InnoDB存储引擎存储结构详解-实战篇
Posted 5ycode
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了InnoDB存储引擎存储结构详解-实战篇相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
之前学习mysql的时候,了解了到了页,段的概念,页的结构是什么,都简单的了解下了,毕竟都是纸面看到的,也没有深入源码了解。总觉的悬在上面,直接通过数据库文件反编译也比较麻烦。媳妇介绍了一个工具innodb_ruby, 说它可以扒mysql数据的结构。这几天扒拉了下,蛮好用的,好多知识也和之前的对上了。
我的mysql的配置文件如下(本地开发单机环境,没做什么优化,也没开启binlog):
[root@localhost data]# cat /etc/my.cnf
[client]
#客户端默认连接字集集,若编译安装时已指定则不用填写
#character-set-server = utf8
#客户端连接通信端口
port = 3306
#客户端通信的用户密码端口等信息保存文件
#socket = /data/mysql/tmp/mysql.sock
default-character-set=utf8
# The MySQL server
[mysqld]
# join_buffer_size = 128M
# sort_buffer_size = 2M
# read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
#配置mysql的内存大小,一般数据库服务器的80%
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2g
##mysql服务端监听端口
port = 3306
# 指定服务器id
server_id = 22
#mysql数据库存放目录
datadir = /data/mysql/data/
#socket = /data/mysql/tmp/mysql.sock
#服务端pid进程文件,若丢失则重启Mysql重新生成,若重启失败,
#则可能由于mysqld进程未杀死,用pkill mysql后则能重启成功Mysql
pid-file =/data/mysql/mysqld.pid
#指定错误日志目录
log-error=/data/mysql/logs/
#slow log
#slow-query-log=1
#slow_query_log_file= "slow.log"
#long_query_time=10
#binlog设置
#log_bin=mysql-bin
#binlog-format=MIXED
#独立表空间设置
innodb-file-per-table=1
explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=true
lower_case_table_names=1
sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
performance_schema_max_table_instances=400
table_definition_cache=400
table_open_cache=256
max_allowed_packet = 32M
# 设置默认引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
#设置默认字符
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
#设置最大链接数
max_connections=500
[root@localhost data]# ll
总用量 188488
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 56 4月 28 23:34 auto.cnf
-rw-------. 1 mysql mysql 1672 4月 28 23:34 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 mysql mysql 1112 4月 28 23:34 ca.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 mysql mysql 1112 4月 28 23:34 client-cert.pem
-rw-------. 1 mysql mysql 1676 4月 28 23:34 client-key.pem
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 1140 7月 24 15:27 ib_buffer_pool
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 79691776 7月 24 17:00 ibdata1
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 50331648 7月 24 17:00 ib_logfile0
-rw-r-----. 1 mysql mysql 50331648 7月 24 17:00 ib_logfile1
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 12582912 7月 24 22:12 ibtmp1
drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 114 7月 23 11:18 innodb_space
drwxr-x---. 2 mysql mysql 4096 4月 28 23:34 mysql
drwxr-x---. 2 mysql mysql 8192 4月 28 23:34 performance_schema
drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 4096 6月 22 22:26 portal
-rw-------. 1 mysql mysql 1676 4月 28 23:34 private_key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 mysql mysql 452 4月 28 23:34 public_key.pem
-rw-r--r--. 1 mysql mysql 1112 4月 28 23:34 server-cert.pem
-rw-------. 1 mysql mysql 1680 4月 28 23:34 server-key.pem
安装
可以参考:https://github.com/jeremycole/innodb_ruby
mac安装
使用ruby,安装innodb_ruby
sudo gem install innodb_ruby
# 安装成功以后
yxkdeMacBook-Pro bin % where innodb_space
/usr/local/bin/innodb_space
centos 7 安装
centos上默认ruby是2.0无法安装的,所以要先升级ruby
#卸载操作系统原有的ruby
sudo yum remove ruby
#下载ruby
wget https://cache.ruby-lang.org/pub/ruby/2.5/ruby-2.5.0.tar.gz
#解压
tar -zxvf ruby-2.5.0.tar.gz
#进入目录
cd ruby-2.5.0
#创建安装目录
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/ruby
#配置并指定安装位置
sudo ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/ruby
#编译与安装
sudo make && sudo make install
#建立软链接
sudo ln -s /usr/local/ruby/bin/ruby /usr/local/bin/ruby
#查看ruby版本
ruby -v
#安装 innodb_ruby
gem install innodb_ruby
使用innodb_space --help 获取到命令的帮助信息
例子:
#使用ibdata1作为系统表空间,从系统表空间中加载表名或索引的元数据,自动生成描述索引的元数据字典
innodb_space -s ibdata1 [-T table-name [-I index-name [-R record-offset]]] [options] <mode>
#使用 *.ibd来读取表空间结构或索引结构
innodb_space -f file-name.ibd [-r ./describer.rb -d DescriberClass] [options] <mode>
使用指定表名的ibd文件 读取表空间结构或索引
支持以下参数:
--help, -? 打印命令的帮助信息
--trace, -t
Enable tracing of all data read. Specify twice to enable even more
tracing (including reads during opening of the tablespace) which can
be quite noisy.
