iOS开发底层之方法的慢速查找流程探索+方法动态决议上 - 10
Posted iOS_developer_zhong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS开发底层之方法的慢速查找流程探索+方法动态决议上 - 10相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、二分查找算法
上篇文章中提到过,苹果底层在查找方法的时候用到了二分查找算法, 觉得是用的代码最少,并且利用了位移,很有巧妙性,不得不佩服苹果的工程师还是牛逼PLUS。
1.仿苹果底层二分查找算法
// 二分查找 swift版本,for 循环体报错,这个地方还没有调试通过,仅供参考思路。
var array = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] //原始数据, 必须是有序的。
var base = 0 //用来做偏移
var findValue = 8 // 自己定义,就是玩儿,现在来查找7,看看几次可以查找到。
var count = array.count //总得查找个数
var probe = 0 //临时存放 下标值
var probeValue = 0 // 历史存放 数据中的值
for (count ; count != 0 ; count >>= 1 )
probe = base + (count >> 1 )
probeValue = array[probe]
if findValue > probeValue // 寻找的值比当前查出的值大,说明值还在右边
base = probe + 1
count-- // 这个地方--,是为了后续的偏移。
else if findValue == probeValue
print("找到了")
break
2. 通过案例玩下这个算法
base = 0
findValue = 8 // 我们要找8这个值,看需要找几次才能找到。
第一次循环:
base = 0
probe = base + count >> 1 = 0 + 0000 1010 >> 1 = 5
probeValue = 6
findValue > probeValue
base = probe + 1 = 5 + 1 = 6
count = 9
第二次循环
count 9>>= 1 = 0000 1001 >> 1 = 4
base = 6
probe = 6 + count >> 1 = 6 + 2 = 8
probevalue = 9
findValue > probevalue 不满足
第三次循环
count 4 >>= 1 = 2
base = 6
probe = 6 + count >> 1 = 6 + 1 = 7
probevalue = 8
findValue == probeValue ,找到了,跳出循环。
二、慢速查找流程图
1.总结下慢速查找的主要过程
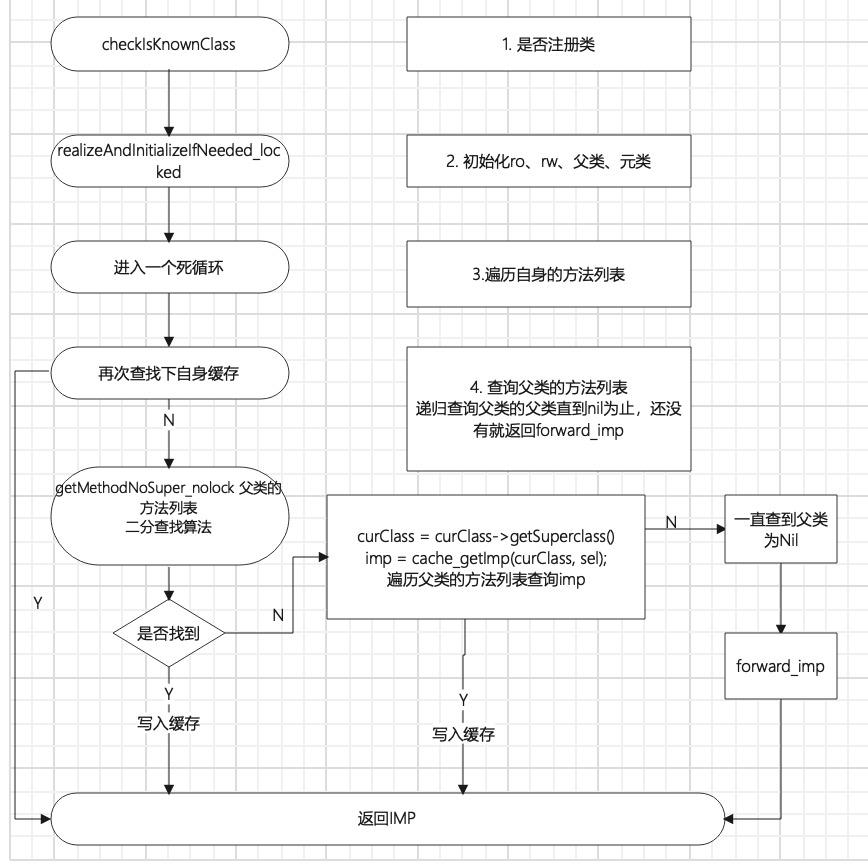
2.imp没有找到, 动态方法决议流程
- 上源码,lookUpImpOrForward 方法中的底部代码
NEVER_INLINE
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
// ----------省略以前讲过的代码---------------
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
// 1. 找不到imp的后续处理, 拦截错误并处理未找到的方法
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER))
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
done:
if (fastpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0))
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
while (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true))
cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass();
#endif
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
done_unlock:
runtimeLock.unlock();
if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp))
return nil;
return imp;
// 解决方法 当imp == nil 的时候,走的处理方法
static NEVER_INLINE IMP
resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
runtimeLock.unlock();
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) // 1. 判断当前类是不是元类 ,对象方法的动态决议
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
else
// 2. 元类就走这个方法。
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
// 走类方法的动态决议。
resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls))
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
// chances are that calling the resolver have populated the cache
// so attempt using it
return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
// 非元类(对象方法)调用的解决方法(动态决议),我们发现了一个重要的方法resolveInstanceMethod
