篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java web后台通过通讯协议拿到数据后怎么主动让其在前端页面上显示出来?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
技术交流群:233513714
这两天正在研究如何让后天主动向前台展现数据,只要后台有数据上传的时候就向前台上传(因为公司有个项目,硬件设备会不断的上传数据,服务端将接收到的数据向前台展示)。在网上查了一下,下面将介绍一下其中的两种解决办法
一、WebSocket
WebSocket 是web客户端和服务器之间新的通讯方式, 依然架构在HTTP协议之上。使用WebSocket连接, web应用程序可以执行实时的交互, 而不是以前的poll方式。
WebSocket是HTML5开始提供的一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通讯的协议,可以用来创建快速的更大规模的健壮的高性能实时的web应用程序。WebSocket通信协议于2011年被IETF定为标准RFC 6455,WebSocketAPI被W3C定为标准。
在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要做一个握手的动作,然后,浏览器和服务器之间就形成了一条快速通道。两者之间就直接可以数据互相传送。
什么是WebSocket?
一个WebSocket是通过一个独立的TCP连接实现的、异步的、双向的、全双工的消息传递实现机制。WebSockets不是一个HTTP连接,却使用HTTP来引导一个WebSocket连接。一个全双工的系统允许同时进行双向的通讯。陆地线路电话是一个全双工设施的例子,因为它们允许两个通话者同时讲话并被对方听到。最初WebSocket被提议作为HTML5规范的一部分,HTML5承诺给现代的交互式的web应用带来开发上的便利和网络效率,但是随后WebSocket被移到一个仅用来存放WebSockets规范的独立的标准文档里。它包含两件事情 -- WebSocket协议规范,即2011年12月发布的RFC 6455,和WebSocket JavaScript API。
WebSocket协议利用HTTP 升级头信息来把一个HTTP连接升级为一个WebSocket连接。HTML5 WebSockets 解决了许多导致HTTP不适合于实时应用的问题,并且它通过避免复杂的工作方式使得应用结构很简单。
最新的浏览器都支持WebSockets,
WebSocket是如何工作的?
每一个WebSocket连接的生命都是从一个HTTP请求开始的。HTTP请求跟其他请求很类似,除了它拥有一个Upgrade头信息。Upgrade头信息表示一个客户端希望把连接升级为不同的协议。对WebSockets来说,它希望升级为WebSocket协议。当客户端和服务器通过底层连接第一次握手时,WebSocket连接通过把HTTP协议转换升级为WebSockets协议而得以建立。一旦WebSocket连接成功建立,消息就可以在客户端和服务器之间进行双向发送
- WebSockets比其它工作方式比如轮询更有效也更高效。因为它需要更少的带宽并且降低了延时。
- WebSockets简化了实时应用的结构体系。
- WebSockets在点到点发送消息时不需要头信息。这显著的降低了带宽。
一些可能的WebSockets使用案例有:
- 聊天应用
- 多人游戏
- 股票交易和金融应用
- 文档合作编辑
- 社交应用
JSR 356,WebSocket的Java API,规定了开发者把WebSockets 整合进他们的应用时可以使用的Java API — 包括服务器端和Java客户端。JSR 356是Java EE 7标准中的一部分。这意味着所有Java EE 7兼容的应用服务器都将有一个遵守JSR 356标准的WebSocket协议的实现。开发者也可以在Java EE 7应用服务器之外使用JSR 356。目前Apache Tomcat 8提供了JSR 356 API的WebSocket支持。 Jboss Wildfly 8 (原JBoss Application Server)也支持JSR 356.
一个Java客户端可以使用兼容JSR 356的客户端实现,来连接到WebSocket服务器。对web客户端来说,开发者可以使用WebSocket JavaScript API来和WebSocket服务器进行通讯。WebSocket客户端和WebSocket服务器之间的区别,仅在于两者之间是通过什么方式连接起来的。一个WebSocket客户端是一个WebSocket终端,它初始化了一个到对方的连接。一个WebSocket服务器也是一个WebSocket终端,它被发布出去并且等待来自对方的连接。在客户端和服务器端都有回调监听方法 -- onOpen , onMessage , onError, onClose。
怎么创建你的第一个WebSocket应用呢?基本上我们还是会使用Javascript API编写WebSocket客户端, 在服务器端, 本文使用JSR 356规范定义的通用模式和技术处理WebSocket的通讯。
下面看一个简单的例子, 演示了如果使用JavaScript WebSocket客户端与运行在Wildfly 8服务器通信.