--system-space-file, -s <arg>
Load the system tablespace file or files <arg>: Either a single file e.g.
'ibdata1', a comma-delimited list of files e.g. 'ibdata1,ibdata1', or a
directory name. If a directory name is provided, it will be scanned for all
files named 'ibdata?' which will then be sorted alphabetically and used to
load the system tablespace.
If using the --system-space-file option, the following options may also
be used:
--table-name, -T <name>
指定表名,简写-T.
--index-name, -I <name>
指定索引名称
--system-space-tables, -x
Allow opening tables from the system space to support system spaces with
tables created without innodb-file-per-table enabled.
--data-directory, -D <directory>
Open per-table tablespace files from <directory> rather than from the
directory where the system-space-file is located.
--space-file, -f <file>
指定表空间文件
--page, -p <page>
指定操作的page
--record, -R <offset>
Operate on the record located at <offset> within the index page.
--level, -l <level>
level=0 为数据层或回表层,level=1或2 索引层级
--list, -L <list>
Operate on the list <list>.
--fseg-id, -F <fseg_id>
指定段的编号
--require, -r <file>
Use Ruby's 'require' to load the file <file>. This is useful for loading
classes with record describers.
--describer, -d <describer>
Use the named record describer to parse records in index pages.
The following modes are supported:
system-spaces : 打印系统中所有表的概要信息.
data-dictionary-tables :打印所有的表
Print all records in the SYS_TABLES data dictionary table.
data-dictionary-columns : 打印所有的字段
Print all records in the SYS_COLUMNS data dictionary table.
data-dictionary-indexes
Print all records in the SYS_INDEXES data dictionary table.
data-dictionary-fields
Print all records in the SYS_FIELDS data dictionary table.
space-summary
统计表空间中的所有页面,可以使用--page/-p指定页码
space-index-pages-summary
统计表空间内的所有’INDEX‘类型的page,对分析page的填充率和每页的记录有用。
除了INDEX类型的页面,ALLOCATED类型的页面也会被打印出来
可以通过-p 指定开始的页号
space-index-fseg-pages-summary
与 space-index-pages-summary 相同,但是一次只能通过-F 指定一个段
space-index-pages-free-plot
Use Ruby's gnuplot module to produce a scatterplot of page free space for
all 'INDEX' and 'ALLOCATED' pages in a tablespace. More aesthetically
pleasing plots can be produced with space-index-pages-summary output,
but this is a quick and easy way to produce a passable plot. A starting
page number can be provided with the --page/-p argument.
space-page-type-regions
Summarize all contiguous regions of the same page type. This is useful to
provide an overall view of the space and allocations within it. A starting
page number can be provided with the --page/-p argument.
space-page-type-summary
按类型统计所有的page,可以通过-p 指定起始页
space-indexes
统计所有索引的申请、使用,以及填充率
space-lists
Print a summary of all lists in a space.
space-list-iterate
Iterate through the contents of a space list.
space-extents
Iterate through all extents, printing the extent descriptor bitmap.
space-extents-illustrate
Iterate through all extents, illustrating the extent usage using ANSI
color and Unicode box drawing characters to show page usage throughout
the space.
space-lsn-age-illustrate
Iterate through all pages, producing a heat map colored by the page LSN
using ANSI color and Unicode box drawing characters, allowing the user to
get an overview of page modification recency.
space-inodes-fseg-id
Iterate through all inodes, printing only the FSEG ID.
space-inodes-summary
Iterate through all inodes, printing a short summary of each FSEG.
space-inodes-detail
遍历所有的inodes节点,打印每个段的详细报告
index-level-summary
Print a summary of all pages at a given level (provided with the --level/-l
argument) in an index.
index-fseg-internal-lists
index-fseg-leaf-lists
Print a summary of all lists in an index file segment. Index root page must
be provided with --page/-p.
page-dump
dump 页面元数据
page-account
Account for a page's usage in FSEGs.
page-validate
Validate the contents of a page.
page-directory-summary
Summarize the record contents of the page directory in a page. If a record
describer is available, the key of each record will be printed.
page-records
Summarize all records within a page.
page-illustrate
Produce an illustration of the contents of a page.
