C中线程信号控制
Posted 我要出家当道士
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C中线程信号控制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、场景介绍
存在三个线程,一个主线程和两个子线程(子线程数量不固定)。为了节省频繁创建销毁线程造成的资源浪费,将这些线程设置为常驻线程。但这样引入了一个新的问题,如何协调这些线程完成工作。
主线程内是循环检测某个文件夹内文件的变动,当文件夹内出现新的文件时,更新可拷贝文件列表,并告知子线程开始干活;子线程拷贝结束后需要告知主线程任务完成了,主线程开始下一轮检测。

二、解决方法
1、临时线程
主线程每次检测完毕后,新建子线程执行拷贝任务,并阻塞等待线程任务的结束。
#include "main.h"
void *filecopy_thread(void *args)
pthread_t id = pthread_self();
PTHREAD_ARGS *thread_args = (PTHREAD_ARGS *)args;
string dst_dir = thread_args->dst_dir;
while (1)
// get the file to copy
pthread_mutex_lock(thread_args->mutex);
// exit when the list is empty
if (thread_args->file_list.empty())
pthread_mutex_unlock(thread_args->mutex);
break;
string src_file = thread_args->file_list.back();
thread_args->file_list.pop_back();
pthread_mutex_unlock(thread_args->mutex);
copy_file(src_file, dst_dir);
return NULL;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
while(1)
bool is_switch = oracle.is_redolog_switch();
// judge whether the redolog has bean switched
if ( is_switch )
printf("pthread create\\n");
pthread_t *pthread_list = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * cfg_utils.m_filecopy_pcount);
if (!pthread_list)
LOG_F(ERROR, "pthread list created failed");
continue;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
PTHREAD_ARGS pthread_args = file_list_src, &mutex, cfg_utils.m_logbk_syspath, &oncebk_count;
struct timeval start, end;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
// start file copy thread
for (int i = 0; i < cfg_utils.m_filecopy_pcount; i++)
printf("creating pthread(%d)\\n", i + 1);
pthread_create(pthread_list + i, NULL, filecopy_thread, &pthread_args);
// block until all file has copied
for (int i = 0; i < cfg_utils.m_filecopy_pcount; i++)
pthread_join(pthread_list[i], NULL);
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
double timeuse = ( end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec ) + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec)/1000000.0;
printf("%.1lf(s)\\n", timeuse);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
free(pthread_list);
sleep(cfg_utils.m_bk_cycle);
return 0;
(1)优点
逻辑简单
(2)缺点
频繁创建与销毁线程,资源浪费。
2、全局变量信号
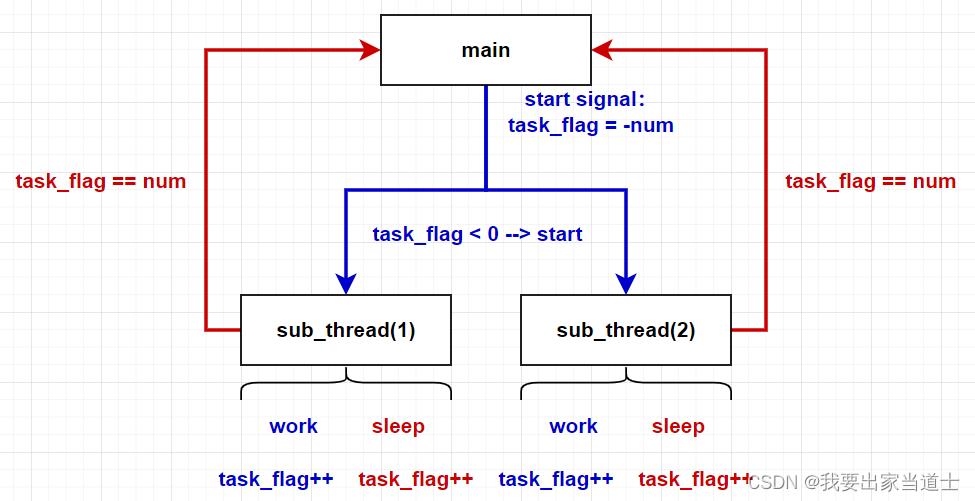
定义一个全局变量作为线程的控制信号。
主线程将该信号设置为子线程的个数的负数,以启动子线程。
当该信号小于 0 时,子线程开始启动。子线程的启动与任务完毕都需要将该信号加一。
当主线程检测到该信号为线程总数时推导子线程本次任务结束。
(1)优点
子线程作为常驻线程,节省了一定的资源。
(2)缺点
子线程与主线程在等待信号的过程中要么造成 CPU 的空转,要么 sleep 会增加程序的处理时延。
而且,子线程启动与结束都对全局信号进行加一的操作,极端情况(某些线程执行速度存在极端差异)下可能造成信号控制的紊乱。
3、信号量
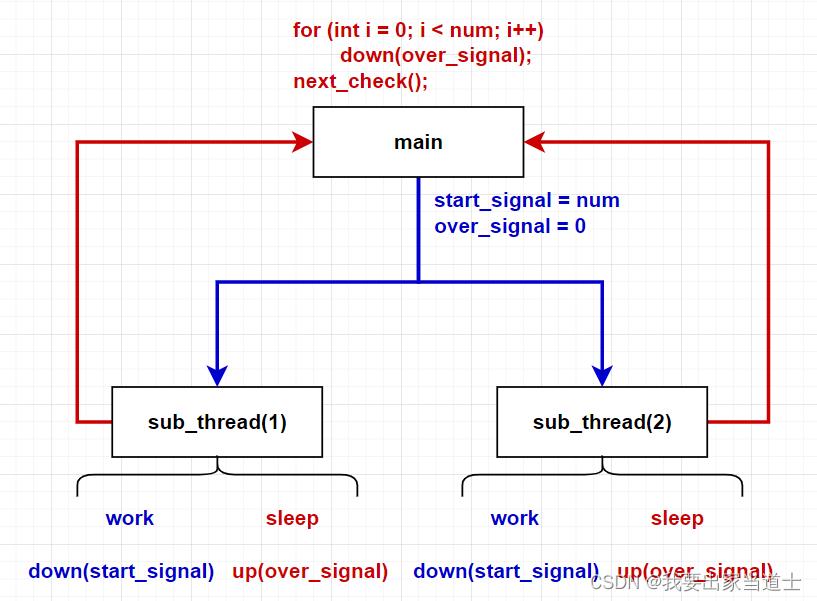
使用两组信号:start_signal 和 over_signal。
主线程启动子线程时,需要将 start_signal 赋值为子线程数,over_signal 赋值为0.
子线程执行down(start_signal) ,该操作执行成功即可执行任务逻辑,执行完后 up(over_signal)。
主线程需要执行 num 次down(over_signal)操作,只有所有子线程执行结束,该操作才可以执行完成。
在等待执行信号down和up的过程中,线程都是阻塞的,不会造成 CPU 的空转,当信号可操作时也会立即执行,不会增加操作时延。
以上是关于C中线程信号控制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章