客户端代码
1 <html>
2 <head>
3 <meta http-equiv="content-type"content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
4 </head>
5
6 <body>
7 <meta charset="utf-8">
8 <title>HelloWorld Web sockets</title>
9 <script language="javascript"type="text/javascript">
10 var wsUri = getRootUri() + "/websocket-hello/hello";
11
12 function getRootUri() {
13 return "ws://" + (document.location.hostname == "" ? "localhost" :document.location.hostname) + ":" +
14 (document.location.port == "" ? "8080" :document.location.port);
15 }
16
17 function init() {
18 output = document.getElementById("output");
19 }
20
21 function send_message() {
22
23 websocket = new WebSocket(wsUri);
24 websocket.onopen = function(evt) {
25 onOpen(evt)
26 };
27 websocket.onmessage = function(evt) {
28 onMessage(evt)
29 };
30 websocket.onerror = function(evt) {
31 onError(evt)
32 };
33
34 }
35
36 function onOpen(evt) {
37 writeToScreen("Connected to Endpoint!");
38 doSend(textID.value);
39
40 }
41
42 function onMessage(evt) {
43 writeToScreen("Message Received: " + evt.data);
44 }
45
46 function onError(evt) {
47 writeToScreen(‘<span style="color: red;">ERROR:</span> ‘ + evt.data);
48 }
49
50 function doSend(message) {
51 writeToScreen("Message Sent: " + message);
52 websocket.send(message);
53 }
54
55 function writeToScreen(message) {
56 var pre = document.createElement("p");
57 pre.style.wordWrap = "break-word";
58 pre.innerHTML = message;
59
60 output.appendChild(pre);
61 }
62
63 window.addEventListener("load", init, false);
64
65 </script>
66
67 <h1 style="text-align: center;">Hello World WebSocket Client</h2>
68
69 <br>
70
71 <div style="text-align: center;">
72 <form action="">
73 <input onclick="send_message()" value="Send"type="button">
74 <input id="textID" name="message"value="Hello WebSocket!" type="text"><br>
75 </form>
76 </div>
77 <div id="output"></div>
78 </body>
79 </html>
如你所见,要想使用WebSocket协议与服务器通信, 需要一个WebSocket对象。它会自动连接服务器.
websocket = new WebSocket(wsUri);
连接上会触发open事件:
1 websocket.onopen = function(evt) {
2 onOpen(evt)
3 };
一旦连接成功,则向服务器发送一个简单的hello消息。
1 websocket.send(message);
服务器端代码
有两种创建服务器端代码的方法:
- 注解方式Annotation-driven: 通过在POJO加上注解, 开发者就可以处理WebSocket 生命周期事件.
- 实现接口方式Interface-driven: 开发者可以实现Endpoint接口和声明周期的各个方法.
建议开发时采用注解方式, 这样可以使用POJO就可以实现WebSocket Endpoint. 而且不限定处理事件的方法名。 代码也更简单。
本例就采用注解的方式, 接收WebSocket请求的类是一个POJO, 通过@ServerEndpoint标注. 这个注解告诉容器此类应该被当作一个WebSocket的Endpoint。value值就是WebSocket endpoint的path.
1 package com.sample.websocket;
2
3 import javax.websocket.*;
4 import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
5
6
7 @ServerEndpoint("/hello")
8 public class HelloWorldEndpoint {
9
10
11 @OnMessage
12 public String hello(String message) {
13 System.out.println("Received : "+ message);
14 return message;
15 }
16
17 @OnOpen
18 public void myOnOpen(Session session) {
19 System.out.println("WebSocket opened: " + session.getId());
20 }
21
22 @OnClose
23 public void myOnClose(CloseReason reason) {
24 System.out.println("Closing a WebSocket due to " + reason.getReasonPhrase());
25 }
26
27 }
注意:这个例子还包括了其它两个回调函数: @OnOpen标注的方法在WebSocket连接开始时被调用, Web Session作为参数。 另外一个@OnClose标注的方法在连接关闭时被调用。
就是这么简单。但是为了编译这个例子你还需要Websockets API的实现,它在WildFly 8发布中(或者你用JSR 356的参考实现,或其它的容器提供的jar, 如tomcat):
1 modulessystemlayersbasejavaxwebsocketapimainjboss-websocket-api_1.0_spec-1.0.0.Final.jar
对于Maven用户, 你需要增加undertow-websockets-jsr依赖
1 <dependency>
2 <groupId>org.jboss.spec.javax.websocket</groupId>
3 <artifactId>jboss-websocket-api_1.0_spec</artifactId>
4 <version>1.0.0.Final</version>
5 </dependency>
这个例子比较早,应该是2013年写的,jsr 256还未发布。 现在,你应该直接使用Java EE提供的API
1 <dependency>
2 <groupId>javax.websocket</groupId>
3 <artifactId>javax.websocket-api</artifactId>
4 <version>1.1</version>
5 </dependency>
编解码器
前面的例子中WebSocket通信的消息类型默认为String。接下来的例子演示如何使用Encoder和Decoder传输更复杂的数据。
Websocket使用Decoder将文本消息转换成Java对象,然后传给@OnMessage方法处理; 而当对象写入到session中时,Websocket将使用Encoder将Java对象转换成文本,再发送给客户端。
更常用的, 我们使用XML 或者 JSON 来传送数据,所以将会会将Java对象与XML/JSON数据相互转换.