Innodb表空间辅助工具使用
前期准备- 表以及数据构建
CREATE DATABASE innodb_space;
use innodb_space;
# 用户表一
drop TABLE if exists `t_user_info`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user_info` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户id',
`nick_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户昵称',
`mobile` varchar(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '用户手机号',
`pwd` varchar(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '加密后的登录密码',
`salt` varchar(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '密码盐值',
`status` char(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '用户状态,1启用,0禁用',
`tenant_id` smallint(4) DEFAULT '1001' COMMENT '租户id',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `unq_user` (`mobile`,`tenant_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='用户表';
# 用户表二(和表已唯一的区别是id` bigint(11) )
drop TABLE if exists `t_user_info1`;
CREATE TABLE `t_user_info1` (
`id` bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户id',
`nick_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户昵称',
`mobile` varchar(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '用户手机号',
`pwd` varchar(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '加密后的登录密码',
`salt` varchar(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '密码盐值',
`status` char(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '用户状态,1启用,0禁用',
`tenant_id` smallint(4) DEFAULT '1001' COMMENT '租户id',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `unq_user` (`mobile`,`tenant_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='用户表';
-- 格式化手机号
drop function if exists `format_mobile`;
CREATE FUNCTION `format_mobile`(m varchar(3),n int) RETURNS varchar(11) CHARSET utf8
NO SQL
begin
return concat(m,LPAD(concat(n,''),9,'0')) ;
end
;
#随机状态
drop function if exists `rand_status`;
CREATE FUNCTION `rand_status`() RETURNS varchar(1) CHARSET utf8
NO SQL
begin
return floor(rand() *100)%2;
end
;
# 生成随机字符串函数,最大32位
drop function if exists `rand_string`;
create function `rand_string`(n int) returns varchar(32) charset utf8 no sql
begin
declare rand_str varchar(32) default "";
declare i int default 0;
while i < n do
set rand_str=substring(replace(uuid(), '-', ''), 1, n);
set i= i+1;
end while;
return rand_str;
end
;
#生成测试数据的存储过程,动态表名需要预处理语句,为了快速插入,就直接改表名
drop procedure if exists `insert_data`;
create procedure `insert_data`(in n int) deterministic
begin
declare i int default 1;
declare start_create_time datetime default now();
-- 自己根据要灌的数据算下,1秒一条记录 一年365*24*3600=31 536 000 一年约3000万
declare sec int default -365*3*24*3600;
set autocommit = 0;
while (i <= n) do
-- 每条记录+1秒
set sec=sec+1;
insert into t_user_info
(`nick_name`,`mobile`,`pwd`,`salt`,`status`,`create_time`,`update_time`)
values
(rand_string(30),format_mobile('13',i),rand_string(32),rand_string(5),rand_status() ,date_add(start_create_time,interval sec second),date_add(start_create_time,interval sec second)) ;
if i%500=0 then
-- 500条提交一次
commit;
end if;
set i=i+1 ;
end while ;
-- 提交剩余的
commit ;
set autocommit = 1;
end
;
CALL insert_data(50000000);
