lombok -- 爱的人爱的疯狂 恨的人恨的切齿
Posted 光光-Leo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了lombok -- 爱的人爱的疯狂 恨的人恨的切齿相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
lombok简介
lombok是一个java库,致力于通过一组注解消除代码中的一些必要但是臃肿的样板代码,精简代码,提高效率,还有耍酷。
如何使用
使用lombok需要在IDE中引入对应的插件,并在项目中引入对应的pom依赖
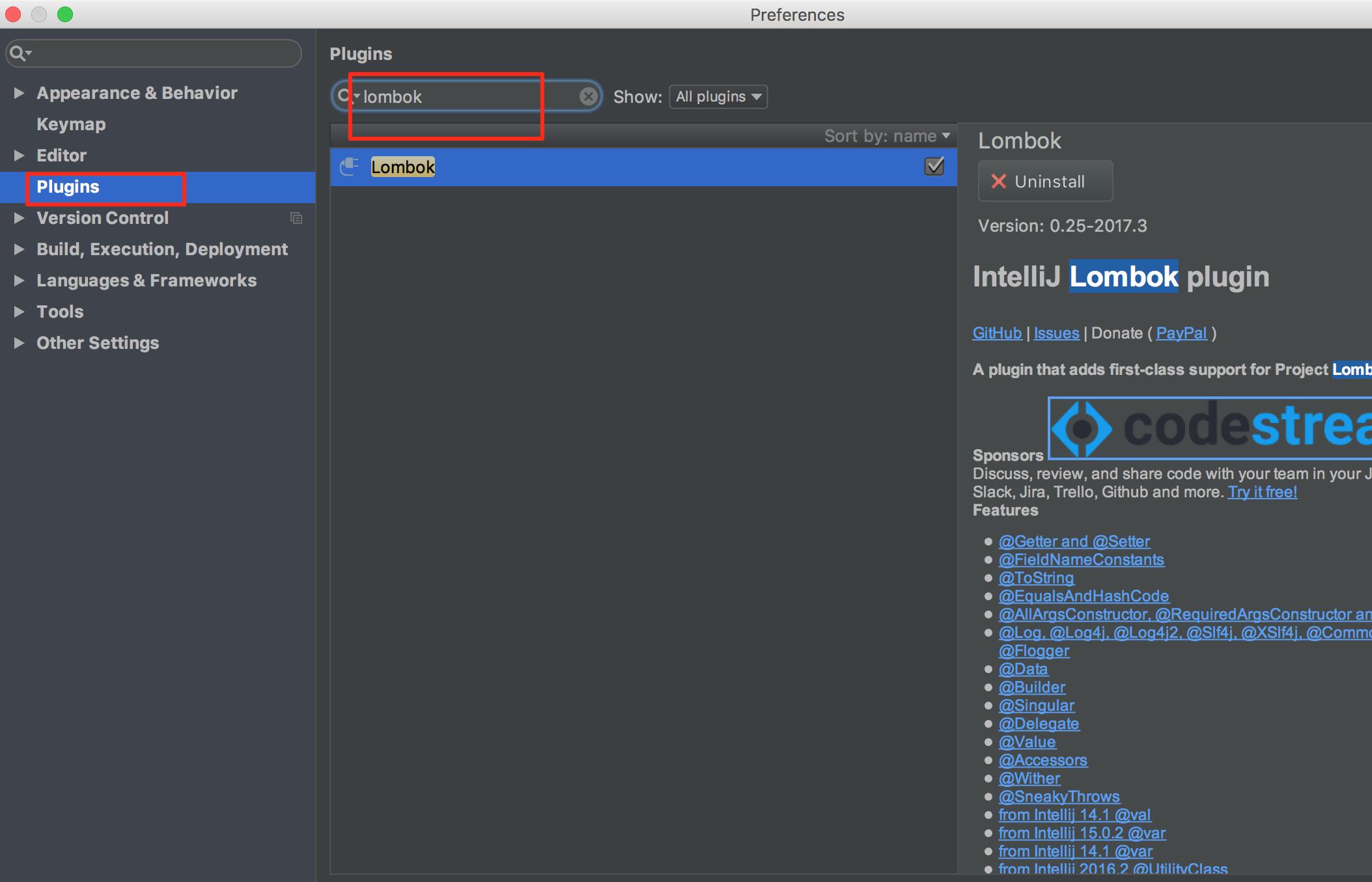
安装插件
在IDEA的插件中搜索lombok然后安装
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
注解
lombok提供了一系列的注解来帮助我们简化代码,下面我们分别对其中一些高频的注解怎么使用进行介绍
@Getter / @Setter
@Getter和@Setter注解可以作用在类上,也可以作用在字段上。
使用前我们的写法如下:
//code1
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
public Long getPersonId()
return personId;
public void setPersonId(Long personId)
this.personId = personId;
public String getMisNum()
return misNum;
public void setMisNum(String misNum)
this.misNum = misNum;
public String getFullName()
return fullName;
public void setFullName(String fullName)
this.fullName = fullName;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
使用后我们的写法如下:
//code2
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
查看编译后的class文件,在编译后会自动生成对应的get和set方法
//code2.class
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
public Person()
public Long getPersonId()
return this.personId;
public String getMisNum()
return this.misNum;
public String getFullName()
return this.fullName;
public String getName()
return this.name;
public void setPersonId(Long personId)
this.personId = personId;
public void setMisNum(String misNum)
this.misNum = misNum;
public void setFullName(String fullName)
this.fullName = fullName;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
@ToString
使用前我们的写法如下:
//code3
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString()
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
sb.append("\\"personId\\":")
.append(personId);
sb.append(",\\"misNum\\":\\"")
.append(misNum).append('\\"');
sb.append(",\\"fullName\\":\\"")
.append(fullName).append('\\"');
sb.append(",\\"name\\":\\"")
.append(name).append('\\"');
sb.append('');
return sb.toString();
使用后我们的写法如下:
//code4
import lombok.ToString;
@ToString
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
编译后的class文件如下,会自动生成toString()方法,但是比较遗憾的是不够灵活,没有办法直接生成Json格式的toString() 方法
//code4.class
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
public Person()
public String toString()
return "Person(personId=" + this.personId + ", misNum=" + this.misNum + ", fullName=" + this.fullName + ", name=" + this.name + ")";
@ToString还提供了一些参数
callSuper = true 可以打印父类,指定exclude可以排除字段,不过都比较鸡肋。
@Data
