Android ANR 机制
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android ANR 机制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A广播的 ANR 处理相对简单,主要是再次判断是否超时、记录日志,记录 ANR 次数等。然后就继续调用 processNextBroadcast 函数,处理下一条广播了。
ContentProvider 超时为 CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT = 10s
Activity 的 ANR 是相对最复杂的,也只有 Activity 中出现的 ANR 会弹出 ANR 提示框。
最终的表现形式是:弹出一个对话框,告诉用户当前某个程序无响应,输入一大堆与 ANR 相关的日志,便于开发者解决问题。
InputDispatching:
Activity 最主要的功能之一是交互,为了方便交互,android 中的 InputDispatcher 会发出操作事件,最终在 InputManagerService 中发出事件,通过 InputChannel,向 Activity 分发事件。交互事件必须得到响应,如果不能及时处理,IMS 就会报出 ANR,交给 AMS 去弹出 ANR 提示框。
KeyDispatching:
如果输入是个 Key 事件,会从 IMS 进入 ActivityRecord.Token.keyDispatchingTimeOut,然后进入 AMS 处理,不同的是,在 ActivityRecord 中,会先截留一次 Key 的不响应,只有当 Key 连续第二次处理超时,才会弹出 ANR 提示框。
窗口焦点:
Activity 总是需要有一个当前窗口来响应事件的,但如果迟迟没有当前窗口(获得焦点),比如在 Activity 切换时,旧 Activity 已经 onPause,新的 Activity 一直没有 onResume,持续超过 5 秒,就会 ANR。
App 的生命周期太慢,或 CPU 资源不足,或 WMS 异常,都可能导致窗口焦点。
1. 判断是否有 focused 组件以及 focused Application:
这种一般是在应用启动时触发,比如启动时间过长在这过程中触发了 keyevent 或者 trackball moteionevent 就会出现。
对应于
2. 判断前面的事件是否及时完成:
对应于
出现这种问题意味着主线程正在执行其他的事件但是比较耗时导致输入事件无法及时处理。
InputDispatcher 超时是最常见的 ANR 类型,而且其类型也比较多。
当用户触摸屏幕或者按键操作,首次触发的是硬件驱动,驱动收到事件后,将该相应事件写入到输入设备节点, 这便产生了最原生态的内核事件。接着,输入系统取出原生态的事件,经过层层封装后成为 KeyEvent 或者 MotionEvent ;最后,交付给相应的目标窗口(Window)来消费该输入事件。可见,输入系统在整个过程起到承上启下的衔接作用。
Input 模块的主要组成:
每一个应用进程都会有一个 SignalCatcher 线程,专门处理 SIGQUIT,来到 art/runtime/signal_catcher.cc :
当应用发生 ANR 之后,系统会收集许多进程,来 dump 堆栈,从而生成 ANR Trace 文件。收集的第一个,也是一定会被收集到的进程,就是发生 ANR 的进程。接着系统开始向这些应用进程发送 SIGQUIT 信号,应用进程收到 SIGQUIT 后开始 dump 堆栈。
[1] developer ANRs
[2] Android ANR 分析详解
[3] 看完这篇 Android ANR 分析,就可以和面试官装逼了!
[4] 微信 Android 团队手把手教你高效监控 ANR
[5] Input 系统—ANR 原理分析 - Gityuan
[6] 彻底理解安卓应用无响应机制 - Gityuan
[7] 理解 Android ANR 的触发原理 - Gityuan
Android带你细看Android input系统中ANR的机制
“本文基于Android13源码,分析Input系统的Anr实现原理“
在文章之前,先提几个问题:
- 如果在activity任意周期(onCreate,onResume等),同步执行耗时超过5s(ANR时间)的任务,期间不进行点击,那会触发ANR吗?
- 如果在button点击的时候,在onClick回调同步执行耗时超过5s的任务。点击一次会触发ANR吗?点击2次呢,3次呢?