static void resolveInstanceMethod(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls)
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
/// ==重要的代码=====
SEL resolve_sel = @selector(resolveInstanceMethod:);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(cls, resolve_sel, cls->ISA(/*authenticated*/true)))
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(cls, resolve_sel, sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls);
//---省略部分代码------
// 类方法的动态决议
// 发现了一个重要的方法 resolveClassMethod
static void resolveClassMethod(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls)
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
ASSERT(cls->isMetaClass());
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, @selector(resolveClassMethod:), cls))
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
Class nonmeta;
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
nonmeta = getMaybeUnrealizedNonMetaClass(cls, inst);
// +initialize path should have realized nonmeta already
if (!nonmeta->isRealized())
_objc_fatal("nonmeta class %s (%p) unexpectedly not realized",
nonmeta->nameForLogging(), nonmeta);
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(nonmeta, @selector(resolveClassMethod:), sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveClassMethod adds to self->ISA() a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls);
//---省略部分代码------
3. 动态方法决议运用及总结
// 代码中举例:
// 场景: person类中申明了有一个say777的实例方法, 但并没有写他的实现方法,父类里面也没有实现这个方法, 仅有一个 sayHello的申明和实现。 下面用resolveInstanceMethod来解决调用say777的时候,就转移调用sayHello,防止程序报错,当然这个只是为了验证底层探索到的这个方法是否有用,可以阻止程序崩溃。
// 1. 对象的方法动态决议走 resolveInstanceMethod 代码中的应用。
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel
if (sel == @selector(say777))
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self , @selector(sayHello));
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(self , @selector(sayHello));
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
return class_addMethod(self , sel , imp, type);
return false ;
- (void) sayHello
printf("--消息转发-%s----", __func__);
// 类方法的动态决议解决方法。
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
if (sel == @selector(say666))
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson") , @selector(sayHello));
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson") , @selector(sayHello));
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
return class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson"), sel , imp, type);
return NO;
//对上面的消息转发,可以写一个分类,统一进行处理。
// 概念扩展:
// oop 什么人做什么事,面向对象编程
// 确定是会产生冗余代码, 提取后,就有个公共类,但就会造成强依赖 -- 强耦合。
// aop 切面编程, 对原有的类与对象进入侵入代码,
// 优点:无侵入 -》 动态注入代码 -》 切入的方法 -》 切入的类。
// 缺点: 性能消耗 , 苹果的转发流程就没有意义。
// 使用场景: 消息转发流程 = 快速 + 慢速。
以上是关于iOS开发底层之方法的慢速查找流程探索+方法动态决议上 - 10的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章