Android Studio基础-Activity生命周期与多个Activity跳转
Posted 徐为波
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Studio基础-Activity生命周期与多个Activity跳转相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
知识点1:android Studio基础-Activity的生命周期
7个方法:
onCreate()、onStart()、onResume()、onRestart()、onPause()、onStop()、onDestroy()。
使用上一节项目的Activity代码编写(https://blog.csdn.net/xwbk12/article/details/115825559?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501),或者看知识点2的内容。
package com.xwb.recyclerview;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity
private RecyclerView mRecyclerView;
private HomeAdapter mHomeAdapter;
private String[] names = "小鸟","小龙","小虫","小鱼";
private int[] icons = R.mipmap.btn_login_n,R.mipmap.btn_login_p,R.mipmap.ic_captain_jack,R.mipmap.ic_drakan;
private String[] instrduces = "小鸟一个伟大的鸟人,可以放六个技能,大招全员减伤30%","不知道是哪个种族","虫族来自人族饲养,技能结合人族使用","在海洋中称霸各类水族种类";
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("生命周期第1个方法","onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mRecyclerView = findViewById(R.id.rec);//绑定item_recycler_view.xml布局中RecyclerView
//设置布局的方式
//mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this));//第一种写法直接写this,会造成不一定是需要的
mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(MainActivity.this));//第二种写法类名.this
mHomeAdapter = new HomeAdapter();
mRecyclerView.setAdapter(mHomeAdapter);//关联Adapter
@Override
protected void onStart()
super.onStart();
Log.i("生命周期第2个方法","onStart");
@Override
protected void onResume()
super.onResume();
Log.i("生命周期第3个方法","onResume执行后,表示Activity可以被用户看到,就是此时APP页面被用户看到了");
@Override
protected void onRestart()
super.onRestart();
Log.i("生命周期第4个方法","onRestart");
@Override
protected void onPause()
super.onPause();
Log.i("生命周期第5个方法","onPause Activity暂停,可能还会被使用,会有数据保留");
