vueJs源码解读0-2
Posted Rank-Bill
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了vueJs源码解读0-2相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上篇文章已经对index.js中的基本调用情况做了说明,接下来的几篇将对各个函数做仔细的分析,能力有限,文章中不足之处,希望大家能够指正!
上篇中提到在instance/vue中使用了9个高阶函数来构建(install)Vue构造函数(并不会调用该构造函数的进行初始化的过程),一切等在使用new Vue(….)的时候将一个全新的对象作为函数内this的值,返回该新对象作为结果(函数 调用中构造函数调用的方法)
function Vue (options)
this._init(options)
创建函数中函数申明的创建的方法(涉及知识函数声明的提升),this为函数方法调用的接收者,一般为构造函数调用的方式 new Vue()
initMixin(Vue)Mixin-mix in( 混入加入) 可能是作者取这个名字的原因吧(只是妄加猜测,具体已作者本人意图为准)
import initMixin from ‘./internal/init’ 会在internal/init中就会存在default的export接下来的分析将会从这个开始着手
逐行代码的分析如
let uid = 0设置了uid只在当前的块中有效,let具体可以在预热解读中有说明
export default function (Vue)
.....
export default 匿名函数具体用法可以在预热解读中找到,接下来的也即是function中的内容,接收参数为Vue
Vue.prototype._init = function (options)
.....
Vue也即是传入进来的参数(函数名),函数会自带一个默认的prototype的属性在新建立之前几乎为空,当使用new创建Vue的实例的时候,会得到自动分配的原型对象,存在User的prototype例如我们使用 var vm=new Vue()来初始化构造方法的时候(先查找自身的属性再去原型链中进行查找)
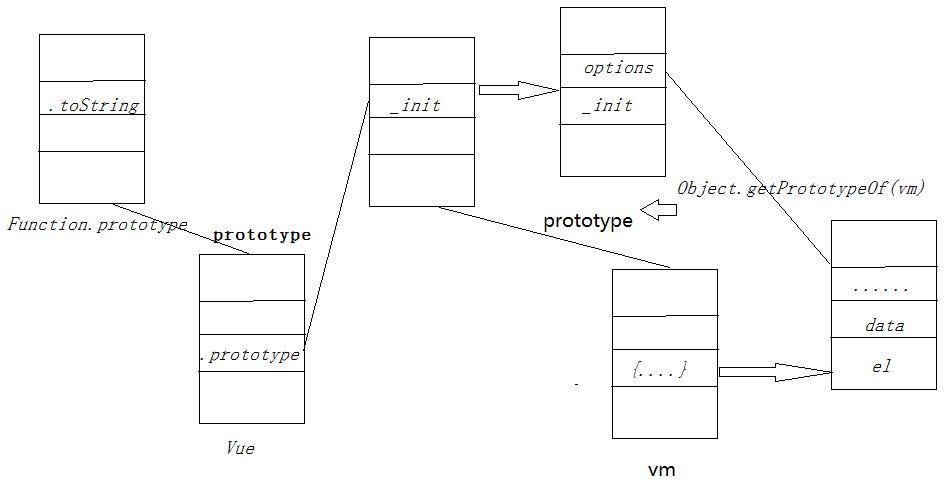
对于javascript的继承机制基于原型链(ES5),javaScript的实例对象由构造函数与在实例件共享的原型对象组成,对于原型用的较多的1个创建的方法(m.prototype)与2个获取原型的方法(obj.getPrototypeOf(m)和obj. _ proto _).其中
options = options ||
判断options是否为null,0,-0,undefined,false,”,NaN等情况(以上也即是js的7大假值),当options不为假则直接执行赋值,否则为。(涉及赋值运算符优先级,||运算时当左边为假才会执行右边;左右options的不一样);
this.$el = null
this.$parent = options.parent
this.$root = this.$parent? this.$parent.$root : this
this.$children = []
this.$refs = // child vm references
this.$els = // element references
this._watchers = [] // all watchers as an array
this._directives = [] // all directivesthis实例化之后也即是Vue对象,未指定调用接收者为undefined;先来了解下基本的含义,在后面涉及到会仔细介绍:
$parent存在的话则为父实例; $root:当前组件树的根 Vue 实例。如果当前实例没有父实例为自身。$children 当前实例的直接子组件。
$refs:一个对象,包含注册有 v-ref 的子组件。\\$els对象中包含注册有 v-el 的 DOM 元素。
// a uid
this._uid = uid++ //上文中定义的let uid
// a flag to avoid this being observed 设置标志避免被检测到
this._isVue = true
// events bookkeeping 事件统计
this._events = // registered callbacks
this._eventsCount = // for $broadcast optimization //$broadcast的优化
// fragment instance properties fragment实例属性
this._isFragment = false
this._fragment = // @type DocumentFragment
this._fragmentStart = // @type Text|Comment
this._fragmentEnd = null // @type Text|Comment
// lifecycle state 生命周期状态
this._isCompiled =
this._isDestroyed =
this._isReady =
this._isAttached =
this._isBeingDestroyed =
this._vForRemoving = false
this._unlinkFn = null各个实例到底什么意思,相信也很困惑,这里只要稍微有印象即可在之后的分析与学习中会逐步解释
// context:
// if this is a transcluded component, context
// will be the common parent vm of this instance
// and its host.
