Spring-Cloud系列-Hystrix源码解析
Posted _微风轻起
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring-Cloud系列-Hystrix源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这一篇我们主要来看下Hystrix是怎样在OpenFiegn上做进一层封装的,主要梳理Hystrix封装逻辑。
一、执行的熔断判断
1、执行案例
我们配置了Hystrix的使用逻辑后
@RequestMapping(value = "simple",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String simpleMethod()
return feignConsumerClient.producerSimple();
@FeignClient(value = "producer-server",fallback = FeignConsumerClientImp.class)
public interface FeignConsumerClient
@RequestMapping(value = "producer/simple",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String producerSimple();
这里就不是像我们上篇介绍的opengeign那样,使用的ReflectiveFeign的代理执行,而是使用hystrix的代理执行HystrixInvocationHandler。
2、HystrixInvocationHandler
@Override
public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args)
throws Throwable
if ("equals".equals(method.getName()))
............
HystrixCommand<Object> hystrixCommand =
new HystrixCommand<Object>(setterMethodMap.get(method))
@Override
protected Object run() throws Exception
try
return HystrixInvocationHandler.this.dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
catch (Exception e)
throw e;
catch (Throwable t)
throw (Error) t;
@Override
protected Object getFallback()
if (fallbackFactory == null)
return super.getFallback();
try
Object fallback = fallbackFactory.create(getExecutionException());
Object result = fallbackMethodMap.get(method).invoke(fallback, args);
if (isReturnsHystrixCommand(method))
return ((HystrixCommand) result).execute();
else if (isReturnsObservable(method))
// Create a cold Observable
return ((Observable) result).toBlocking().first();
else if (isReturnsSingle(method))
// Create a cold Observable as a Single
return ((Single) result).toObservable().toBlocking().first();
else if (isReturnsCompletable(method))
((Completable) result).await();
return null;
else if (isReturnsCompletableFuture(method))
return ((Future) result).get();
else
return result;
........
;
if (Util.isDefault(method))
return hystrixCommand.execute();
else if (isReturnsHystrixCommand(method))
return hystrixCommand;
else if (isReturnsObservable(method))
// Create a cold Observable
return hystrixCommand.toObservable();
else if (isReturnsSingle(method))
// Create a cold Observable as a Single
return hystrixCommand.toObservable().toSingle();
else if (isReturnsCompletable(method))
return hystrixCommand.toObservable().toCompletable();
else if (isReturnsCompletableFuture(method))
return new ObservableCompletableFuture<>(hystrixCommand);
return hystrixCommand.execute();
这里hystrix的执行逻辑主要是封装在HystrixCommand中,并且hystrix与openfeign一样,同样是使用RxJava封装调用关系。十一我们可以看到其在hystrixCommand.execute()的执行返回中,会判断不同的你本身调用的不同类型。
if (Util.isDefault(method))
return hystrixCommand.execute();
else if (isReturnsHystrixCommand(method))
return hystrixCommand;
else if (isReturnsObservable(method))
..........
同时在HystrixCommand的run方法中return HystrixInvocationHandler.this.dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);就是对
openfeign逻辑的封装:
这里的SynchronousMethodHandler就是我们上篇梳理的feign的逻辑调用。
虽然这里表面是比较好理解,但内部是有很多通过Rxjava封装的逻辑。例如失败统计数、是否需要熔断请求等。这里的逻辑是在HystrixCommand的父类AbstractCommand中。
3、HystrixCommand
public Observable<R> toObservable()
final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd = this;
............
final Func0<Observable<R>> applyHystrixSemantics = new Func0<Observable<R>>()
@Override
public Observable<R> call()
if (commandState.get().equals(CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED))
return Observable.never();
return applyHystrixSemantics(_cmd);
;
..........
这里的主要执行方法就是applyHystrixSemantics(_cmd)
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd)
// mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook
// if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent
executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
/* determine if we're allowed to execute */
if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest())
final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore();
final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false);
..........
if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire())
try
/* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */
executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
catch (RuntimeException e)
return Observable.error(e);
else
return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();
else
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
通常我们刷面试体,例如hystrix的执行熔断判断,例如hystrix会有一个基础数量,然后在规定的单位中请求的数量要达到一定数量才会去触发熔断统计的逻辑,如果达到了就会根据成功、失败的请求触发熔断、已经之后的恢复逻辑。这里的逻辑描述判断主要是在circuitBreaker.allowRequest()中,我们可以看到,如果返回false的话,就表示不能访问、会直接执行handleShortCircuitViaFallback(),直接熔断回调。
1)、allowRequest()
@Override
public boolean allowRequest()
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get())
// properties have asked us to force the circuit open so we will allow NO requests
return false;
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get())
// we still want to allow isOpen() to perform it's calculations so we simulate normal behavior
isOpen();
// properties have asked us to ignore errors so we will ignore the results of isOpen and just allow all traffic through
return true;
return !isOpen() || allowSingleTest();
这里的properties是HystrixCommandProperties,这个是在配置文件中的关于熔断的一些判断数值配置
public abstract class HystrixCommandProperties
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HystrixCommandProperties.class);
/* defaults */
/* package */ static final Integer default_metricsRollingStatisticalWindow = 10000;// default => statisticalWindow: 10000 = 10 seconds (and default of 10 buckets so each bucket is 1 second)
private static final Integer default_metricsRollingStatisticalWindowBuckets = 10;// default => statisticalWindowBuckets: 10 = 10 buckets in a 10 second window so each bucket is 1 second
private static final Integer default_circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold = 20;// default => statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold: 20 requests in 10 seconds must occur before statistics matter
......