使用@Data写法如下:
//code5
@Data
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
编译后的class文件如下:
//code5.class
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
public Person()
public Long getPersonId()
return this.personId;
public String getMisNum()
return this.misNum;
public String getFullName()
return this.fullName;
public String getName()
return this.name;
public void setPersonId(Long personId)
this.personId = personId;
public void setMisNum(String misNum)
this.misNum = misNum;
public void setFullName(String fullName)
this.fullName = fullName;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public boolean equals(Object o)
if (o == this)
return true;
else if (!(o instanceof Person))
return false;
else
Person other = (Person)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this))
return false;
else
label59:
Object this$personId = this.getPersonId();
Object other$personId = other.getPersonId();
if (this$personId == null)
if (other$personId == null)
break label59;
else if (this$personId.equals(other$personId))
break label59;
return false;
Object this$misNum = this.getMisNum();
Object other$misNum = other.getMisNum();
if (this$misNum == null)
if (other$misNum != null)
return false;
else if (!this$misNum.equals(other$misNum))
return false;
Object this$fullName = this.getFullName();
Object other$fullName = other.getFullName();
if (this$fullName == null)
if (other$fullName != null)
return false;
else if (!this$fullName.equals(other$fullName))
return false;
Object this$name = this.getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null)
if (other$name != null)
return false;
else if (!this$name.equals(other$name))
return false;
return true;
protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
return other instanceof Person;
public int hashCode()
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $personId = this.getPersonId();
int result = result * 59 + ($personId == null ? 43 : $personId.hashCode());
Object $misNum = this.getMisNum();
result = result * 59 + ($misNum == null ? 43 : $misNum.hashCode());
Object $fullName = this.getFullName();
result = result * 59 + ($fullName == null ? 43 : $fullName.hashCode());
Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
return result;
public String toString()
return "Person(personId=" + this.getPersonId() + ", misNum=" + this.getMisNum() + ", fullName=" + this.getFullName() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ")";
@Data注解自动生成了getter/setter方法、toString()方法、覆写了hashCode()和equals()方法.