-- 修改下表名为t_user_info1
CALL insert_data(100000000);
/* 动态表名的模板
drop procedure if exists selectByTableName;
create procedure selectByTableName(in tableName varchar(50))
begin
#定义语句
set @stmt = concat('select * from ',tableName);
#预定义sql语句,从用户变量中获取
prepare stmt from @stmt;
#执行sql语句
execute stmt;
#释放资源,后续还可以使用
deallocate prepare stmt;
end;
*/
我两张表分别灌了5000w的数据,磁盘各占用7.7gb
[root@localhost innodb_space]# ll -h
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 61 7月 16 17:38 db.opt
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 8.8K 7月 23 11:18 t_user_info1.frm
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 7.7G 7月 24 17:00 t_user_info1.ibd
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 8.8K 7月 16 18:42 t_user_info.frm
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 7.7G 7月 16 22:22 t_user_info.ibd
概念说明
段、区、页
InnoDB 为了管理好页,提出了表空间(Tablespace)的概念。
- 表空间是一个逻辑结构,它可以对应文件系统上一个或多个真实文件
- 表空间可以看成是InnoDB存储引擎逻辑结构的最高层,所有的数据都存放在表空间中;
- 表空间由段(segment)、区(extent)、页(page)组成
- 表空间分为系统表空间和独立表空间
- 系统表空间是InnoDB默认提供的一个表空间,也可以理解为共享表空间,在mysql数据目录下,名称是ibdata1
- 存储表的最顶层索引(可以理解为起点指针),undo log、事务相关的信息、双写缓冲(double write buffer)
- 对应的1和2区是双写缓冲区
- 会随着mysql的运行一直不停的增大
- 如果没有开启独立表空间,所有表的数据、索引,插入缓冲也放在这里
- 表删除以后占用空间降不下来
- 存储表的最顶层索引(可以理解为起点指针),undo log、事务相关的信息、双写缓冲(double write buffer)
- 独立表空间,在my.cnf中开启了
innodb_file_per_table=1,mysql会为每张表创建一个独立表空间(表名.ibd)- 存储表的数据、索引和插入缓冲
- 表删除后占用空间直接删除
- 在mysql5.6.6及以后的版本中,InnoDB默认会使用独立表空间
- 其他表空间
- 通用表空间
- undo表空间
- 临时表空间
- 系统表空间是InnoDB默认提供的一个表空间,也可以理解为共享表空间,在mysql数据目录下,名称是ibdata1
段 (segment) 包含256区
-
段(segment)是逻辑概念
-
段中不要求区与区之间是相邻的
-
分为索引段、数据段、回滚段等
- 当我们创建数据表、索引的时候,就会相应的创建对应的段
- 回滚段主要用于数据回滚和多版本控制。
区(extent)包含64 页
- 区是页的集合,一个区包含64个连续的页,一个区默认大小为1MB
- 区能保证上面的64个页在物理上是连续的(有利于IO)
- InnoDB每次从磁盘一次申请4~5个区
- 申请的64个页在使用的时候会确定类型,可能存储多张表的数据
- 在区中有这些:
- **FSP_HDR类型:**这个类型的页面是用来登记整个表空间的一些整体属性以及本组所有的区,也就是extent 0 ~ extent 255这256个区的属性。需要注意的一点是,
整个 表空间只有一个FSP_HDR类型的页面 - **IBUF_BITMAP类型:**这个类型的页面是存储本组所有的区的所有页面关于INSERT BUFFER的信息
- **INODE类型:**这个类型的页面存储了许多称为INODE的数据结构
- **XDES类型:**全称是extent descriptor,用来登记本组256个区的属性,也就是说对于在extent 256区中的该类型页面存储的就是extent 256 ~ extent 511这些区的属性
- **FSP_HDR类型:**这个类型的页面是用来登记整个表空间的一些整体属性以及本组所有的区,也就是extent 0 ~ extent 255这256个区的属性。需要注意的一点是,
页(page)默认16kb
- 页是InnoDB管理的最小单位
- 页包含(文件头:38字节,文件尾8字节,其他填充数据)
- 每个页面分配一个32位整数页码,通常称为偏移量(offset),只是页面与空间开头的偏移量
- InnoDB的数据限制为64TB,是有页码的限制
看下独立表空间的结构
[root@localhost data]# ll innodb_space/ -h
总用量 16G
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 61 7月 16 17:38 db.opt
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 8.8K 7月 23 11:18 t_user_info1.frm
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 7.7G 7月 24 17:00 t_user_info1.ibd
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 8.8K 7月 16 18:42 t_user_info.frm
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 7.7G 7月 16 22:22 t_user_info.ibd
表的基础信息
-- 查询表所属的表空间id
SELECT * FROM information_schema.innodb_sys_tablespaces WHERE name LIKE '%user_info';

从结果上,可以看出来, 行格式为dynamic,一页的大小为16kb,表空间类型为single,文件大小
该表的表空间id是53,
-- 查询表的表id