1、ANR 分类
首先看一下anr的分类:
- Input ANR:按键或触摸事件在5s内没有相应,主要在activity、fragment中。
- Service anr:前台service 响应时间是20s,后台service是200s。
- Broadcast anr:前台广播是10s,后台广播是60s。
- ContentProvider anr:publish执行未在10s内完成。
- startForgoundService:应用调用startForegroundService,然后5s内未调用startForeground出现ANR或者Crash
有些小伙伴可能好奇,为啥没有Activity ANR的分类?Activity ANR准确的来说是——Input系统检测,触发activity 的anr。所以本文将通过input系统来讲述Android是如何触发activity的anr。
2、InputDispatcher
在了解Input Anr 原理之前,我们简单了解一下InputDispatcher是如何分发按键事件的。
Inputdispatcher中,在线程里面调用到dispatchOnce方法,该方法中主要做:
- 通过dispatchOnceInnerLocked(),取出mInboundQueue 里面的 EventEntry事件
- 通过enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(),生成事件DispatchEntry并加入connection的
outbound队列。 - 通过startDispatchCycleLocked(),从outboundQueue中取出事件DispatchEntry, 重新放入connection的
waitQueue队列。同时通过inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent() 方法将按键事件分发给java层。 - 通过processAnrsLocked(),判断是否需要触发ANR。
按键事件存储在3个queue中:
- InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue:存储的是从InputReader 送来的输入事件。
- Connection的outboundQueue:该队列是存储即将要发送给应用的输入事件。
- Connection的waitQueue:队列存储的是已经发给应用的事件,但是应用还未处理完成的。
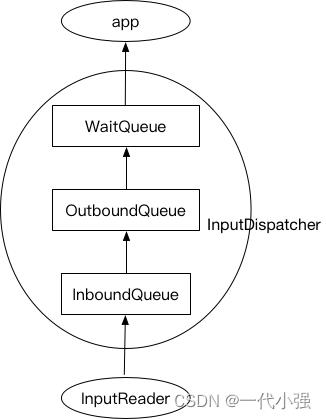
2.1 dispatchOnce
dispatchOnce() 中主要就是调用如下的两个方法:
- 事件分发:dispatchOnceInnerLocked()
- 检查ANR:processAnrsLocked()
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
...
// 如果没有挂起的命令,则运行调度循环。调度循环可能会将命令排入队列,以便稍后运行。
if (!haveCommandsLocked())
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
// 运行所有挂起的命令(如果有)。如果运行了任何命令,则强制下一次轮询立即唤醒。
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable())
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
...
// 我们可能必须早点醒来以检查应用程序是否正处于anr
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();
// 等待回调、超时或唤醒。
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
我们先简单回顾下事件分发过程
3、事件分发
3.1 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
该方法主要是:
-
从mInboundQueue 中取出mPendingEvent
-
通过mPendingEvent的type决定事件类型和分发方式。比如当前是key类型。
主要代码如下:
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime)
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
...
// 优化应用切换的延迟。本质上,当按下应用程序切换键(HOME)时,我们会开始一个短暂的超时。
// 当它过期时,我们会抢占调度并删除所有其他挂起的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
// 当前没有PendingEvent(即EventEntry),则取一个
if (!mPendingEvent)
...
// mInboundQueue不为空 ,就从队列前面取一个PendingEvent
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();
mInboundQueue.pop_front();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
...
3.2 enqueueDispatchEntryLocked
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked() 会创建一个新的DispatchEntry,然后将DispatchEntry 加入到connection#outboundQueue 中
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget,
int32_t dispatchMode)
// 这是一个新事件。将新的调度条目排队到此连接的出站队列中。
std::unique_ptr<DispatchEntry> dispatchEntry =
createDispatchEntry(inputTarget, eventEntry, inputTargetFlags);
...
// 将生成的dispatchEntry 加入到 connection的outboundQueue 中
connection->outboundQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry.release());
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
3.3 startDispatchCycleLocked
该方法主要通过connection 发布最终的事件,至此,InputDispatcher完成事件的发布,并且将发布的事件保存在connection的waitQueue中。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection)
while (connection->status == Connection::Status::NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty())
// 从outboundQueue 队列中取出 DispatchEntry
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front();
const std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(connection);
// 设置超时时间
dispatchEntry->timeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();
// 发布事件
status_t status;
const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
...