下图描绘了客户端和服务器使用encoder/decoder标准通信过程。
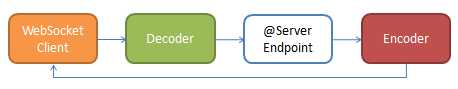
声明Encoder/Decoder也是相当的简单: 你只需在@ServerEndpoint注解中增加encoder/decoder设置:
1 package com.sample.websocket;
2
3 import java.util.logging.Level;
4 import java.util.logging.Logger;
5 import javax.websocket.*;
6 import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
7
8 @ServerEndpoint(value = "/hello",
9 decoders = {
10 MessageDecoder.class,},
11 encoders = {
12 MessageEncoder.class
13 })
14 public class HelloWorldEndpoint {
15
16 @OnMessage
17 public Person hello(Person person, Session session) {
18 if (person.getName().equals("john")) {
19 person.setName("Mr. John");
20 }
21 try {
22 session.getBasicRemote().sendObject(person);
23 System.out.println("sent ");
24 } catch (Exception ex) {
25 Logger.getLogger(HelloWorldEndpoint.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
26 }
27 return person;
28
29 }
30
31 @OnOpen
32 public void myOnOpen(Session session) {
33 }
34
35 }
正像你看到的, OnMessage方法使用Java Object person作为参数, 我们为名字增加个尊称再返回给客户端。通过session.getBasicRemote().sendObject(Object obj)返回数据.
容器负责使用你指定的Decoder将接收到的XML消息转为Java对象:
1 package com.sample.websocket;
2
3 import java.io.StringReader;
4
5 import javax.websocket.Decoder;
6 import javax.websocket.EndpointConfig;
7 import javax.xml.bind.*;
8
9
10 public class MessageDecoder implementsDecoder.Text<Person> {
11
12 @Override
13 public Person decode(String s) {
14 System.out.println("Incoming XML " + s);
15 Person person = null;
16 JAXBContext jaxbContext;
17 try {
18 jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Person.class);
19
20 Unmarshaller unmarshaller = jaxbContext.createUnmarshaller();
21
22 StringReader reader = new StringReader(s);
23 person = (Person) unmarshaller.unmarshal(reader);
24 } catch (Exception ex) {
25 ex.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 return person;
28 }
29
30 @Override
31 public boolean willDecode(String s) {
32
33 return (s != null);
34 }
35
36 @Override
37 public void init(EndpointConfig endpointConfig) {
38 // do nothing.
39 }
40
41 @Override
42 public void destroy() {
43 // do nothing.
44 }
45 }
这里我们使用JAXB做转换。我们只要实现一个泛型接口Decoder.Text 或者 Decoder.Binary, 根据你传输的数据是文本还是二进制选择一个.
所以数据由Decoder解码, 传给Endpoint (这里的 HelloWorldEndpoint), 在返回给client之前, 它还会被下面的Encoder转换成XML:
1 package com.sample.websocket;
2
3 import java.io.StringWriter;
4
5 import javax.websocket.EncodeException;
6 import javax.websocket.Encoder;
7 import javax.websocket.EndpointConfig;
8 import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
9 import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
10
11 public class MessageEncoder implementsEncoder.Text<Person> {
12
13 @Override
14 public String encode(Person object) throws EncodeException {
15
16 JAXBContext jaxbContext = null;
17 StringWriter st = null;
18 try {
19 jaxbContext = JAXBContext.newInstance(Person.class);
20
21 Marshaller marshaller = jaxbContext.createMarshaller();
22 st = new StringWriter();
23 marshaller.marshal(object, st);
24 System.out.println("OutGoing XML " + st.toString());
25
26 } catch (Exception ex) {
27 ex.printStackTrace();
28 }
29 return st.toString();
30 }
31
32 @Override
33 public void init(EndpointConfig endpointConfig) {
34 // do nothing.