@Slf4j
使用@Slf4j注解可以省去实例化log对象的代码
使用方式如下:
//code6
@Slf4j
public class Person
编译后的class文件如下:
//code6.class
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Person
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Person.class);
public Person()
@Builder
@Builder作用在类上可以将类转换为建造者模式
//code7
import lombok.Builder;
@Builder
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
编译后的class文件如下
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
Person(Long personId, String misNum, String fullName, String name)
this.personId = personId;
this.misNum = misNum;
this.fullName = fullName;
this.name = name;
public static PersonBuilder builder()
return new PersonBuilder();
实例化对象时可以按照下面的方式写:
public class PersonTest
public static void main(String[] args)
Person person = Person.builder().personId(1L).misNum("zhangsan").build();
也可以指定默认值:
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Singular;
import lombok.ToString;
@Builder
@ToString
public class Person
private Long personId;
private String misNum;
private String fullName;
private String name;
@Builder.Default
private int tenant = 1;
其他的一些方法比较鸡肋 就不一一列出了
原理
lombok的基本流程是:
定义编译期的注解
利用JSR269 api(Pluggable Annotation Processing API )创建编译期的注解处理器
利用tools.jar的javac api处理AST(抽象语法树)
将功能注册进jar包
因为是在编译期生效的 所以其实直接从代码上来看,代码可能都是错误的,所以需要安装对应的IDE 插件对这些错误进行排除
想要了解lombok的原理,肯定是手撸代码来的快
前边提到lombok提供的toString方法不是json格式的,不如我们先来写一个json格式的toString方法 姑且叫做ToJsonString
@ToJsonString
先定义注解类:
package lombok;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//作用到类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
//只在编译期起作用
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface ToJsonString
然后定义对应的处理器:
package lombok;
import com.sun.source.tree.Tree;
import com.sun.tools.javac.api.JavacTrees;
import com.sun.tools.javac.code.Flags;
import com.sun.tools.javac.code.TypeTag;
import com.sun.tools.javac.processing.JavacProcessingEnvironment;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.JCTree;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.TreeMaker;
import com.sun.tools.javac.tree.TreeTranslator;
import com.sun.tools.javac.util.*;
import javax.annotation.processing.*;
import javax.lang.model.SourceVersion;
import javax.lang.model.element.Element;
import javax.lang.model.element.TypeElement;
import javax.tools.Diagnostic;
import java.util.Set;
@SupportedAnnotationTypes("lombok.ToJsonString")
@SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.RELEASE_8)
public class ToJsonStringProcessor extends AbstractProcessor
//主要是用来在编译期打log用的
private Messager messager;
//提供了待处理的抽象语法树
private JavacTrees trees;
//封装了创建AST节点的一些方法
private TreeMaker treeMaker;
//提供了创建标识符的方法
private Names names;
/**
* 从环境里获取一些关键信息
* @param processingEnv
*/
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv)
super.init(processingEnv);
this.messager = processingEnv.getMessager();
this.trees = JavacTrees.instance(processingEnv);
Context context = ((JavacProcessingEnvironment) processingEnv).getContext();
this.treeMaker = TreeMaker.instance(context);
this.names = Names.instance(context);
@Override
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv)
//获取被ToJsonString标记的类
Set<? extends Element> set = roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(ToJsonString.class);
//遍历 生成语法树
set.forEach(element ->
JCTree jcTree = trees以上是关于lombok -- 爱的人爱的疯狂 恨的人恨的切齿的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章