@Override
protected void onStop()
super.onStop();
Log.i("生命周期第6个方法","onStop Activity被停止,数据不会保留");
@Override
protected void onDestroy()
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("生命周期第7个方法","onDestroy Activity彻底不见了,只有销毁了,再打开时,就会重新调用noCreate()方法");
class HomeAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<HomeAdapter.MyViewHolder>
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType)
//创建holder
MyViewHolder holder = new MyViewHolder(LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.item_recycler_view,parent,false));
return holder;
@Override
//绑定数据到单元格的控件上
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, int position)
holder.tv_name.setText(names[position]);
holder.tv_introduce.setText(instrduces[position]);
holder.tv_icon.setImageResource(icons[position]);
@Override
public int getItemCount()
return names.length;//把names、icons、instrduces任意一个长度告知即可
class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder
TextView tv_name;
TextView tv_introduce;
ImageView tv_icon;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView)
super(itemView);
//绑定控件
tv_name = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
tv_introduce = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_introduce);
tv_icon = itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_icon);
运行后查看日志信息

在模拟器的手机上点击“返回”
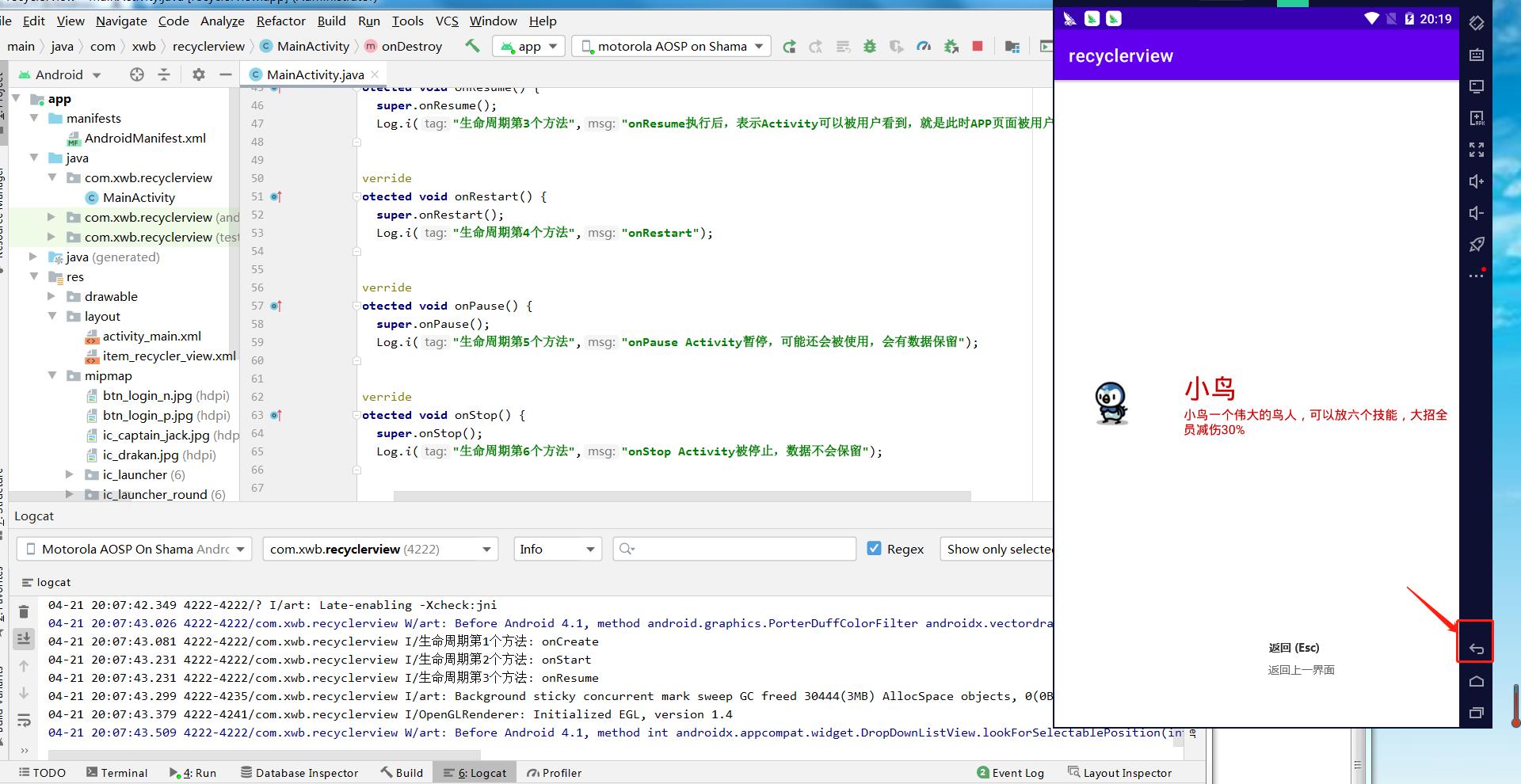
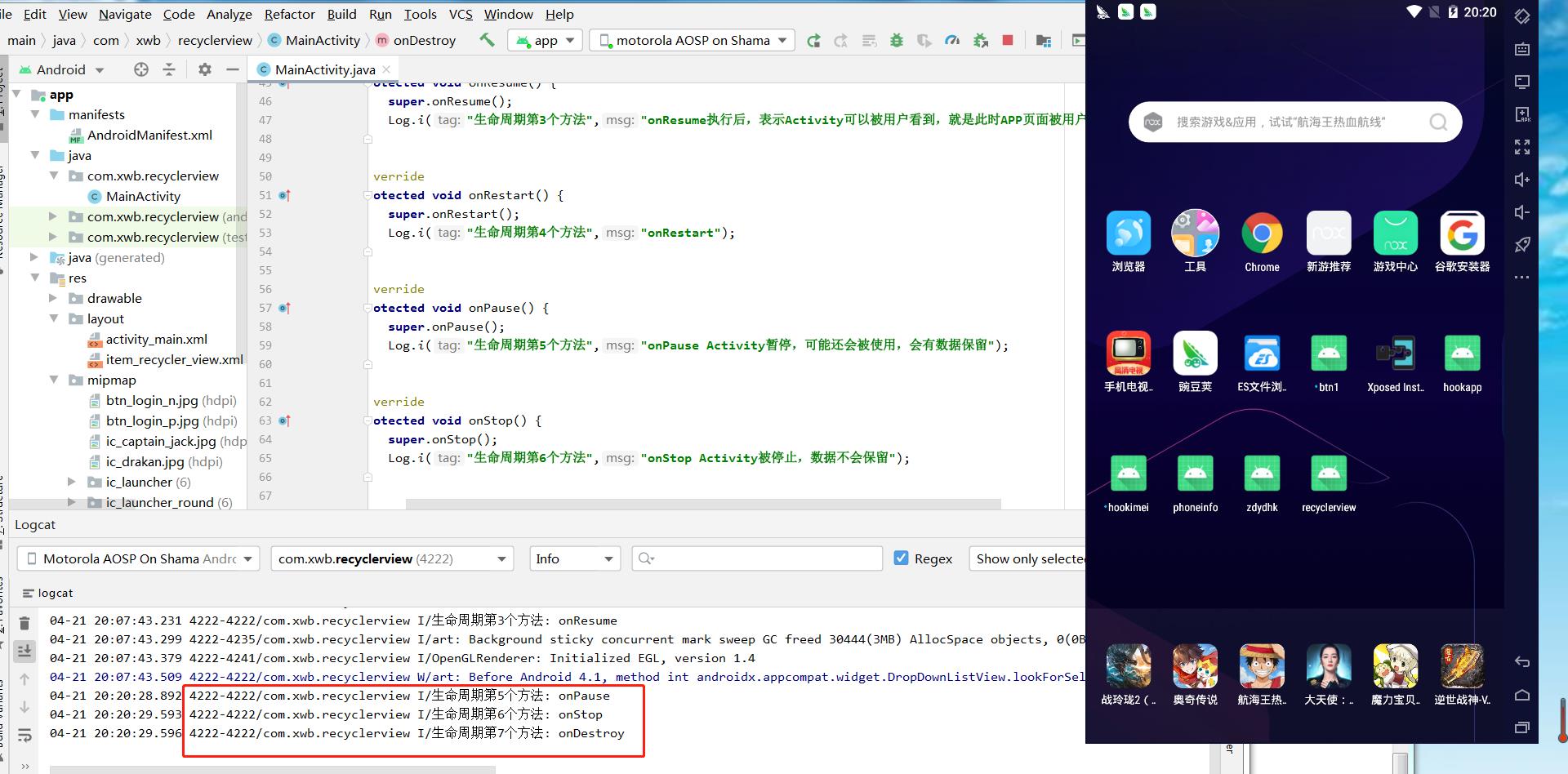
查看logcat日志信息
知识点2:多个Activity的跳转
作用:第一个布局xml中按钮点击后,跳转至第二个布局xml中。
第一步:第一个布局xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="跳转到另外一个Activity界面"
android:onClick="tiaozhuan"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第一个MainActivity
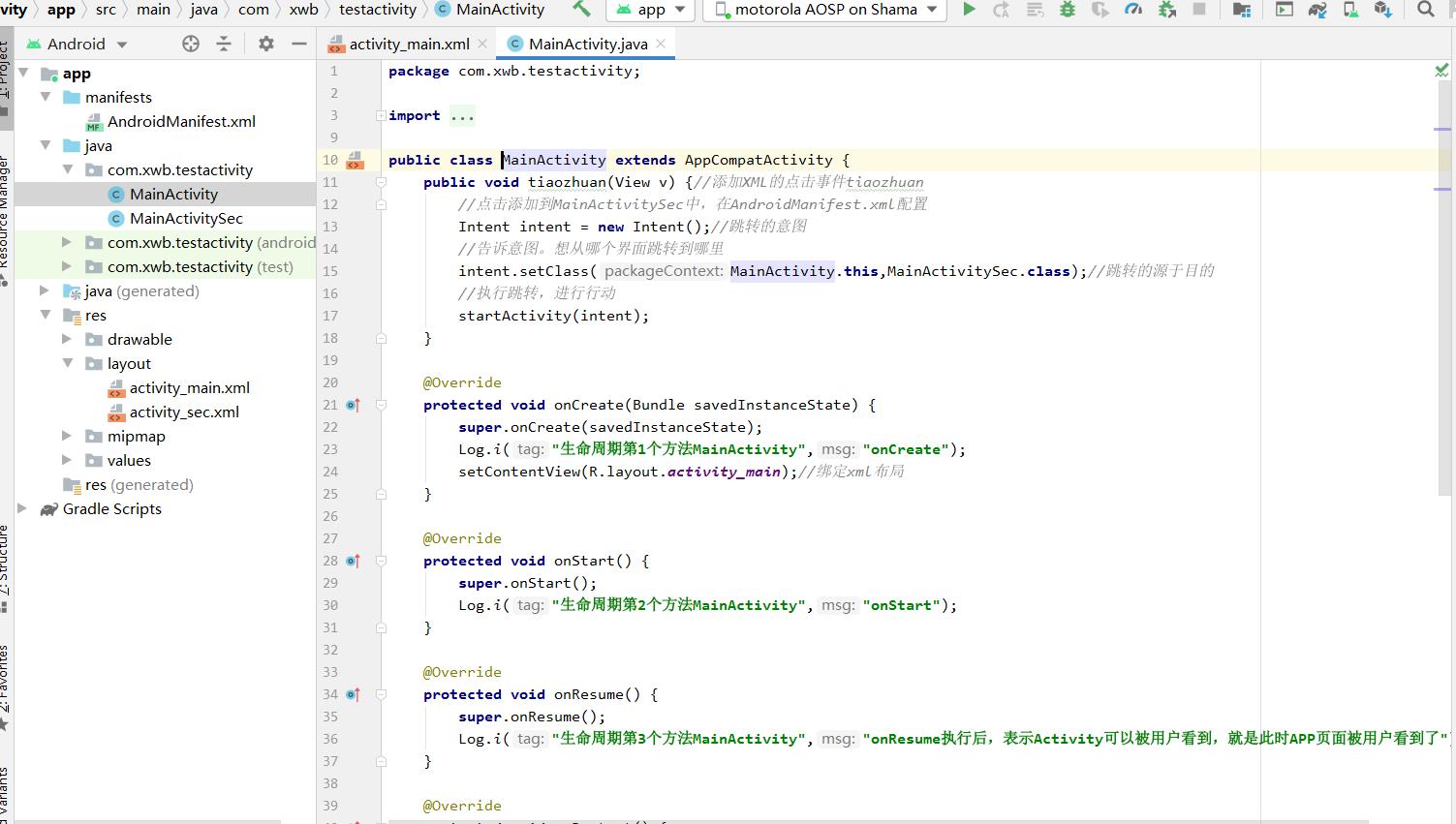
