静态库(.a)文件怎么拆分成(.o)文件
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了静态库(.a)文件怎么拆分成(.o)文件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 使用ar命令 ar -x 提取 参考技术B C或php中的Rust 我的基本出发点就是写一些可以编译的Rust代码到一个库里面,并写为它一些C的头文件,在C中为被调用的PHP做一个拓展。虽然并不是很简单,但是很有趣。 Rust FFI(foreign function interface) 我所做的第一件事情就是摆弄Rust与C连接的Rust的外部函数接口。我曾用简单的方法(hello_from_rust)写过一个灵活的库,伴有单一的声明(a pointer to a C char, otherwise known as a string),如下是输入后输出的“Hello from Rust”。 // hello_from_rust.rs #![crate_type = "staticlib"] #![feature(libc)] extern crate libc; use std::ffi::CStr; #[no_mangle] pub extern "C" fn hello_from_rust(name: *const libc::c_char) let buf_name = unsafe CStr::from_ptr(name).to_bytes() ; let str_name = String::from_utf8(buf_name.to_vec()).unwrap(); let c_name = format!("Hello from Rust, ", str_name); println!("", c_name); 我从C(或其它!)中调用的Rust库拆分它。这有一个接下来会怎样的很好的解释。 编译它会得到.a的一个文件,libhello_from_rust.a。这是一个静态的库,包含它自己所有的依赖关系,而且我们在编译一个C程序的时候链接它,这让我们能做后续的事情。注意:在我们编译后会得到如下输出: note: link against the following native artifacts when linking against this static library note: the order and any duplication can be significant on some platforms, and so may need to be preserved note: library: Systemnote: library: pthread note: library: c note: library: m 这就是Rust编译器在我们不使用这个依赖的时候所告诉我们需要链接什么。 从C中调用Rust 既然我们有了一个库,不得不做两件事来保证它从C中可调用。首先,我们需要为它创建一个C的头文件,hello_from_rust.h。然后在我们编译的时候链接到它。 下面是头文件: // hello_from_rust.h #ifndef __HELLO #define __HELLO void hello_from_rust(const char *name); #endif 这是一个相当基础的头文件,仅仅为了一个简单的函数提供签名/定义。接着我们需要写一个C程序并使用它。 // hello.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "hello_from_rust.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) hello_from_rust("Jared!"); 我们通过运行一下代码来编译它: gcc -Wall -o hello_c hello.c -L /Users/jmcfarland/code/rust/php-hello-rust -lhello_from_rust -lSystem -lpthread -lc -lm 注意在末尾的-lSystem -lpthread -lc -lm告诉gcc不要链接那些“本地的古董”,为了当编译我们的Rust库时Rust编译器可以提供出来。 经运行下面的代码我们可以得到一个二进制的文件: $ ./hello_c Hello from Rust, Jared! 漂亮!我们刚才从C中调用了Rust库。现在我们需要理解Rust库是如何进入一个PHP扩展的。 从 php 中调用 c 该部分花了我一些时间来弄明白,在这个世界上,该文档在 php 扩展中并不是最好的。最好的部分是来自绑定一个脚本 ext_skel 的 php 源(大多数代表“扩展骨架”)即生成大多数你需要的样板代码。 你可以通过下载来开始,和未配额的 php 源,把代码写进 php 目录并且运行: $ cd ext/ $ ./ext_skel --extname=hello_from_rust 这将生成需要创建 php 扩展的基本骨架。现在,移动你处处想局部地保持你的扩展的文件夹。并且移动你的 .rust 源 .rust库 .c header 进入同一个目录。因此,现在你应该看看像这样的一个目录: . ├── CREDITS ├── EXPERIMENTAL ├── config.m4 ├── config.w32 ├── hello_from_rust.c ├── hello_from_rust.h ├── hello_from_rust.php ├── hello_from_rust.rs ├── libhello_from_rust.a ├── php_hello_from_rust.h └── tests └── 001.phpt 一个目录,11个文件 你可以在 php docs 在上面看到关于这些文件很好的描述。建立一个扩展的文件。我们将通过编辑 config.m4 来开始吧。 