机器学习实例--预测美国人口收入状况
Posted yue-guan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习实例--预测美国人口收入状况相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一. 问题描述
每个人都希望自己能获得更高的收入,而影响收入高低的因素有很多,能否通过大数据分析来找出对收入影响相对较大的因素?
二. 研究意义
如果我们知道对收入高低起决定性的作用,或者哪些因素组合在一起也能增大收入的可能性,那可以帮助很多人少走弯路,朝着正确的方向努力,早日达到目标。
三. 数据预处理
1. 选取数据集
本报告选取“adult”数据集,由美国人口普查数据集库抽取而来。
该数据集类变量为年收入是否超过50k,属性变量包含年龄,工种,学历,职业,人种等14个属性变量,其中有7个类别型变量。共有30000多条数据。
2. 预处理
由于capital-gain、capital-loss属性缺失70%以上的数据,所以选择删去这两个属性。
在其他类变量中,有缺少或异常属性400多条,占总数据比重较小,也选择删去。
四. 数据可视化
1.workclass
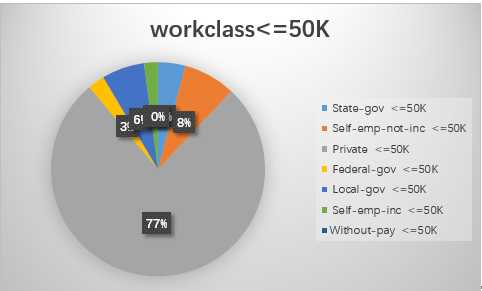
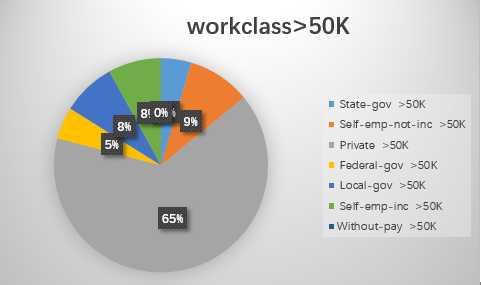
2.education
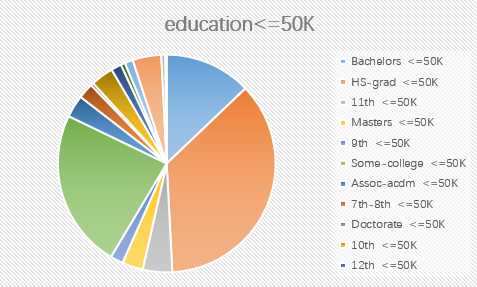
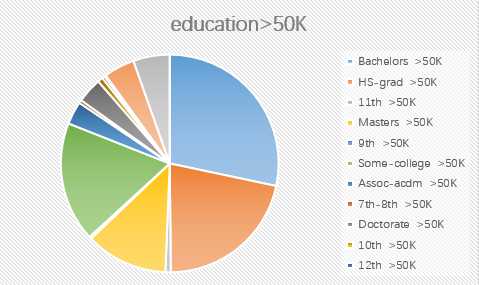
3.race
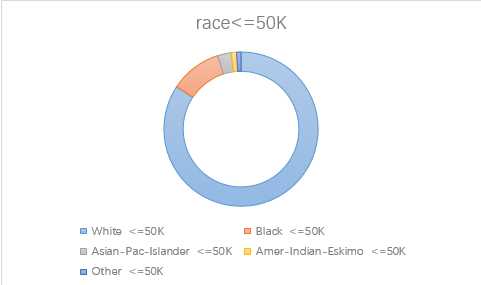
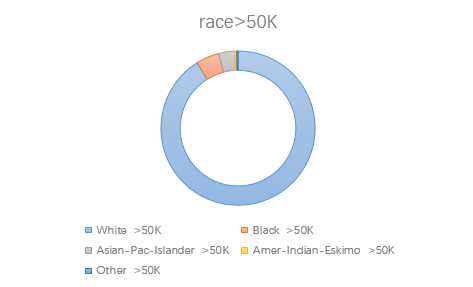
4.sex
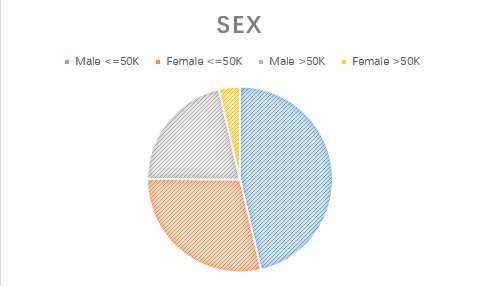
5.marital-status
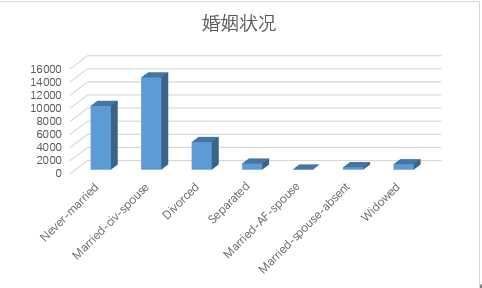
五. 算法选取与实现
本次报告中选用决策树算法。决策树是一种依托决策而建立起来的一种树。在机器学习中,决策树是一种预测模型,代表的是一种对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系,每一个节点代表某个对象,树中的每一个分叉路径代表某个可能的属性值,而每一个叶子节点则对应从根节点到该叶子节点所经历的路径所表示的对象的值。决策树仅有单一输出,如果有多个输出,可以分别建立独立的决策树以处理不同的输出。
由于数据量过大,普通决策树不能达到预期效果,所以再用预剪枝进行处理。预剪枝是在决策树生成过程中,在划分节点时,若该节点的划分没有提高其在训练集上的准确率,则不进行划分。
下面是预剪枝决策树程序
1. 计算数据集的基尼系数
def calcGini(dataSet): numEntries=len(dataSet) labelCounts={} #给所有可能分类创建字典 for featVec in dataSet: currentLabel=featVec[-1] if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel]=0 labelCounts[currentLabel]+=1 Gini=1.0 #以2为底数计算香农熵 for key in labelCounts: prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries Gini-=prob*prob return Gini
2. 对离散变量划分数据集,取出该特征取值为value的所有样本
def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value): retDataSet=[] for featVec in dataSet: if featVec[axis]==value: reducedFeatVec=featVec[:axis] reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet
3. 对连续变量划分数据集,direction规定划分的方向,决定是划分出小于value的数据样本还是大于value的数据样本集
def splitContinuousDataSet(dataSet,axis,value,direction): retDataSet=[] for featVec in dataSet: if direction==0: if featVec[axis]>value: reducedFeatVec=featVec[:axis] reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) else: if featVec[axis]<=value: reducedFeatVec=featVec[:axis] reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet
4. 选择最好的数据集划分方式