// 在等待队列上重新排队事件。
connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),
connection->outboundQueue.end(),
dispatchEntry));
// 在waitQueue 尾部重新插入
connection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);
if (connection->responsive)
// 插入事件对应的anr检查时间
mAnrTracker.insert(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,
connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
3.4 ANR超时时间
由 startDispatchCycleLocked() 方法,知道是通过getDispatchingTimeoutLocked 获取到超时时间
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
// 如果没有用于确定适当调度超时的焦点应用程序或暂停窗口,则默认输入调度超时。
const std::chrono::duration DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT = std::chrono::milliseconds(
android::os::IInputConstants::UNMULTIPLIED_DEFAULT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_MILLIS *
HwTimeoutMultiplier());
std::chrono::nanoseconds InputDispatcher::getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(
const sp<Connection>& connection)
if (connection->monitor)
// 返回监控的超时时间
return mMonitorDispatchingTimeout;
const sp<WindowInfoHandle> window =
getWindowHandleLocked(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
if (window != nullptr)
// 可以找到focused Window
return window->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
// 获取默认的值
return DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT;
WindowInfoHandle#getDispatchingTimeout 返回的值如下
> libs/gui/include/gui/WindowInfo.h
class WindowInfoHandle : public RefBase
inline std::chrono::nanoseconds getDispatchingTimeout(
std::chrono::nanoseconds defaultValue) const
return mInfo.token ? std::chrono::nanoseconds(mInfo.dispatchingTimeout) : defaultValue;
struct WindowInfo : public Parcelable
std::chrono::nanoseconds dispatchingTimeout = std::chrono::seconds(5); // 5 秒
DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT 主要由UNMULTIPLIED_DEFAULT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_MILLIS * HwTimeoutMultiplier() 计算得到
UNMULTIPLIED_DEFAULT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_MILLIS的值如下
> android/os/IInputConstants.h
class IInputConstants : public ::android::IInterface
public:
enum : int32_t UNMULTIPLIED_DEFAULT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT_MILLIS = 5000 ;
....
; // class IInputConstants
HwTimeoutMultiplier() 方法定义如下,即读ro.hw_timeout_multiplier 属性值,默认是1。
> system/libbase/include/android-base/properties.h
static inline int HwTimeoutMultiplier()
return android::base::GetIntProperty("ro.hw_timeout_multiplier", 1);
3.5 调用栈
native层的事件分发调用栈如下
libs/input/InputTransport.cpp : InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()
services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp : InputDispatcher::start()
4、ANR触发
在dispatchOnce(),会调用processAnrsLocked 方法来决定是否需要触发anr
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()
...
// 我们可能必须早点醒来以检查应用程序是否正处于anr
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();
....
4.1 processAnrsLocked
该方法是用于检查队列中是否有太旧的事件,如果存在就触发ANR
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
// 检查是否有任何连接的等待队列具有太旧的事件。如果我们等待事件被确认的时间超过窗口超时,
// 请引发 ANR。返回我们下次应该醒来的时间。
nsecs_t InputDispatcher::processAnrsLocked()
const nsecs_t currentTime = now();
nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = LONG_LONG_MAX; // 下一次检查anr的时间
// 检查我们是否正在等待一个聚焦窗口出现。如果等待时间过长就报 ANR
if (mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value() && mAwaitedFocusedApplication != nullptr)
if (currentTime >= *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime)
// 场景1: 触发noFocusedWindow的anr
processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked();
mAwaitedFocusedApplication.reset();
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = std::nullopt;
return LONG_LONG_MIN;
else
// 请继续等待。我们将在mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime到来时放弃该事件。
nextAnrCheck = *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime;
// 检查是否有任何连接 ANR 到期,mAnrTracker 中保存所有已分发事件(未被确认消费的事件)的超时时间
nextAnrCheck = std::min(nextAnrCheck, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());
if (currentTime < nextAnrCheck) // 最有可能的情况
// 一切正常,在 nextAnrCheck 再检查一次
return nextAnrCheck;
// 如果我们到达这里,则连接无响应。
sp<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked(mAnrTracker.firstToken());
// 停止为此无响应的连接唤醒
mAnrTracker.eraseToken(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
// 场景2: 触发ANR
onAnrLocked(connection);
return LONG_LONG_MIN;
其中,mAnrTracker 存储已经成功分发给应用的事件。详情见startDispatchCycleLocked() 方法。
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime 是在findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked() 方法中赋值的,在分发事件的时候会调用到findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked() :
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputEventInjectionResult InputDispatcher::findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const EventEntry& entry, std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets,
nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime)
...