不解释,下面就是我的成果: PHP_ARG_WITH(hello_from_rust, for hello_from_rust support, [ --with-hello_from_rust Include hello_from_rust support]) if test "$PHP_HELLO_FROM_RUST" != "no"; then PHP_SUBST(HELLO_FROM_RUST_SHARED_LIBADD) PHP_ADD_LIBRARY_WITH_PATH(hello_from_rust, ., HELLO_FROM_RUST_SHARED_LIBADD) PHP_NEW_EXTENSION(hello_from_rust, hello_from_rust.c, $ext_shared) fi 正如我所理解的那样,这些是基本的宏命令。但是有关这些宏命令的文档是相当糟糕的(比如:google"PHP_ADD_LIBRARY_WITH_PATH"并没有出现PHP团队所写的结果)。我偶然这个PHP_ADD_LIBRARY_PATH宏命令在有些人所谈论的在一个PHP拓展里链接一个静态库的先前的线程里。在中其它的推荐使用的宏命令是在我运行ext_skel后产生的。 既然我们进行了配置设置,我们需要从PHP脚本中实际地调用库。为此我们得修改自动生成的文件,hello_from_rust.c。首先我们添加hello_from_rust.h头文件到包含命令中。然后我们要修改confirm_hello_from_rust_compiled的定义方法。 #include "hello_from_rust.h" // a bunch of comments and code removed... PHP_FUNCTION(confirm_hello_from_rust_compiled) char *arg = NULL; int arg_len, len; char *strg; if (zend_parse_parameters(ZEND_NUM_ARGS() TSRMLS_CC, "s", &arg, &arg_len) == FAILURE) return; hello_from_rust("Jared (from PHP!!)!"); len = spprintf(&strg, 0, "Congratulations! You have successfully modified ext/%.78s/config.m4. Module %.78s is now compiled into PHP.", "hello_from_rust", arg); RETURN_STRINGL(strg, len, 0); 注意:我添加了hello_from_rust("Jared (fromPHP!!)!");。 现在,我们可以试着建立我们的扩展: $ phpize $ ./configure $ sudo make install 就是它,生成我们的元配置,运行生成的配置命令,然后安装该扩展。安装时,我必须亲自使用sudo,因为我的用户并不拥有安装目录的 php 扩展。 现在,我们可以运行它啦! $ php hello_from_rust.php Functions available in the test extension: confirm_hello_from_rust_compiled Hello from Rust, Jared (from PHP!!)! Congratulations! You have successfully modified ext/hello_from_rust/config.m4. Module hello_from_rust is now compiled into PHP. Segmentation fault: 11 还不错,php 已进入我们的 c 扩展,看到我们的应用方法列表并且调用。接着,c 扩展已进入我们的 rust 库,开始打印我们的字符串。那很有趣!但是......那段错误的结局发生了什么? 正如我所提到的,这里是使用了 Rust 相关的 println! 宏,但是我没有对它做进一步的调试。如果我们从我们的 Rust 库中删除并返回一个 char* 替代,段错误就会消失。 这里是 Rust 的代码: 复制代码 代码如下: #![crate_type = "staticlib"] #![feature(libc)] extern crate libc; use std::ffi::CStr, CString; #[no_mangle] pub extern "C" fn hello_from_rust(name: *const libc::c_char) -> *const libc::c_char let buf_name = unsafe CStr::from_ptr(name).to_bytes() ; let str_name = String::from_utf8(buf_name.to_vec()).unwrap(); let c_name = format!("Hello from Rust, ", str_name); CString::new(c_name).unwrap().as_ptr() 并变更 C 头文件: #ifndef __HELLO #define __HELLO const char * hello_from_rust(const char *name); #endif 还要变更 C 扩展文件: PHP_FUNCTION(confirm_hello_from_rust_compiled) char *arg = NULL; int arg_len, len; char *strg; if (zend_parse_parameters(ZEND_NUM_ARGS() TSRMLS_CC, "s", &arg, &arg_len) == FAILURE) return; char *str; str = hello_from_rust("Jared (from PHP!!)