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet,labels): numFeatures=len(dataSet[0])-1 bestGiniIndex=100000.0 bestFeature=-1 bestSplitDict={} for i in range(numFeatures): featList=[example[i] for example in dataSet] #对连续型特征进行处理 if type(featList[0]).__name__==‘float‘ or type(featList[0]).__name__==‘int‘: #产生n-1个候选划分点 sortfeatList=sorted(featList) splitList=[] for j in range(len(sortfeatList)-1): splitList.append((sortfeatList[j]+sortfeatList[j+1])/2.0) bestSplitGini=10000 slen=len(splitList) #求用第j个候选划分点划分时,得到的信息熵,并记录最佳划分点 for j in range(slen): value=splitList[j] newGiniIndex=0.0 subDataSet0=splitContinuousDataSet(dataSet,i,value,0) subDataSet1=splitContinuousDataSet(dataSet,i,value,1) prob0=len(subDataSet0)/float(len(dataSet)) newGiniIndex+=prob0*calcGini(subDataSet0) prob1=len(subDataSet1)/float(len(dataSet)) newGiniIndex+=prob1*calcGini(subDataSet1) if newGiniIndex<bestSplitGini: bestSplitGini=newGiniIndex bestSplit=j #用字典记录当前特征的最佳划分点 bestSplitDict[labels[i]]=splitList[bestSplit] GiniIndex=bestSplitGini #对离散型特征进行处理 else: uniqueVals=set(featList) newGiniIndex=0.0 #计算该特征下每种划分的信息熵 for value in uniqueVals: subDataSet=splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value) prob=len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) newGiniIndex+=prob*calcGini(subDataSet) GiniIndex=newGiniIndex if GiniIndex<bestGiniIndex: bestGiniIndex=GiniIndex bestFeature=i #若当前节点的最佳划分特征为连续特征,则将其以之前记录的划分点为界进行二值化处理 #即是否小于等于bestSplitValue #并将特征名改为 name<=value的格式 if type(dataSet[0][bestFeature]).__name__==‘float‘ or type(dataSet[0][bestFeature]).__name__==‘int‘: bestSplitValue=bestSplitDict[labels[bestFeature]] labels[bestFeature]=labels[bestFeature]+‘<=‘+str(bestSplitValue) for i in range(shape(dataSet)[0]): if dataSet[i][bestFeature]<=bestSplitValue: dataSet[i][bestFeature]=1 else: dataSet[i][bestFeature]=0 return bestFeature
5. 特征若已经划分完,节点下的样本还没有统一取值,则需要进行投票
def majorityCnt(classList): classCount={} for vote in classList: if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote]=0 classCount[vote]+=1 return max(classCount)
6.由于在Tree中,连续值特征的名称以及改为了 feature<=value的形式,因此对于这类特征,需要利用正则表达式进行分割,获得特征名以及分割阈值
def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec): firstStr=list(inputTree.keys())[0] if ‘<=‘ in firstStr: featvalue=float(re.compile("(<=.+)").search(firstStr).group()[2:]) featkey=re.compile("(.