Flutter 的缓存策略
Posted 会煮咖啡的猫咪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Flutter 的缓存策略相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Flutter 的缓存策略

原文 https://medium.com/@romaingreaume/implementing-a-cache-strategy-in-your-flutter-app-5db3e316e7c9
前言
在移动应用程序中,缓存管理是一件非常重要的事情。
在本文中,我将告诉您如何在我的公司 Beapp 中设置策略缓存。

正文
W 怎么了?
如果你读了这篇文章,我想你知道缓存是什么,但是以防万一..。
缓存基本上是将数据存储在设备的存储器中。
W 为什么使用缓存?
-
如果用户连接不好或者没有互联网 -
限制 API 调用,特别是对于不需要经常刷新的数据 -
存储敏感数据(我们稍后讨论)
一张图片胜过千言万语:
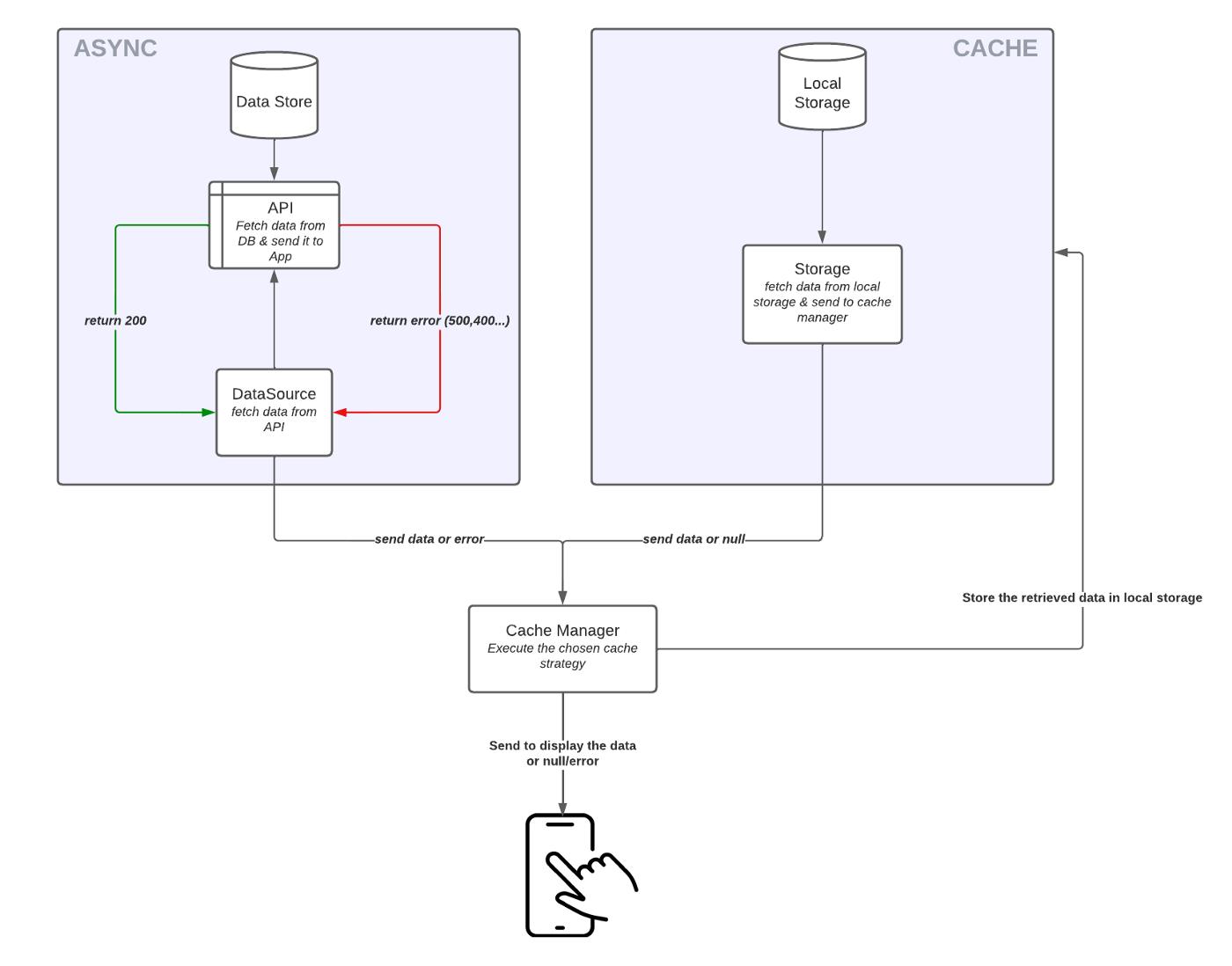
Cache Strategy Scheme
缓存策略计划
如您所见,缓存的主要用途是始终尝试向用户显示数据。
关于敏感数据,出于以下原因,我将用户缓存与网络缓存分离:
-
网络缓存比用户缓存更短暂。 -
相反,用户缓存存储敏感数据,如访问令牌、刷新令牌,这些数据必须是安全的,用户不能访问。 -
更具体地说,刷新令牌的有效期可能很长(长达几个月) ,而经典数据可能在一小时后刷新,这将导致不必要的 API 调用。
因此,将这些策略分离开来是一种很好的做法,即使它们可以被合并。
现在我们了解了什么是缓存,让我们深入研究代码吧!
