梦开始的地方 —— C语言内存函数memcpy-memmove-memset(使用+模拟实现)
Posted 爱敲代码的三毛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了梦开始的地方 —— C语言内存函数memcpy-memmove-memset(使用+模拟实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
内存函数
1.memcpy
memcpy是C语言提供的复制内存块的函数,和字符拷贝函数strcpy有点像,但是strcpy只适用于字符,而memcpy适用整形、浮点型等于各种类型的数据拷贝。它有三个参数:
- destination:拷贝的目的地
- source:要拷贝的源字符串
- num:要拷贝的字节个数
void * memcpy ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );
注意
- C语言标准规定,memcpy适用于两块不同内存空间的拷贝
- 当
destination和source有重叠的时候,结果是不可预计的, - 这个函数在遇到
\\0的时候并不会停下来 - 该函数需要头文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
int arr[20] = 1,2,3,4,5 ;
int array[] = 6,7,8,9,10;
memcpy(arr+5, array, 20);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
memcpy函数模拟实现
这里的实现是按照C语言标准规定,因为这里是从前想后拷贝,如果这里拷贝同一块空间的内容就会出现覆盖的情况。而有些编译使用memcpy函数对同一块空间内容进行拷贝,也不会出现覆盖的情况,但不能保证所有编译器都能不覆盖。
void* my_memcpy(void* destination, const void* source, size_t num)
assert(destination && source);
void* ret = destination;
while (num--)
*(char*)destination = *(char*)source;
++(char*)destination;
++(char*)source;
return ret;
2.memmove
memmove也是内存块拷贝函数,他和memcpy的区别就是destination和source两个块空间可以重叠,不会出现覆盖情况
void * memmove ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
int arr[20] = 1,2,3,4,5 ;
memmove(arr+2,arr,20);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\\n");
return 0;
memmove函数模拟实现
- C语言标准规定,该函数可以对对同一块内存空间进行操操作
- 那么就需要考虑到两种情况,重叠和不重叠情况
如果拷贝的空间不重叠,从后向前或者是从前想后都没啥问题的
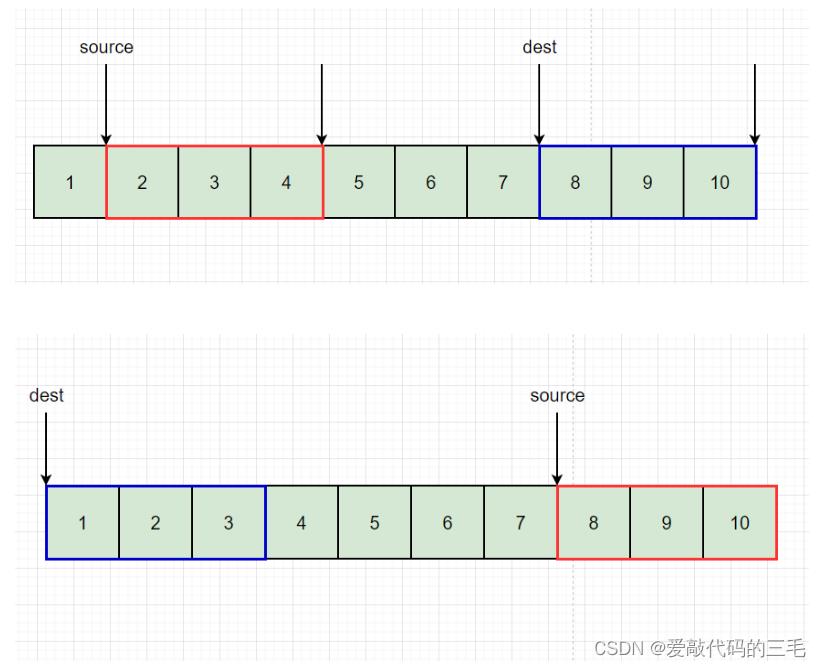
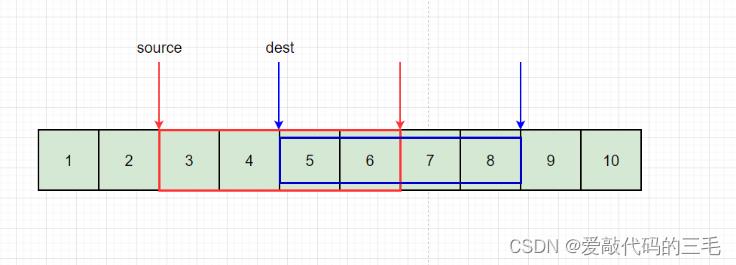
如果内存空间有重叠就得重后向前拷贝,如果从前向后拷贝有些数据就会被覆盖。
比如这里先把6拷到8的位置,再把5拷到7的位置。就不会被覆盖,如果从前往后拷贝,那么5和6就会被直击覆盖
模拟实现代码
#include <assert.h>
void* my_memmove(void* destination, const void* source, size_t num)
assert(destination && source);
void* ret = destination;
//不冲突情况
if (((char*)source) + num < destination || ((char*)destination) + num < source)
//从前往后拷贝
while (num--)
*((char*)destination) = *((char*)destination);
++((char*)destination);
++((char*)source);
else
//如果有冲突,从后往前拷贝
while (num--)
*(((char*)destination) + num) = *(((char*)source) + num);
return ret;
3. memset
memset是C语言提供的内存块填充函数,它有三个参数
- ptr:填充的起始地址
- value:要填充的元素
- num:填充多少个字节
void * memset ( void * ptr, int value, size_t num );
简单示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
char str[20] = "hello world!";
printf("%s\\n", str);
memset(str, '#', 5);
printf("%s\\n", str);
return 0;
输出
hello world!
##### world!
如果我们填充整形?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
int arr[20] = 1,2,3,4,5,6 ;
memset(arr, 1, 4);
printf("%d\\n", arr[0]);
return 0;
输出结果
16843009
这里填充1,每个字节都填充了1
arr数组名是首元素地址,在内存中arr[0]占四个字节,我们这里是VS2019的X86环境,是小端存储
内存中存储的是16进制,那么就是 01 00 00 00,没两个16进制位表示一个字节
所以填充完后,就是 01 01 01 01 ,转换为10进制就是 16843009
memset函数模拟实现
#include <assert.h>
void* my_memset(void* ptr, int value, size_t num)
assert(ptr != NULL);
void* ret = ptr;
while (num--)
*((char*)ptr) = value;
++((char*)ptr);
return ret;
以上是关于梦开始的地方 —— C语言内存函数memcpy-memmove-memset(使用+模拟实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章