如果这是一个嵌入式的组件,上下文将是这个实例共有父实例(或宿主)
this._context = options._context || this.$parent
// scope:
// if this is inside an inline v-for, the scope
// will be the intermediate scope created for this
// repeat fragment. this is used for linking props
// and container directives.
如果这是在一个内联的v-for,将由这个循环的片段产生中间的作用域范围,被用在链接父组件的数据和指令容器
this._scope = options._scope
// fragment:
// if this instance is compiled inside a Fragment, it
// needs to reigster itself as a child of that fragment
// for attach/detach to work properly.
如果这个实例在某个片段里已经编译,需要在该片段上进行注册,利于attach或detach的正常工作
this._frag = options._frag
if (this._frag)
this._frag.children.push(this)
// push self into parent / transclusion host
如果存在父实例则将其建立双方的链接
if (this.$parent)
this.$parent.$children.push(this)
// merge options.
合并options,含有一个mergeOptions的函数
options = this.$options = mergeOptions(
this.constructor.options,
options,
this
)import mergeOptions from ‘../../util/index’
export * from './lang'
export * from './env'
export * from './dom'
export * from './options' //options
export * from './component'
export * from './debug'
export defineReactive from '../observer/index'export * 也即是将所有的标记过的均导出
在options.js中可以看到
/**
* Merge two option objects into a new one.
* Core utility used in both instantiation and inheritance.
* 主要用于在实例化与继承
* @param Object parent
* @param Object child
* @param Vue [vm] - if vm is present, indicates this is
* an instantiation merge.
*
options = this.$options = mergeOptions(
this.constructor.options,
options,
this
)
*/
export function mergeOptions (parent, child, vm)
下面均是该函数内的代码片段
guardComponents(child)
guardProps(child) function guardComponents (options)
...
对于guardComponents主要用作options中的组件构造,下文的代码为guardComponents中的代码
var vm = new Vue(
el: '...',
data:,
components:
'a':,
'b':
) if (options.components)
......
如果在options中存在components的存在,则会进行下部分的代码
var components = options.components =
guardArrayAssets(options.components)赋值语句从右至左,使用guardArrayAssets函数将数组形式的转化为键值对的形式
guardArrayAssets:
function guardArrayAssets (assets)
//assets 也即是传递过来的options.components
//1.components:'s':,'d':
//2.componets:['name':'...','id':'...']
//3.?
if (isArray(assets))
var res =
var i = assets.length
var asset
//数组循环取值组成键值对的形式 key值由id决定
while (i--)
asset = assets[i]
var id = typeof asset === 'function'
? ((asset.options && asset.options.name) || asset.id)
: (asset.name || asset.id)
//id异常情况
if (!id)
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'Array-syntax assets must provide a "name" or "id" field.'
)
else
//规整为key-value的形式
res[id] = asset
return res
return assets
可以看出有3种方式填写的option.components,主要目的是规整为字典的形式便于后面的直接调用
下面回到guardComponents
var components = options.components =
guardArrayAssets(options.components)
var ids = Object.keys(components)这里用到了一个Object.keys方法,获取规整后的components的键值数组
The Object.keys() method returns an array of a given object’s own enumerable properties, in the same order as that provided by a for…in loop (the difference being that a for-in loop enumerates properties in the prototype chain as well).
