2)执行语句p2=p1时,调用自定义的赋值运算符重载函数,释放掉了 p2 指针 ptr 所指的旧区域, 又按照新长度分配新的内存空间给 p2,再把对象 p1 的数据成员赋给 p2 的对应的数据成员中。
(3)主程序结束,对象逐个撤销。
执行 p2=p1 之前:
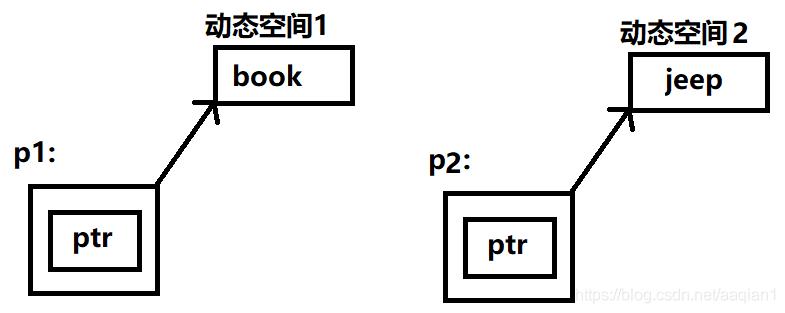
执行 p2=p1 之后:

撤销对象 p2 后:

注意:
类的赋值运算符 “=” 只能重载为成员函数,而不能把它重载为友元函数,因为如果重载为友元函数:
friend STRING &operator=(STRING &p2,STRING &p1);
表达式 p1=“book” 将被解释为:
operator=(p1,“book”);
这没有问题。但是对于表达式 “book”=p1 将被解释为:
operator=(“book”,p1);
即 C++ 编译器首先将 “book” 转换成一个隐藏的 string 对象,然后使用对象 p2 引用该隐藏对象,编译器并不认为这个表达式是错误的,从而将导致赋值语句上的混乱。因此双目赋值运算符应重载为成员函数的形式,而不能重载为友元函数的形式。
以上是关于关于C++默认拷贝构造函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章