mybtis 基础
Posted kyleinjava
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybtis 基础相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、什么是mybatis
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。对于有一定sql基础的开发人员来说,非常好用。
二、mybatis的配置方法
1.引入jar包
2.创建表
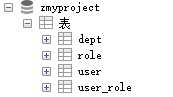
3.创建数据库配置文件 dbconfig.properties
#### 数据库配置文件 ####### jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zmyproject?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
4.创建mybatis配置文件 mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" " http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 引入外部文件 --> <properties resource="dbconfig.properties"></properties> <environments default="development"> <!-- 可以配置多个,这样就能进行切换了 --> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <dataSource type="UNPOOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- 实体类对应的映射文件 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper2.xml"/> <mapper resource="mapper/deptMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="mapper/roleMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
5.创建mapper文件,下面是用代码生成插件自动生成的映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 如果不和接口关联则namespace只要唯一就行 如果和接口关联则namespace需要和接口全类名一致 --> <mapper namespace="test.dao.UserMapper"> </mapper>
三、mybatis的基本使用方法
1.使用纯配置文件的方式来操作数据库
①mapper文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 如果不和接口关联则namespace只要唯一就行 如果和接口关联则namespace需要和接口全类名一致 --> <mapper namespace="test.dao.UserMapper"> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="test.entity.User"> <id column="user_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userId" /> <result column="account" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="account" /> <result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" /> <result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="nikname" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="nikname" /> <result column="gender" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="gender" /> <result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="dep_id" jdbcType="CHAR" property="depId" /> <result column="dept_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="deptName" /> <result column="image_url" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="imageUrl" /> <result column="location" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="location" /> <result column="per_status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="perStatus" /> </resultMap> <sql id="Base_Column_List"> user_id, account, password, name, nikname, gender, age, dep_id, dept_name, image_url, location, per_status </sql> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> </mapper>
public static void xmlConfig(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); //使用namespace+sql的id来保证唯一性 User user = (User)session.selectOne("test.dao.UserMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", "d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); System.out.println(user); MybatisUtil.closeSession(); }
2.使用接口对数据库进行操作
/** *使用mybatis接口对数据库进行操作的时候需要接口的全路径名与映射文件中的namespace相同,这是接口与映射文件之间的关联 *接口的方法要和sql的id一致,否则无法找到对应的sql *接口之所以没有实现类也能正常调用,因为使用了动态代理 */ public interface UserMapper { /** * 对于多参数的情况,可以使用Map封装参数,也可以使用@Param注解来进行标注 */ User selectInfo(@Param("gender") int gender, @Param("age") int age); }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 如果不和接口关联则namespace只要唯一就行 如果和接口关联则namespace需要和接口全类名一致 --> <mapper namespace="test.dao.UserMapper"> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="test.entity.User"> <id column="user_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userId" /> <result column="account" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="account" /> <result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" /> <result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="nikname" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="nikname" /> <result column="gender" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="gender" /> <result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="dep_id" jdbcType="CHAR" property="depId" /> <result column="dept_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="deptName" /> <result column="image_url" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="imageUrl" /> <result column="location" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="location" /> <result column="per_status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="perStatus" /> </resultMap> <sql id="Base_Column_List"> user_id, account, password, name, nikname, gender, age, dep_id, dept_name, image_url, location, per_status </sql> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select <include refid="Base_Column_List" /> from user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> </mapper>
/** * 使用接口进行操作 */ public static void testInterface(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); System.out.println(user); User user2 = userMapper.selectInfo(1, 28); System.out.println(user2); MybatisUtil.closeSession(); }