35 }
36
37 @Override
38 public void destroy() {
39 // do nothing.
40 }
41 }
为了测试这个例子,将客户端的网页稍微修改一下以便能在textarea中粘帖XML:
1 <html>
2 <head>
3 <meta http-equiv="content-type"content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
4 </head>
5
6 <body>
7 <meta charset="utf-8">
8 <title>HelloWorld Web sockets</title>
9 <script language="javascript"type="text/javascript">
10 var wsUri = getRootUri() + "/websocket-hello/hello";
11
12 function getRootUri() {
13 return "ws://" + (document.location.hostname == "" ? "localhost" :document.location.hostname) + ":" +
14 (document.location.port == "" ? "8080" :document.location.port);
15 }
16
17 function init() {
18 output = document.getElementById("output");
19 }
20
21 function send_message() {
22
23 websocket = new WebSocket(wsUri);
24 websocket.onopen = function(evt) {
25 onOpen(evt)
26 };
27 websocket.onmessage = function(evt) {
28 onMessage(evt)
29 };
30 websocket.onerror = function(evt) {
31 onError(evt)
32 };
33
34 }
35
36 function onOpen(evt) {
37 writeToScreen("Connected to Endpoint!");
38 doSend(textID.value);
39
40 }
41
42 function onMessage(evt) {
43 writeToScreen("Message Received: " + evt.data);
44 }
45
46 function onError(evt) {
47 writeToScreen(‘<span style="color: red;">ERROR:</span> ‘ + evt.data);
48 }
49
50 function doSend(message) {
51 writeToScreen("Message Sent: " + message);
52 websocket.send(message);
53 }
54
55 function writeToScreen(message) {
56 alert(message);
57
58 }
59
60 window.addEventListener("load", init, false);
61
62 </script>
63
64 <h1 style="text-align: center;">Hello World WebSocket Client</h2>
65
66 <br>
67
68 <div style="text-align: center;">
69 <form action="">
70 <input onclick="send_message()" value="Send"type="button">
71 <textarea id="textID" rows="4" cols="50"name="message" >
72 </textarea>
73 </form>
74 </div>
75 <div id="output"></div>
76 </body>
77 </html>
在文本框中输入下面的XML进行测试。
1 <person>
2 <name>john</name>
3 <surname>smith</surname>
4 </person>
这篇文章摘自http://colobu.com/2015/02/27/WebSockets-tutorial-on-Wildfly-8/(翻译自 mastertheboss的 WebSockets tutorial on Wildfly 8)
1 二、轮询
2 前台代码:
3 $(document).ready(function() {
4 setInterval(checkIsExist, 1000);
5 });
6
7 function checkIsExist() {
8 var urls = "/LogForPage/getShiftCarOrderCarId.do?ajax=1";
9 var htmlobj = $.ajax({
10 url : urls,
11 async : false
12 });
13 var list = eval(htmlobj.responseText);
14 $("#textarea-input").html(list);
15 }
16
17
18
19 后台代码:
20
21 import javax.annotation.Resource;
22 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
23
24 import org.codehaus.jackson.map.ObjectMapper;
25 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
26 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
27
28 import com.aotoso.control.ConnectionManage.PortCommunication;
29 import com.aotoso.control.base.BaseController;
30 import com.aotoso.server.FirstDataManage.EverydayPlanService;
31
32
33 @Controller
34 @RequestMapping("/LogForPage")
35 public class LogForPage extends BaseController {
36 @Resource(name = "everydayPlanService")
37 EverydayPlanService everydayPlanService;
38
39 /**
40 * 实时打印上传的信息!
41 * @param session
42 * @param request
43 * @param response
44 */
45 @RequestMapping(value = "/TMRInfromation")
46 public void getShiftCarOrderCarId(HttpServletResponse response) {
47 pd = this.getPageData();
48 logger.info("实时打印上传的信息!");
49 ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
50 try {
51 objectMapper.writeValue(response.getOutputStream(),new PortCommunication().getInfo());
52 System.out.println(new PortCommunication().getInfo());
53 } catch (Exception e) {
54 e.printStackTrace();
55 }
56 }
57 }