返回一个枚举所有对象属性的数组,类似于for-in 枚举(并不保证按对象的顺序输各个属性 ,不可预测的顺序unpredicted order)
接下来飘逸与自然的for循环如下:
for (var i = 0, l = ids.length; i < l; i++)
var key = ids[i]
if (commonTagRE.test(key) || reservedTagRE.test(key))
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'Do not use built-in or reserved html elements as component ' +
'id: ' + key
)
continue
// record a all lowercase <-> kebab-case mapping for
// possible custom element case error warning
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production')
map[key.replace(/-/g, '').toLowerCase()] = hyphenate(key)
def = components[key]
if (isPlainObject(def))
components[key] = Vue.extend(def)
其中commonTagRE与reservedTagRE为options.js中导入的两个属性
import commonTagRE, reservedTagRE from './component'
export const commonTagRE = /^(div|p|span|img|a|b|i|br|ul|ol|li|h1|h2|h3|h4|h5|h6|code|pre|table|th|td|tr|form|label|input|select|option|nav|article|section|header|footer)$/i
export const reservedTagRE = /^(slot|partial|component)$/iconst为es6中的关键字,表示不可以修改常量只在当前模块中有效,想要在其他模块中引用也即是利用前面提到的export命令,不会提升,必须先申明后使用
变量的提升:某一作用域范围内
console.info(v) ==> var v
var v=’tev’ console.info(v)
v=’tev’
正则表达式中:
/i (忽略大小写)
/g (全文查找出现的所有匹配字符)
/m (多行查找)
/gi(全文查找、忽略大小写)
/ig(全文查找、忽略大小写)
键值中
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'Do not use built-in or reserved HTML elements as component ' +
'id: ' + key
)不要使用保留的slot,partial,component与Html的标签作为键值
def = components[key]
if (isPlainObject(def))
components[key] = Vue.extend(def)
使用vue.extend定义组件,如下例子将更好解释
components:
'my-component':
template:'<div>A custom component!</div>'
,html页面中使用<\\my-component><\\/\\my-component>等同于
components:[
// 'id':'my-component',
'name':'my-component',
'template':'<div>A custom component!</div>'
],等同于:
var MyComponent = Vue.extend(
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
)
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)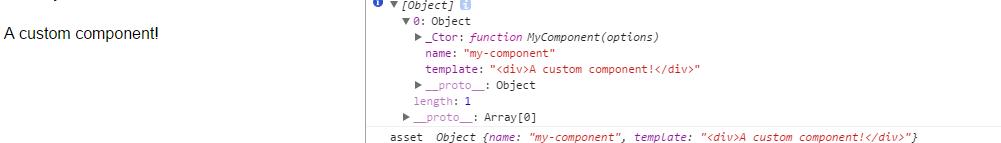
上面的代码中,这里涉及到两个isplainObject与Vue.extend,x下面将对其进分析
if (isPlainObject(def))
components[key] = Vue.extend(def)
import
isArray,
isPlainObject,
from './lang'/**
* Strict object type check. Only returns true
* for plain JavaScript objects.
*
* @param * obj
* @return Boolean
*/
//使用toString()方法判断类型,可以表面toString对null的判断方法,如下图所示
var toString = Object.prototype.toString
var OBJECT_STRING = '[object Object]'
export function isPlainObject (obj)
return toString.call(obj) === OBJECT_STRING
/**
* Array type check.
*
* @param * obj
* @return Boolean
*/
//也即是调用Array方法中的isArray方法
export const isArray = Array.isArray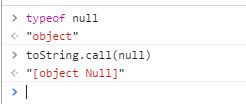
Vue.extend在global-api.js中在接下来的中会分析
感觉跑偏了很远这样流水式的分析要知道自己要回到哪个地方
mergeOptions
export function mergeOptions (parent, child, vm)
//在Options之前将options:components与props定义好
guardComponents(child)
guardProps(child)
....
Vue.prototype._init
Vue.prototype._init = function (options)
...
options = this.$options = mergeOptions(
this.constructor.options,
options,
this
)
props的定义
A list/hash of attributes that are exposed to accept data from the parent component(从父组件中获得数据). It has a simple Array-based syntax (数组形式)and an alternative Object-based(对象形式) syntax that allows advanced configurations such as type checking, custom validation and default values(对象形式用于高级的设置如 类型检查,自定义验证,默认值等).
guardProps(child)将所有的props规格化为基于对象的格式(虽然支持数组与对象的两种形式),child也即是为init中传入的options
props: ['size', 'myMessage']
props: ['name':'size','name':'myMessage'],
props:
// 只检测类型
size: Number,
// 检测类型 + 其它验证
name:
type: String,
required: true,
// 双向绑定
twoWay: true
function guardProps (options)
var props = options.props
var i, val
if (isArray(props)) //为数组类型
options.props =
i = props.length
while (i--)
val = props[i]
if (typeof val === 'string')
//为String类型的时候将其值设置为空 'size':null
options.props[val] = null
else if (val.name)
//取val.name
options.props[val.name] = val
else if (isPlainObject(props))
var keys = Object.keys(props)
i = keys.length
while (i--)
val = props[keys[i]]
if (typeof val === 'function') // 初始为Object类型
props[keys[i]] = type: val
以上是关于vueJs源码解读0-2的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章