H 如何建立这些策略?
文件树如下所示:
-- lib
----- core
------- cache
--------- storage
--------- strategy
在子文件夹存储中,我们创建了一个文件 Storage.dart,其中包含一个抽象类 Storage
这个类是一个“契约 contrac”,我们在其中声明操作数据的方法。
abstract class Storage
Future<void> write(String key, String value);
Future<String?> read(String key);
Future<void> delete(String key);
Future<int> count(String? prefix);
Future<void> clear(String? prefix);
正如我所说,我们将通过我们的应用程序操纵它们,但为此,我们需要在设备中存储它们的方法。
我们使用 Hive 包,它是一个基于键/值的存储解决方案。
总而言之,Hive 在设备的存储中创建了一个文件夹,您可以在其中存储一个 hiveBox,其中包含 key: value 数据。
我们可以很容易地通过它的名字进入这个盒子。
现在我们可以从 Storage 抽象类中实现这些方法。
class CacheStorage implements Storage
static const _hiveBoxName = "cache";
CacheStorage()
Hive.initFlutter() ;
@override
Future<void> clear(String? prefix) async
final box = await Hive.openBox(_hiveBoxName);
if (prefix == null)
await box.clear() ;
else
for (var key in box.keys)
if (key is String && key.startsWith(prefix))
await box.delete(key);
@override
Future<void> delete(String key) async
final box = await Hive.openBox(_hiveBoxName);
return box.delete(key);
@override
Future<String?> read(String key) async
final box = await Hive.openBox(_hiveBoxName);
return box.get(key);
@override
Future<void> write(String key, String value) async
final box = await Hive.openBox(_hiveBoxName);
return box.put(key, value);
@override
Future<int> count(String? prefix) async
final box = await Hive.openBox(_hiveBoxName);
if (prefix == null)
return box.length;
else
var count = 0;
for (var key in box.keys)
if (key is String && key.startsWith(prefix))
count++;
return count;
原则很简单:
-
我们在创建 CacheStorage 时创建一个 hive 实例。 -
每次我们操作数据时,我们将打开我们的 Hive 框(使用它的名称)并执行触发的方法(获取、写入、删除...)。 -
我们可以很容易地通过它的键来访问数据值。
现在我们已经有了操作数据的方法,我们可以设置不同的策略,使用统一的调用语法来适应应用程序中的不同用例。
我们开始创建一个契约缓存_策略。缓存根中的 Dart 。该合同允许我们应用其中一种策略并对其进行配置。
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'cache_manager.dart';
import 'cache_wrapper.dart';
import 'storage/storage.dart';
abstract class CacheStrategy
static const defaultTTLValue = 60 * 60 * 1000;
Future _storeCacheData<T>(String key, T value, Storage storage) async
final cacheWrapper = CacheWrapper<T>(value, DateTime.now() .millisecondsSinceEpoch);
await storage.write(key, jsonEncode(cacheWrapper.toJsonObject() ));
_isValid<T>(CacheWrapper<T> cacheWrapper, bool keepExpiredCache, int ttlValue) => keepExpiredCache || DateTime.now() .millisecondsSinceEpoch < cacheWrapper.cachedDate + ttlValue;
Future<T> invokeAsync<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, Storage storage) async
final asyncData = await asyncBloc() ;
_storeCacheData(key, asyncData, storage);
return asyncData;
Future<T?> fetchCacheData<T>(String key, SerializerBloc serializerBloc, Storage storage, bool keepExpiredCache = false, int ttlValue = defaultTTLValue) async
final value = await storage.read(key);
if (value != null)
final cacheWrapper = CacheWrapper.fromJson(jsonDecode(value));
if (_isValid(cacheWrapper, keepExpiredCache, ttlValue))
if (kDebugMode) print("Fetch cache data for key $key: $cacheWrapper.data");
return serializerBloc(cacheWrapper.data);