!"); printf("%s\n", str); len = spprintf(&strg, 0, "Congratulations! You have successfully modified ext/%.78s/config.m4. Module %.78s is now compiled into PHP.", "hello_from_rust", arg); RETURN_STRINGL(strg, len, 0); 无用的微基准 那么为什么你还要这样做?我还真的没有在现实世界里使用过这个。但是我真的认为斐波那契序列算法就是一个好的例子来说明一个PHP拓展如何很基本。通常是直截了当(在Ruby中): def fib(at) do if (at == 1 at == 0) return at else return fib(at - 1) + fib(at - 2) end end 而且可以通过不使用递归来改善这不好的性能: def fib(at) do if (at == 1 at == 0) return at elsif (val = @cache[at]).present? return val end total = 1 parent = 1 gp = 1 (1..at).each do i total = parent + gp gp = parent parent = total end return total end 那么我们围绕它来写两个例子,一个在PHP中,一个在Rust中。看看哪个更快。下面是PHP版: def fib(at) do if (at == 1 at == 0) return at elsif (val = @cache[at]).present? return val end total = 1 parent = 1 gp = 1 (1..at).each do i total = parent + gp gp = parent parent = total end return total end 这是它的运行结果: $ time php php_fib.php real 0m2.046s user 0m1.823s sys 0m0.207s 现在我们来做Rust版。下面是库资源: 复制代码 代码如下: #![crate_type = "staticlib"] fn fib(at: usize) -> usize if at == 0 return 0; else if at == 1 return 1; let mut total = 1; let mut parent = 1; let mut gp = 0; for _ in 1 .. at total = parent + gp; gp = parent; parent = total; return total; #[no_mangle] pub extern "C" fn rust_fib(at: usize) -> usize fib(at) 注意,我编译的库rustc - O rust_lib.rs使编译器优化(因为我们是这里的标准)。这里是C扩展源(相关摘录): PHP_FUNCTION(confirm_rust_fib_compiled) long number; if (zend_parse_parameters(ZEND_NUM_ARGS() TSRMLS_CC, "l", &number) == FAILURE) return; RETURN_LONG(rust_fib(number)); 运行PHP脚本: <?php $br = (php_sapi_name() == "cli")? "":"<br>"; if(!extension_loaded('rust_fib')) dl('rust_fib.' . PHP_SHLIB_SUFFIX); for ($i = 0; $i < 100000; $i ++) confirm_rust_fib_compiled(92); ?> 这就是它的运行结果: $ time php rust_fib.php real 0m0.586s user 0m0.342s sys 0m0.221s 你可以看见它比前者快了三倍!完美的Rust微基准!Linux之静态库
命名规则:
lib + 库的名字 + .a
制作步骤
生成对应.o文件 .c à .o
将生成的.o文件打包 ar rcs + 静态库的名字(libMytest.a) + 生成的所有的.o
发布和使用静态库:
1) 发布静态
2) 头文件
文件如下图所示:
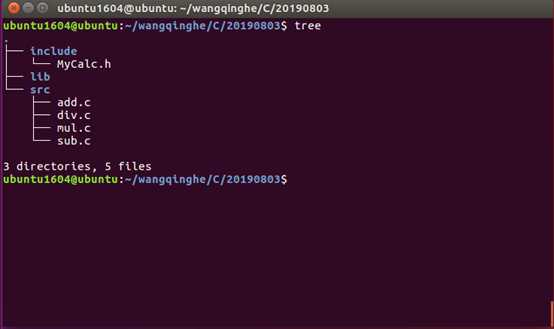
1) 生成对应的.o文件
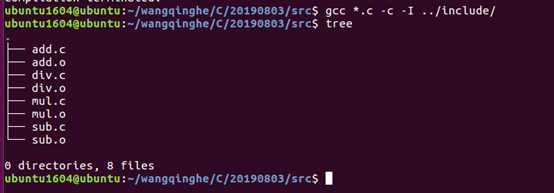
2) 将所生成的.o文件打包,并移动到lib文件夹中
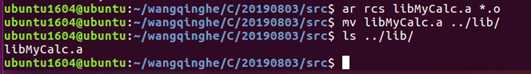
3) 验证生成的库文件数据
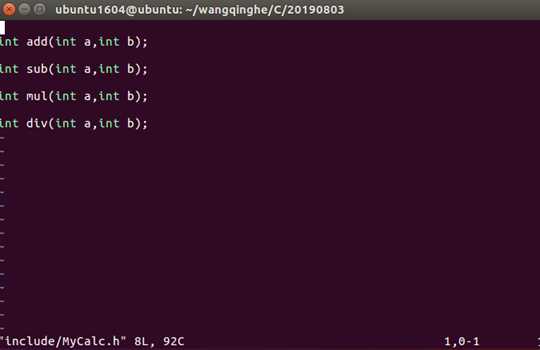
写一个测试代码main.c使用上图中的函数
/*** main.c ***/ #include<stdio.h> #include"MyCalc.h" int main() int a = 10; int b = 20; int result = a + b; printf("a + b = %d\\n",result); return 0;
编译运行:
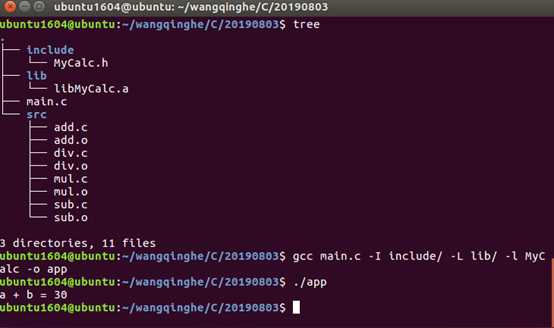
静态库的优缺点:
查看静态库内容
nm 静态库名字
nm 可以查看可执行程序内容
优点:
- 发布程序的时候,不需要提供对应的库
- 库的加载速度比较快
缺点:
- 库打包到应用程序中,库的体积很大
- 库发生了变化,需要重新编译程序。
以上是关于静态库(.a)文件怎么拆分成(.o)文件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章