3.使用注解操作数据库,不需要映射文件文件中有sql,但还是需要mapper文件。
/** *使用mybatis接口对数据库进行操作的时候需要接口的全路径名与映射文件中的namespace相同,这是接口与映射文件之间的关联 *接口的方法要和sql的id一致,否则无法找到对应的sql *接口之所以没有实现类也能正常调用,因为使用了动态代理 */ public interface UserMapper { @Select("select user_id, account, password, name, nikname " + "from user where user_id = #{userId}") User selectByPrimaryKey2(String UserId); }
public static void testAnnotation(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey2("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); System.out.println(user); MybatisUtil.closeSession(); }
四、mybatis的高级映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 如果不和接口关联则namespace只要唯一就行 如果和接口关联则namespace需要和接口全类名一致 --> <mapper namespace="test.dao.User2Mapper"> <resultMap id="UserResultMap" type="test.entity.User2"> <id column="user_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userId" /> <result column="account" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="account" /> <result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" /> <result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="nikname" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="nikname" /> <result column="gender" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="gender" /> <result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="image_url" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="imageUrl" /> <result column="location" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="location" /> <result column="per_status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="perStatus" /> </resultMap> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap1" type="test.entity.User2" extends="UserResultMap"> <id column="user_id" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userId" /> <result column="account" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="account" /> <result column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="password" /> <result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="nikname" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="nikname" /> <result column="gender" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="gender" /> <result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="image_url" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="imageUrl" /> <result column="location" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="location" /> <result column="per_status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="perStatus" /> <result column="dep_id" jdbcType="CHAR" property="dept.depId" /> <result column="dept_name" jdbcType="CHAR" property="dept.deptName" /> </resultMap> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap2" type="test.entity.User2" extends="UserResultMap"> <association property="dept" javaType="test.entity.Dept" resultMap="test.dao.DeptMapper.BaseResultMap"> <!-- 如果用 resultMap 就无需配置下面的result标签,相当于是用DeptMapper.xml文件中的resultMap--> <!-- <result column="dep_id" jdbcType="CHAR" property="depId" /> <result column="dept_name" jdbcType="CHAR" property="deptName" /> --> </association> </resultMap> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap3" type="test.entity.User2" extends="UserResultMap"> <association property="dept" column="deptId" select="test.dao.DeptMapper.selectByPrimaryKey"></association> </resultMap> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap4" type="test.entity.User3" extends="BaseResultMap2"> <collection property="roleList" javaType="java.util.List" ofType="test.entity.Role" resultMap="test.dao.RoleMapper.BaseResultMap"> </collection> </resultMap> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap5" type="test.entity.User3" extends="BaseResultMap2"> <collection property="roleList" column="rid" select="test.dao.RoleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey"> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- 一对一映射的三种方式 1.通过属性.子属性直接进行映射; 2.通过resultMap来进行映射; 3.使用 resultMap 的 association 标签配置一对一映射 4.通过association 标签的嵌套查询,这种方式与根据业务逻辑于动执行多次 SQL 的方式相像,最后会将结果组 合成一个对象。 --> <!-- 1.使用resultMap进行一对一映射 --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap1"> select * from user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- 2.直接进行一对一映射 --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey2" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="test.entity.User2"> SELECT user_id AS userId, account AS account, `password` AS `password`, `name` AS `name`, nikname AS nikname, gender AS gender, age AS age, image_url AS imageUrl, location AS location, per_status AS perStatus, dep_id AS `dept.depId`, dept_name AS `dept.deptName` FROM `user` WHERE user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- 3.使用 resultMap 的 association 标签配置一对一映射 --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey3" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap2"> select * from user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- 4.