private static final ExecutionIsolationStrategy default_executionIsolationStrategy = ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD;
private static final Boolean default_executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout = true;
private static final Boolean default_executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnFutureCancel = false;
private static final Boolean default_metricsRollingPercentileEnabled = true;
allowRequest()首先是判断circuitBreakerForceOpen断路器是否强制打开,如果打开就直接返回false表示拒绝,在判断如果circuitBreakerForceClosed强制关闭,就直接返回true表示能通过。然后的话,就是通过isOpen()来执行具体的判断逻辑了。
2)、isOpen()
@Override
public boolean isOpen()
if (circuitOpen.get())
// if we're open we immediately return true and don't bother attempting to 'close' ourself as that is left to allowSingleTest and a subsequent successful test to close
return true;
// we're closed, so let's see if errors have made us so we should trip the circuit open
HealthCounts health = metrics.getHealthCounts();
// check if we are past the statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold
if (health.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get())
// we are not past the minimum volume threshold for the statisticalWindow so we'll return false immediately and not calculate anything
return false;
if (health.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get())
return false;
else
// our failure rate is too high, trip the circuit
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(false, true))
// if the previousValue was false then we want to set the currentTime
circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
else
// How could previousValue be true? If another thread was going through this code at the same time a race-condition could have
// caused another thread to set it to true already even though we were in the process of doing the same
// In this case, we know the circuit is open, so let the other thread set the currentTime and report back that the circuit is open
return true;
这个就是具体根据熔断的指标来判断是否需要熔断。这里还有metrics,这个类是用来放统计过程中的各个统计指标数据。
private final HystrixCommandMetrics metrics;
然后上面的判断,例如当health.getTotalRequests()也就是请求的总的数量要小于配置的请求数的话,是不会断路的,然后是计算的失败请求百分比与配置的比例阈值。如果比例没有到达,可能是目前已经熔断了,就再设置circuitOpen来重新打开熔断,看之后请求是否正常。
private AtomicBoolean circuitOpen = new AtomicBoolean(false);
二、请求策略处理
1、信号量请求限制判断
在我们判断这个请求是否需要熔断后,下面是请求的策略处理
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd)
// mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook
// if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent
executionHook.onStart(_cmd);
/* determine if we're allowed to execute */
if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest())
final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore();
........
if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire())
try
/* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */
executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
catch (RuntimeException e)
return Observable.error(e);
else
return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();
else
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
protected TryableSemaphore getExecutionSemaphore()
if (properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get() == ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE)
if (executionSemaphoreOverride == null)
TryableSemaphore _s = executionSemaphorePerCircuit.get(commandKey.name());
if (_s == null)
// we didn't find one cache so setup
executionSemaphorePerCircuit.putIfAbsent(commandKey.name(), new TryableSemaphoreActual(properties.executionIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests()));
// assign whatever got set (this or another thread)
return executionSemaphorePerCircuit.get(commandKey.name());
else
return _s;
else
return executionSemaphoreOverride;
else
// return NoOp implementation since we're not using SEMAPHORE isolation
return TryableSemaphoreNoOp.DEFAULT;
protected static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, TryableSemaphore> executionSemaphorePerCircuit = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, TryableSemaphore>();
这里就是先使用信号量判断,其是否已经达到请求的限制数,如果达到了就是handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback()方法来处理拒绝策略。
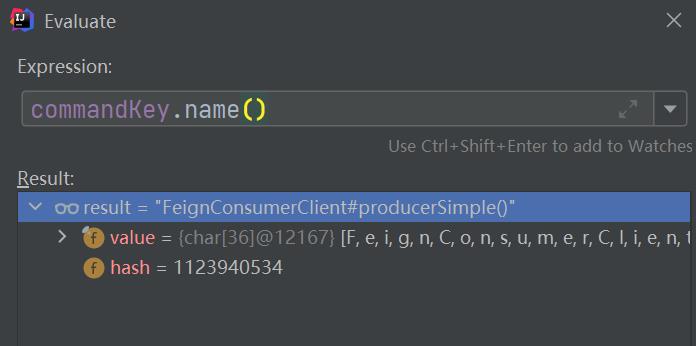
这个commandKey.name我们可以看到默认就是类名+方法名。获取信号量与获取线程池一样,都是解析了类级别的隔离。
如果我们的请求处理部署使用信号量而是使用线程的话,这里就会返回TryableSemaphoreNoOp.DEFAULT。
public static final TryableSemaphore DEFAULT = new TryableSemaphoreNoOp();
@Override
public boolean tryAcquire()
return true;
我们可以看到其是直接返回true。
2、请求策略选择执行
在通过上面的逻辑后,最终会在这里选择对应的执行策略处理
private Observable<R> executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd)
if (properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get() == ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD)
@Override
public Observable<R> call()
............
).subscribeOn(threadPool.getScheduler(new Func0<Boolean>()
@Override
public Boolean call()
return properties.executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout().get() && _cmd.isCommandTimedOut.get() ==<以上是关于Spring-Cloud系列-Hystrix源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章