return null;
Future<T?> applyStrategy<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, SerializerBloc serializerBloc, int ttlValue, Storage storage);
-
DefaultTTLValue 是存储在缓存中的数据的实时值。换句话说: 在这段时间之后,数据被认为是无效的。 -_storeCacheData() 通过 CacheWrapper 允许存储数据,我们将在后面看到它。 -_isValid() 与 defaultTTLValue 相比,检查缓存获取是否仍然有效 -
InvkeAsync() 将使用作为参数传递的 syncBloc 方法从远程位置(通常来自 Web 服务)获取数据,并存储和返回检索到的数据。 -
FetchCacheData() 将通过 key 参数从缓存中获取数据,转换 Cache Wrapper 接收到的 JSON 来检查它是否仍然有效,如果有效,则返回具有相应类型的 Dart 对象中的序列化数据,这要感谢 seralizerBloc。 -
ApplicyStrategy() 将执行要选择的策略,其中包含所需的所有参数。
通过这些解释,我们可以看到任何战略的实施路径:
-
我们调用 applicyStrategy() 来指出我们想要应用哪个策略,以及所需的参数。 -
要检查缓存的数据 fetchCacheData() ,该方法使用_isValid() 检查有效性并返回数据或 null。 -
为了从 WS 获取数据,我们触发了 invekAsync() ,一旦接收到数据,就将它们与_storeCacheData() 一起放到 cache 中。
class CacheWrapper<T>
final T data;
final int cachedDate;
CacheWrapper(this.data, this.cachedDate);
CacheWrapper.fromJson(json)
: cachedDate = json['cachedDate'],
data = json['data'];
Map toJson() => 'cachedDate': cachedDate, 'data': data;
@override
String toString() => "CacheWrappercachedDate=$cachedDate, data=$data";
关于 CacheWrapper,您可以在根缓存文件夹中创建一个文件 cache_wrapper. dart。
正如其名称所示,CacheWrapper 是一个允许包装接收数据的类。它有两个参数,一个是允许包装任何类型数据的通用类型数据,另一个是在数据存储在缓存中的日期和时间自动设置的 cachedDate。
From JSON() 和 toJson() 方法将接收到的数据转换为用于缓存的 JSON 或者在代码中使用它的 Map。
因此,可以将 CacheWrapper 解释为包含缓存数据并允许对这些数据进行编码/解码的“包装器”。
在本文的这个步骤中,我们的结构文件夹如下所示:
-- lib
----- core
------- cache
--------- storage
----------- storage.dart
----------- cache_storage.dart
--------- cache_strategy.dart
现在我们已经看到了我们的策略可以做什么的定义,让我们深入研究它们的实现。
在缓存根目录中的新策略文件夹中,我们将创建所有策略的文件。
每个策略都是单例的,所以应用程序中每个策略只有一个实例。
我们可以使用 get_it 来注入我们的策略,但是这增加了对包的依赖以及我们所知道的第三方的所有缺点,所以我们自己创建了它们。
每个策略都将继承自抽象的 CacheStrategy 类,它们将分别使用 applicyStrategy() 方法实现各自的策略。
AsyncOrCache
这个策略将首先调用端点来检索数据。如果抛出错误(出于各种原因: 错误 401,403,500...) ,我们将检索存储在设备缓存中的最后数据。如果缓存中没有任何内容或无效数据,我们将返回先前引发的错误,以便在状态管理器中处理它(稍后将看到它)。
class AsyncOrCacheStrategy extends CacheStrategy
static final AsyncOrCacheStrategy _instance = AsyncOrCacheStrategy._internal() ;
factory AsyncOrCacheStrategy()
return _instance;
AsyncOrCacheStrategy._internal() ;
@override
Future<T?> applyStrategy<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, SerializerBloc<T> serializerBloc, int ttlValue, Storage storage) async => await invokeAsync(asyncBloc, key, storage).onError(
(RestException restError, stackTrace) async
if (restError.code == 403 || restError.code == 404)
storage.clear(prefix: key);
return Future.error(restError);
else
return await fetchCacheData(key, serializerBloc, storage, ttlValue: ttlValue) ?? Future.error(restError);
,
);
CacheOrAsync
最后一个策略和前一个一样,只是反过来而已。首先,我们检查数据是否存储在缓存中,如果结果为 null,则触发 WS 调用。如果抛出错误,我们在状态管理器中处理它。
class CacheOrAsyncStrategy extends CacheStrategy
static final CacheOrAsyncStrategy _instance = CacheOrAsyncStrategy._internal() ;
factory CacheOrAsyncStrategy()
return _instance;
CacheOrAsyncStrategy._internal() ;
@override
Future<T?> applyStrategy<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, SerializerBloc<T> serializerBloc, int ttlValue, Storage storage) async =>