package com.xwb.testactivity;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity
public void tiaozhuan(View v) //添加XML的点击事件tiaozhuan
//点击添加到MainActivitySec中,在AndroidManifest.xml配置
Intent intent = new Intent();//跳转的意图
//告诉意图。想从哪个界面跳转到哪里
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,MainActivitySec.class);//跳转的源于目的
//执行跳转,进行行动
startActivity(intent);
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("生命周期第1个方法MainActivity","onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//绑定xml布局
@Override
protected void onStart()
super.onStart();
Log.i("生命周期第2个方法MainActivity","onStart");
@Override
protected void onResume()
super.onResume();
Log.i("生命周期第3个方法MainActivity","onResume执行后,表示Activity可以被用户看到,就是此时APP页面被用户看到了");
@Override
protected void onRestart()
super.onRestart();
Log.i("生命周期第4个方法MainActivity","onRestart");
@Override
protected void onPause()
super.onPause();
Log.i("生命周期第5个方法MainActivity","onPause Activity暂停,可能还会被使用,会有数据保留");
@Override
protected void onStop()
super.onStop();
Log.i("生命周期第6个方法MainActivity","onStop Activity被停止,数据不会保留");
@Override
protected void onDestroy()
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("生命周期第7个方法MainActivity","onDestroy Activity彻底不见了,只有销毁了,再打开时,就会重新调用noCreate()方法");
第二个布局XML

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这是第二个Actiity界面"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:background="@color/purple_200"/>
</LinearLayout>第二个MainActivitySec

package com.xwb.testactivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivitySec extends AppCompatActivity
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("生命周期第1个方法MainActivitySec","onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sec);//绑定xml布局
@Override
protected void onStart()
super.onStart();