SELECT * FROM information_schema.innodb_sys_tables WHERE name LIKE '%user_info';

该表的table_id为57
-- 查看表的索引id
SELECT * FROM information_schema.innodb_sys_indexes WHERE table_id=57
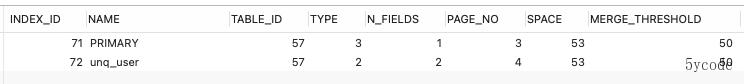
对应的索引id为71,72
以上信息我们先记着,后面会用到
开始使用
进度mysql的data目录,看自己mysql的配置文件,数据存储在哪里。
[root@localhost data]# ls
auto.cnf client-cert.pem ibdata1 ibtmp1 performance_schema public_key.pem sys
ca-key.pem client-key.pem ib_logfile0 innodb_space portal server-cert.pem xportal
ca.pem ib_buffer_pool ib_logfile1 mysql private_key.pem server-key.pem
概要信息
我们先看下我们这两张表的概要信息
[root@localhost data]# innodb_space -s ibdata1 system-spaces |grep t_user_info
name pages indexes (grep 以后这行会丢失)
innodb_space/t_user_info 502528 2
innodb_space/t_user_info1 502528 2
列出了表占用的页数,以及索引个数,相对比较简单
表的索引信息
我们先看下对应表的索引信息
innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info space-indexes
输出:
[root@localhost data]# innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info space-indexes
id name root fseg fseg_id used allocated fill_factor
71 PRIMARY 3 internal 1 465 480 96.88%
71 PRIMARY 3 leaf 2 406505 406560 99.99%
72 unq_user 4 internal 3 177 224 79.02%
72 unq_user 4 leaf 4 87720 87776 99.94%
[root@localhost data]# innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info1 space-indexes
id name root fseg fseg_id used allocated fill_factor
73 PRIMARY 3 internal 1 465 480 96.88%
73 PRIMARY 3 leaf 2 406505 406560 99.99%
74 unq_user 4 internal 3 177 224 79.02%
74 unq_user 4 leaf 4 87720 87776 99.94%
解释:
- id:索引ID列
- name 索引名称 PRIMARY 表示聚簇索引
- root 索引根节点位于的数据页编号
- fseg 索引类型(internal为内部节点,我们一般称为非叶子节点,leaf为叶子节点)
-
索引存储在非叶子节点上
-
数据存储在叶子节点上
-
- fseg_id 索引所属段ID
- 虽然两张表t_user_info和t_user_info1的段都一样,但是表示的都是对应表的.ibd文件里的,分属于不同的表空间
- used 使用的page页数量
- 通过表一(t_user_info)和表二(t_user_info1)的的对比,bigint类型创建表的时候是固定大小,并不会取你创建表的()中的数值
- allocated 申请的数据页数量
- 一共申请了495040个数据页,使用了494867个数据页
- 从这里可以看出不是一个个的申请,是一次申请一批,预留一定的buffer,这里保证连贯性,从磁盘里读取的时候,不是只读对应的一页,而是相关的数据连着一片,这种方式对
- 我们算下
select (480+406560+224+87776)* 16*1024/(1024*1024*1024) = 7.5537 GB接近物理存储的空间,物理磁盘还会有些填充
- fill_factor used/allocated 使用百分比
统计每个类型占用连续空间的页的数量
统计的是t_user_info.ibd文件里的信息
[root@localhost data]# innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info space-page-type-regions
start end count type
0 0 1 FSP_HDR
1 1 1 IBUF_BITMAP
2 2 1 INODE
3 16383 16381 INDEX
16384 16384 1 XDES
16385 16385 1 IBUF_BITMAP
16386 16388 3 INDEX
16389 16447 59 FREE (ALLOCATED)
16448 32767 16320 INDEX
......
475200 491519 16320 INDEX
491520 491520 1 XDES
491521 491521 1 IBUF_BITMAP
491522 491583 62 FREE (ALLOCATED)
491584 496839 5256 INDEX
496840 496895 56 FREE (ALLOCATED)
496896 496904 9 INDEX
496905 497151 247 FREE (ALLOCATED)
解释:
- Start 表示起始页的页码
- end 表示同类型结束的页码
- count 为当前类型page的连续数量
统计表空间中各页类型占比
innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info space-page-type-summary
结果
[root@localhost data]# innodb_space -s ibdata1 -T innodb_space/t_user_info space-page-type-summary
type count percent description
INDEX 494867以上是关于InnoDB存储引擎存储结构详解-实战篇的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章