+<=)").search(firstStr).group()[:-2] secondDict=inputTree[firstStr] featIndex=featLabels.index(featkey) if testVec[featIndex]<=featvalue: judge=1 else: judge=0 for key in secondDict.keys(): if judge==int(key): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__==‘dict‘: classLabel=classify(secondDict[key],featLabels,testVec) else: classLabel=secondDict[key] else: secondDict=inputTree[firstStr] featIndex=featLabels.index(firstStr) for key in secondDict.keys(): if testVec[featIndex]==key: if type(secondDict[key]).__name__==‘dict‘: classLabel=classify(secondDict[key],featLabels,testVec) else: classLabel=secondDict[key] return classLabel def testing(myTree,data_test,labels): error=0.0 for i in range(len(data_test)): if classify(myTree,labels,data_test[i])!=data_test[i][-1]: error+=1 print (‘myTree %d‘ %error) return float(error) def testingMajor(major,data_test): error=0.0 for i in range(len(data_test)): if major!=data_test[i][-1]: error+=1 print (‘major %d‘ %error) return float(error)
7.主程序,递归产生决策树
def createTree(dataSet,labels,data_full,labels_full,data_test): classList=[example[-1] for example in dataSet] if classList.count(classList[0])==len(classList): return classList[0] if len(dataSet[0])==1: return majorityCnt(classList) temp_labels=copy.deepcopy(labels) bestFeat=chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet,labels) bestFeatLabel=labels[bestFeat] myTree={bestFeatLabel:{}} if type(dataSet[0][bestFeat]).__name__==‘str‘: currentlabel=labels_full.index(labels[bestFeat]) featValuesFull=[example[currentlabel] for example in data_full] uniqueValsFull=set(featValuesFull) featValues=[example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals=set(featValues) del(labels[bestFeat]) #针对bestFeat的每个取值,划分出一个子树。 for value in uniqueVals: subLabels=labels[:] if type(dataSet[0][bestFeat]).__name__==‘str‘: uniqueValsFull.remove(value) myTree[bestFeatLabel][value]=createTree(splitDataSet (dataSet,bestFeat,value),subLabels,data_full,labels_full, splitDataSet(data_test,bestFeat,value)) if type(dataSet[0][bestFeat]).__name__==‘str‘: for value in uniqueValsFull: myTree[bestFeatLabel][value]=majorityCnt(classList) #进行测试,若划分没有提高准确率,则不进行划分,返回该节点的投票值作为节点类别 if testing(myTree,data_test,temp_labels)<testingMajor(majorityCnt(classList),data_test): return myTree return majorityCnt(classList)
六. 结果分析
1. 未剪枝决策树
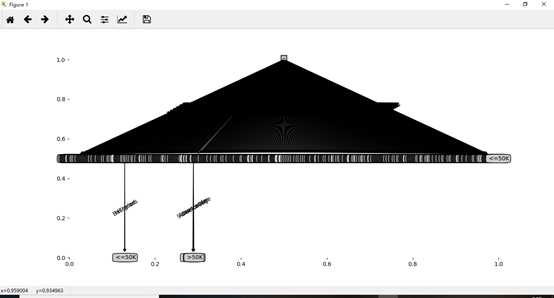
2. 预剪枝决策树
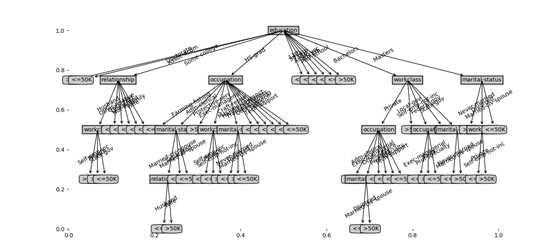
以上是关于机器学习实例--预测美国人口收入状况的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
ML之shap:基于adult人口普查收入二分类预测数据集(预测年收入是否超过50k)利用Shap值对XGBoost模型实现可解释性案例之详细攻略
《Python机器学习及实践》----良/恶性乳腺癌肿瘤预测