Log.i("生命周期第2个方法MainActivitySec","onStart");
@Override
protected void onResume()
super.onResume();
Log.i("生命周期第3个方法MainActivitySec","onResume执行后,表示Activity可以被用户看到,就是此时APP页面被用户看到了");
@Override
protected void onRestart()
super.onRestart();
Log.i("生命周期第4个方法MainActivitySec","onRestart Activity没有被销毁,重新被启用");
@Override
protected void onPause()
super.onPause();
Log.i("生命周期第5个方法MainActivitySec","onPause Activity暂停,可能还会被使用,会有数据保留");
@Override
protected void onStop()
super.onStop();
Log.i("生命周期第6个方法MainActivitySec","onStop Activity被停止,数据不会保留");
@Override
protected void onDestroy()
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("生命周期第7个方法MainActivitySec","onDestroy Activity彻底不见了,只有销毁了,再打开时,就会重新调用noCreate()方法");
第二步:设置AndroidManifest.xml
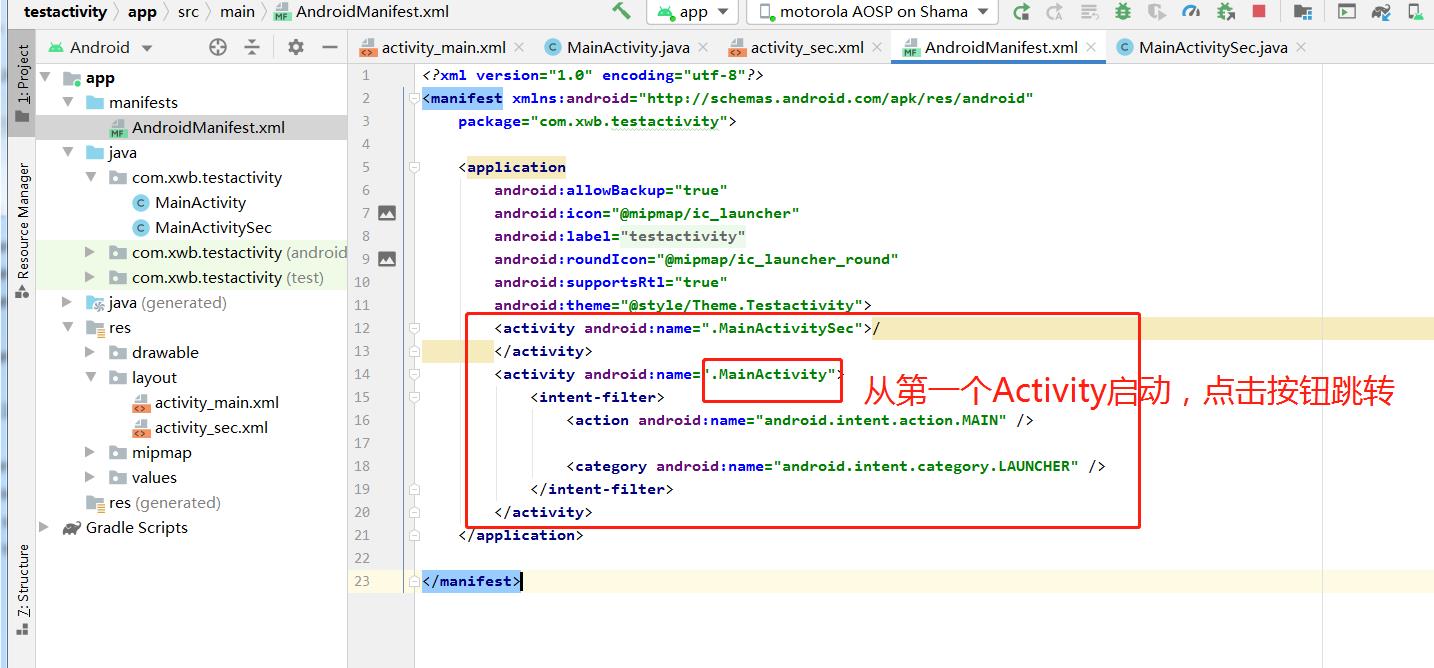
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.xwb.testactivity">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Testactivity">