通过association 标签的嵌套查询,这种方式与根据业务逻辑于动执行多次 SQL 的方式相像,最后会将结果组 合成一个对象。 --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey4" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap3"> select * from user where user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- 两种一对多映射方式 5.collection 集合的嵌套结果映射 6.collection 集合的嵌套查询 (这种方式貌似有bug,只能查出一个角色,不推荐使用。以后再找原因) --> <!-- 5.collection 集合的嵌套结果映射 --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey5" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap4"> SELECT user.*, role.* FROM USER INNER JOIN user_role ON user.user_id = user_role.user_id INNER JOIN role ON user_role.role_id = role.role_id WHERE user.user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- 6.collection 集合的嵌套查询 (这种方式貌似有bug,只能查出一个角色,不推荐使用。以后再找原因) --> <select id="selectByPrimaryKey6" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap5"> SELECT user.*, user_role.role_id as rid FROM USER INNER JOIN user_role ON user.user_id = user_role.user_id WHERE user.user_id = #{userId,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </select> <!-- mybatis 执行存储过程 1.不要将出参和返回混淆,返回是通过return接受;出参是通过入参的Map和javaBean来接受,不过属性要有对应的setter 2.入参不需要写jdbcType,出参一定要写jdbcType 3.出参和入参最好不要和表中的字段一样,否则可能会出现问题 --> <!-- DELIMITER ;; DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `selectUserByAccount`;; CREATE PROCEDURE `selectUserByAccount`(IN saccount VARCHAR(50)) BEGIN SELECT `name` , nikname FROM `user` WHERE account = saccount; END;; DELIMITER ; --> <select id="selectUserByAccount" statementType="CALLABLE" useCache="false" resultMap="UserResultMap"> { call selectUserByAccount( #{account,mode=IN} ) } </select> <!-- DELIMITER ;; DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `selectUserByAccount2`;; CREATE PROCEDURE `selectUserByAccount2`(IN saccount VARCHAR(50),OUT `oname` VARCHAR(80),OUT onikname VARCHAR(80)) BEGIN SELECT `name` , nikname INTO `oname`,onikname FROM `user` WHERE account = saccount; END;; DELIMITER ; --> <select id="selectUserByAccount2" statementType="CALLABLE" useCache="false"> { call selectUserByAccount2( #{saccount,mode=IN}, #{oname,mode=OUT,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{onikname,mode=OUT,jdbcType=VARCHAR} ) } </select> </mapper>
public interface User2Mapper { User2 selectByPrimaryKey(String userId); User2 selectByPrimaryKey2(String userId); User2 selectByPrimaryKey3(String userId); User3 selectByPrimaryKey5(String string); User3 selectByPrimaryKey6(String string); User2 selectUserByAccount(String string); void selectUserByAccount2(Map<String,String> map); }
public class testService2 { /** * 一对一 */ public static void testOneToOne(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); User2Mapper user2Mapper = session.getMapper(User2Mapper.class); User2 user21 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); User2 user22 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey2("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); User2 user23 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey3("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); User2 user24 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey3("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); System.out.println(user21); System.out.println(user22); System.out.println(user23); System.out.println(user24); MybatisUtil.closeSession(); } /** * 一对多 */ public static void testOneToMany(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); User2Mapper user2Mapper = session.getMapper(User2Mapper.class); User3 user31 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey5("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); User3 user32 = user2Mapper.selectByPrimaryKey6("d96b17cbce8c11e79871f07959e0e549"); System.out.println(user31); System.out.println(user32); MybatisUtil.closeSession(); } /** * 存储过程 */ public static void testCallable(){ SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.openSession(); User2Mapper user2Mapper = session.getMapper(User2Mapper.class); User2 user21 = user2Mapper.selectUserByAccount("80074567"); System.out.println(user21); Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("saccount", "80074567"); user2Mapper.selectUserByAccount2(map); System.out.println(map);//出参直接从map中可以获取 MybatisUtil.closeSession(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //testOneToOne(); //testOneToMany(); testCallable(); } }
五、mybatis缓存
1.mybatis有两级缓存,第一级默认开启,无法控制;
MyBatis 的一级缓存存在于 SqlSession 的生命周期中,在同一个 SqlSession 中查询 时, MyBatis 会把执行的方法和参数通过算法生成缓存的键值,将键值和查询结果存入一个 Map 对象中。
如果同一个 SqlSession 中执行的方法和参数完全一致,那么通过算法会生成相同的 键值,当 Map 缓存对象中己经存在该键值时,则会返回缓存中的对象。
2.第二级缓存存在于SqlSessionFacotry的生命周期中。
在 MyBatis的全局配置 settings中有 一个参数 cacheEnabled,这个参数是二级缓存的全局开关,默认值是 true,初始状态 为启用状态。
如果把这个参数设置为 false,即使有后面的二级缓存配置,也不会生效。 由于这个参数值默认为 true ,所以不必配置,如果想要配置,
可以在 mybatis-config.xml中配置如下:
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
在保证二级缓存的全局配置开启的情况下,给 RoleMapper.xml 开启 二级缓存只需要在 UserMapper.xml
中添加<cache/>元素即可,添加后的 UserMapper.xml 如下。
以上是关于mybtis 基础的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章