// 兼容性行为:如果存在焦点应用程序但没有焦点窗口,则引发 ANR。只有当我们有重点事件要调度时,才开始计数。
// 如果我们开始通过触摸(应用程序开关)与另一个应用程序交互,则 ANR 将被取消。
// 如果将“无聚焦窗口 ANR”移动到策略中,则可以删除此代码。输入不知道应用是否应具有焦点窗口。
if (focusedWindowHandle == nullptr && focusedApplicationHandle != nullptr)
if (!mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value())
// 发现没有focusedWindow,就添加ANR定时器。
std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = focusedApplicationHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(
DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();
....
return InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;
// 找到一个focusedwindow,就取消ANR定时器
resetNoFocusedWindowTimeoutLocked();
...
void InputDispatcher::resetNoFocusedWindowTimeoutLocked()
// 取消ANR定时器
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = std::nullopt;
mAwaitedFocusedApplication.reset();
从上面的代码我们能小结出两个场景ANR的条件:
- 有等待获取焦点的应用:当前时间超过Timeout,调用processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked() 进一步确认
- 存在window:当前时间超过事件响应的超时时间。调用onAnrLocked() 进一步确认。
4.2 processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked
该方法触发anr的条件是:
- 当前关注的应用程序必须与我们等待的应用程序相同。
- 确保我们仍然没有聚焦窗口。
processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked 最后也是调用到onAnrLocked。
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
// 如果没有聚焦窗口,请触发ANR。在触发 ANR 之前,请执行最终状态检查:
void InputDispatcher::processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked()
std::shared_ptr<InputApplicationHandle> focusedApplication =
getValueByKey(mFocusedApplicationHandlesByDisplay, mAwaitedApplicationDisplayId);
if (focusedApplication == nullptr ||
focusedApplication->getApplicationToken() !=
mAwaitedFocusedApplication->getApplicationToken())
// 出乎意料,因为当前焦点应用程序已被更改,我们应该重置 ANR 计时器
return;
const sp<WindowInfoHandle>& focusedWindowHandle =
getFocusedWindowHandleLocked(mAwaitedApplicationDisplayId);
if (focusedWindowHandle != nullptr)
//我们现在有一个焦点window,不需要再触发ANR
return;
onAnrLocked(mAwaitedFocusedApplication);
onAnrLocked 有两种实现:
- 能找到当前focus的window
- 找不到当前focus的window,但是可以找到当前前台应用。
我们先看情况1
4.3 onAnrLocked(connection)
> frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
//情况1: 能找到window的情况
void InputDispatcher::onAnrLocked(const sp<Connection>& connection)
// 由于我们允许策略延长超时,因此 waitQueue 可能已经再次正常运行。在这种情况下不要触发 ANR
if (connection->waitQueue.empty())
return;
// “最旧的条目”是首次发送到应用程序的条目。但是,该条目可能不是导致超时发生的条目。
// 一种可能性是窗口超时已更改。这可能会导致较新的条目在已分派的条目之前超时。
// 在这种情况下,最新条目会导致 ANR。但很有可能,该应用程序会线性处理事件。
// 因此,提供有关最早条目的信息似乎是最有用的。
DispatchEntry* oldestEntry = *connection->waitQueue.begin();
// 获取到超时时长
const nsecs_t currentWait = now() - oldestEntry->deliveryTime;
std::string reason =
android::base::StringPrintf("%s is not responding. Waited %" PRId64 "ms for %s",
connection->inputChannel->getName().c_str(),
ns2ms(currentWait),
oldestEntry->eventEntry->getDescription().c_str());
sp<IBinder> connectionToken = connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken();
// 生成 reason 报告
updateLastAnrStateLocked(getWindowHandleLocked(connectionToken), reason);
processConnectionUnresponsiveLocked(*connection, std::move(reason));
// 停止唤醒此连接上的事件,它已经没有响应
cancelEventsForAnrLocked(connection);
// 捕获 ANR 时 InputDispatcher 状态的记录。
void InputDispatcher::updateLastAnrStateLocked(const std::string& windowLabel,
const std::string& reason)
....
dumpDispatchStateLocked(mLastAnrState);
4.3.1 dumpDispatchStateLocked
dumpDispatchStateLocked 函数主要打印当前window和事件队列信息。执行dumpsys input 命令,dumpDispatchStateLocked函数输出的内容如下:
Input Dispatcher State:
....
PendingEvent: <none> // 当前正在调度转储事件。
InboundQueue: <empty> // Inbound 队列
ReplacedKeys: <empty>
Connections:
317: channelName='cf1eda9 com.example.anrdemo/com.example.anrdemo.MainActivity (serverAndroid带你细看Android input系统中ANR的机制
Android带你细看Android input系统中ANR的机制
Android 进阶——Framework 核心ANR( Applicatipon No Response)机制设计思想详解