<activity android:name=".MainActivitySec">/
</activity>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>第三步:运行APP
启动APP的日志

点击按钮跳转的日志
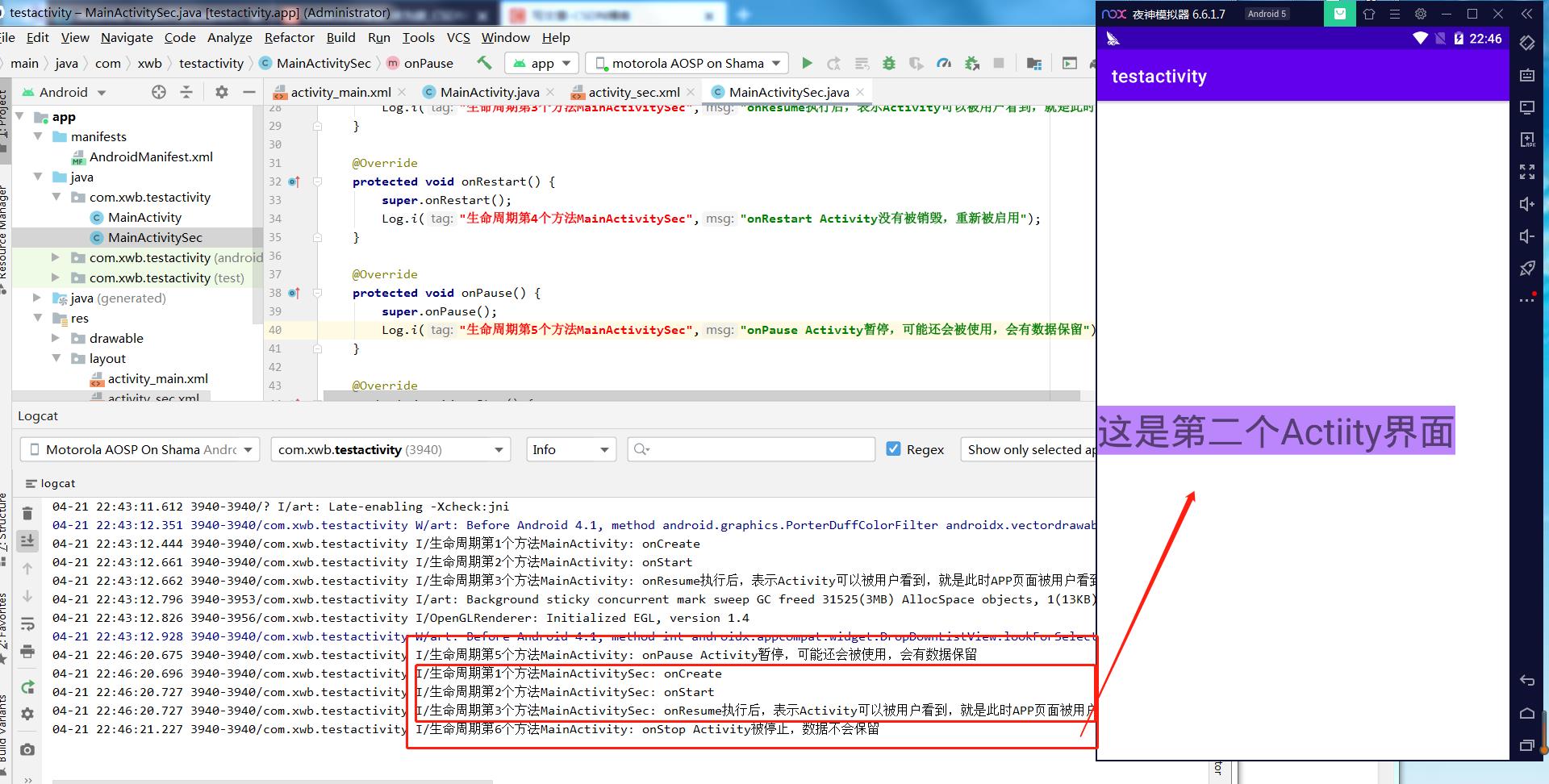
点击系统的返回键
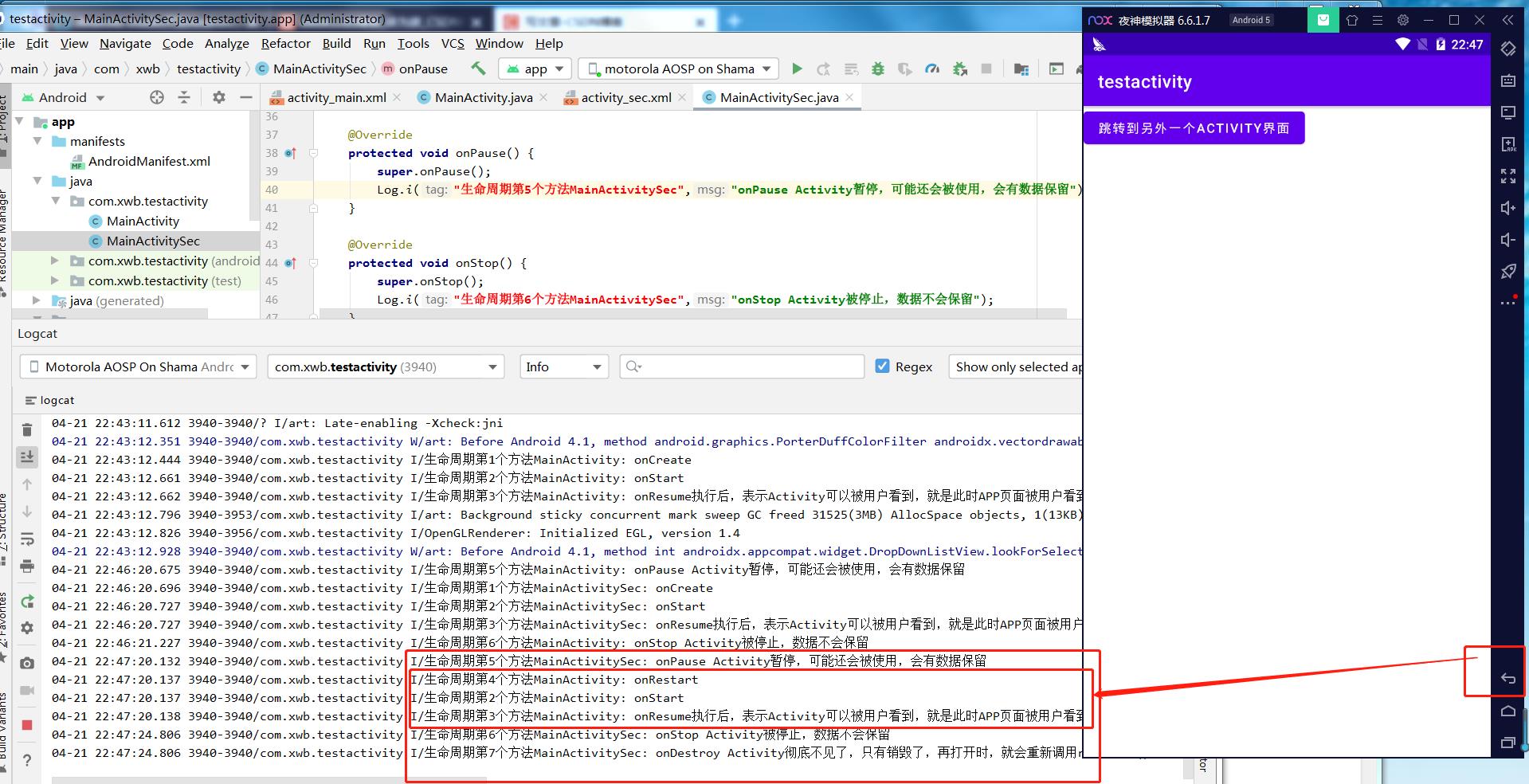
把改APP退到后台
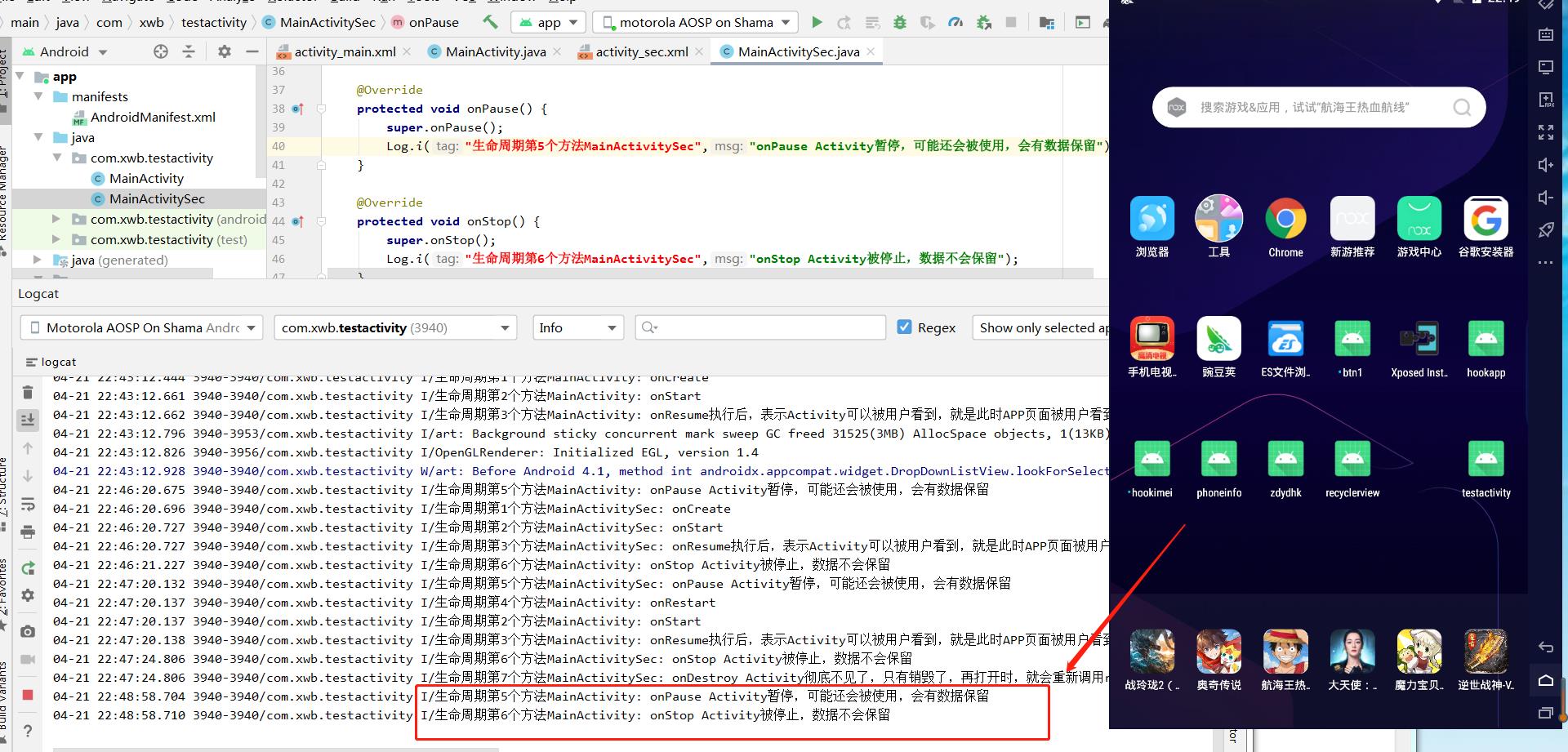
退出该APP

以上是关于Android Studio基础-Activity生命周期与多个Activity跳转的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent传值自定义类数据(如数据库数据读取)。
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent传值自定义类数据(如数据库数据读取)。
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent传值自定义类数据(如数据库数据读取)。
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent传值自定义类数据(如数据库数据读取)。
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent跳转与传值,并onActivityResult回传一个/多个值,与回传消息内容。
Android Studio基础项目-两个Activity的Intent跳转与传值,并onActivityResult回传一个/多个值,与回传消息内容。