await fetchCacheData(key, serializerBloc, storage, ttlValue: ttlValue) ?? await invokeAsync(asyncBloc, key, storage);
只是同步
此策略调用 Web 服务来获取数据。
class JustAsyncStrategy extends CacheStrategy
static final JustAsyncStrategy _instance = JustAsyncStrategy._internal() ;
factory JustAsyncStrategy()
return _instance;
JustAsyncStrategy._internal() ;
@override
Future<T?> applyStrategy<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, SerializerBloc<T> serializerBloc, int ttlValue, Storage storage) async => await invokeAsync(asyncBloc, key, storage);
JustCache
class JustCacheStrategy extends CacheStrategy
static final JustCacheStrategy _instance = JustCacheStrategy._internal() ;
factory JustCacheStrategy()
return _instance;
JustCacheStrategy._internal() ;
@override
Future<T?> applyStrategy<T>(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc, String key, SerializerBloc<T> serializerBloc, int ttlValue, Storage storage) async =>
await fetchCacheData(key, serializerBloc, storage, ttlValue: ttlValue);
此策略仅使用存储在设备缓存中的数据。缺点是如果应用程序找不到数据,则返回 null。
对于最后两种策略,它们可以直接由对缓存或网络的直接调用来替代,但是这里我们保留了一种统一的调用方式。
现在我们已经看到了不同的策略,让我们使用它们!
在根缓存文件夹中,我们创建一个 cache_manager.dart 文件。
这个文件将包含构建缓存策略的所有逻辑。它将被直接注入到我们的代码中(稍后我将回到这一点)。
import 'cache_strategy.dart';
import 'storage/cache_storage.dart';
typedef AsyncBloc<T> = Function;
typedef SerializerBloc<T> = Function(dynamic);
class CacheManager
final CacheStorage cacheStorage;
CacheManager(
this.cacheStorage,
);
String? defaultSessionName;
StrategyBuilder from<T>(String key) => StrategyBuilder<T>(key, cacheStorage).withSession(defaultSessionName);
Future clear(String? prefix) async
if (defaultSessionName != null && prefix != null)
await cacheStorage.clear(prefix: "$defaultSessionName_$prefix");
else if (prefix != null)
await cacheStorage.clear(prefix: prefix);
else if (defaultSessionName != null)
await cacheStorage.clear(prefix: defaultSessionName);
else
await cacheStorage.clear() ;
class StrategyBuilder<T>
final String _key;
final CacheStorage _cacheStorage;
StrategyBuilder(this._key, this._cacheStorage);
late AsyncBloc<T> _asyncBloc;
late SerializerBloc<T> _serializerBloc;
late CacheStrategy _strategy;
int _ttlValue = CacheStrategy.defaultTTLValue;
String? _sessionName;
StrategyBuilder withAsync(AsyncBloc<T> asyncBloc)
_asyncBloc = asyncBloc;
return this;
StrategyBuilder withStrategy(CacheStrategy strategyType)
_strategy = strategyType;
return this;
StrategyBuilder withTtl(int ttlValue)
_ttlValue = ttlValue;
return this;
StrategyBuilder withSession(String? sessionName)
_sessionName = sessionName;
return this;
StrategyBuilder withSerializer(SerializerBloc serializerBloc)
_serializerBloc = serializerBloc;
return this;
String buildSessionKey(String key) => _sessionName != null ? "$_sessionName_$key" : key;
Future<T?> execute() async
try
return await _strategy.applyStrategy<T?>(_asyncBloc, buildSessionKey(_key), _serializerBloc, _ttlValue, _cacheStorage);
以上是关于Flutter 的缓存策略的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章