Java课程案例学习
Posted 康小庄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java课程案例学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【案例3-1】基于控制台的购书系统
【案例介绍】
- 案例描述
伴随互联网的蓬勃发展,网络购书系统作为电子商务的一种形式,正以其高效、低成本的优势逐步成为新兴的经营模式,人们已经不再满足互联网的用途仅仅局限于信息的浏览和发布,更渴望着能够充分享受互联网所带来的更多便利。网络购书系统正适应了当今社会快节奏地生活,使顾客足不出户便可以方便快捷轻松地选购自己喜欢的图书。
本任务要求,使用所学知识编写一个基于控制台的购书系统,实现购书功能。输出所有图书的信息:包括每本书的编号、书名、单价、库存。
顾客购买书时,根据提示输入图书编号来选购需要的书,并根据提示输入购买书的的数量。
购买完毕后输出顾客的订单信息,包括:订单号、订单明细、订单总额。
【案例目标】
l 学会分析“基于控制台的购书系统”程序任务实现的逻辑思路。
l 能独立完成“基于控制台的购书系统”程序的源代码编写、编译及运行。
l 理解和掌握面向对象的设计程序。
l 会用类图进行面向对象设计。
l 掌握封装的实现及好处。
l 包和访问控制修饰符的使用。
【案例分析】
(1)通过任务描述可知,该系统中必须包括3个实体类,类名及属性设置如下:
-
图书类(Book):
a) 图书编号(id)
b) 图书名称(name)
c) 图书单价(price)
d) 库存数量(storage)
-
订单项类(OrderItem):
a) 图书(book)
b) 购买数量(num)
-
订单类(Order):
a) 订单号(orderID)
b) 订单总额(total)
c) 订单项列表(items)
(2)由于购买图书时,需要选择图书的数量,所以需要在订单项类里定义获取图书对象以及图书数量的方法。
(3)由于需要指定订单项以及获取订单的订单列表、订单号、订单总额等信息,所以需要有订单列表、订单号、订单总额指定订单项等方法。
【案例实现】
定义图书类Book,其代码如下所示。
Book.java
上述代码中,声明了图书标号id、书名name、价格price、库存storage,并提供了其getter和setter方法。
定义订单项类OrderItem,其代码如下所示。
OrderItem.java
上述代码中,声明了图书对象Book,购买数量num,并提供了其getter和setter方法。
定义订单类Order,其代码如下所示。
Order.java
上述代码中,声明了订单id、订单项数组,并声明了获取订单号方法getOrderId()、获取订单列表方法getItems()、获取订单总额方法getTotal()、指定一个订单项setItem()、计算订单总额的方法calTotal()。
PayBooks.java
上述代码中,输出了图书列表信息包括:图书编号、图书名称、图书单价、库存数量,用户根据图书列表信息,输入图书编号、购买数量等,系统根据用户输入的图书编号及购买数量计算总金额。
Book
public class Book
/**
* 图书编号
*/
private int id;
/**
* 图书名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 图书单价
*/
private double price;;
/**
* 库存数量
*/
private int storage;
public int getId()
return id;
public void setId(int id)
this.id = id;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public double getPrice()
return price;
public void setPrice(int price)
this.price = price;
public int getStorage()
return storage;
public void setStorage(int storage)
this.storage = storage;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + ", storage=" + storage + "]";
public Book(int id, String name, double price, int storage)
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.storage = storage;
public Book()
super();
Order
public class Order
private String orderID;
private OrderItem[] items;
private double total;
public Order(String orderID)
this.orderID = orderID;
this.items = new OrderItem[3];
public String getOid()
return orderID;
public void setOid(String orderID)
this.orderID = orderID;
public OrderItem[] getItems()
return items;
public void setItems(OrderItem item, int idx)
this.items[idx] = item;
public double getTotal()
calcTotal();
return total;
private void calcTotal()
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; ++i)
total += items[i].getNums() * items[i].getBook().getPrice();
this.total = total;
public void setTotal(double total)
this.total = total;
OrderItem
public class OrderItem
private Book book;
private int nums;
public OrderItem(Book book, int nums)
this.book = book;
this.nums = nums;
public Book getBook()
return book;
public int getNums()
return nums;
public void setBook(Book book)
this.book = book;
public void setNums(int nums)
this.nums = nums;
BookClient
public class BookClient
public static void main(String[] args)
Book[] books = new Book[3]; // 存储图书
outBookInfo(books);
// 购买图书
Order order = purchase(books);
// 打印订单
outOrderInfo(order);
/**
*
* @Title: outBookInfo
* @Description: 订购书的方法
* @author: KangXiaoZhuang
* @param: @param books
* @return: void
* @throws
*/
private static void outBookInfo(Book[] books)
books[0] = new Book(1, "Java基础案例编程", 16.9, 100);
books[1] = new Book(2, "Python数据分析", 26.9, 56);
books[2] = new Book(3, "Java编程思想", 69.9, 220);
System.out.println("-------------------\\t图书列表\\t--------------------");
System.out.println("编号\\tISBN\\t名称\\t价格\\t库存");
String line = null;
for (int i = 0; i < books.length; i++)
line = books[i].getId() + "\\t" + books[i].getName() + "\\t" + books[i].getPrice() + "\\t"
+ books[i].getStorage();
System.out.println(line);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------");
/**
*
* @Title: purchase
* @Description: 购买图书的方法
* @author: KangXiaoZhuang
* @param: @param books
* @param: @return
* @return: Order
* @throws
*/
private static Order purchase(Book[] books)
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
OrderItem item = null;
Order order = new Order("book-order-" + LocalTime.now().toString());
for (int i = 0; i < books.length; i++)
System.out.println("请选择需要购买的图书编号:");
int bno = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("购买数量:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
item = new OrderItem(books[bno - 1], num);
order.setItems(item, i);
System.out.println("请继续购买图书。");
sc.close();
return order;
/**
*
* @Title: outOrderInfo
* @Description: 处理订单信息
* @author: KangXiaoZhuang
* @param: @param order
* @return: void
* @throws
*/
private static void outOrderInfo(Order order)
System.out.println("-------------------\\t图书订单\\t--------------------");
System.out.println("订单编号:" + order.getOid());
System.out.println("\\t图书名称\\t\\t购买数量\\t图书单价");
OrderItem[] items = order.getItems();
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; ++i)
System.out.println(
items[i].getBook().getName() + "\\t" + items[i].getNums() + "\\t" + items[i].getBook().getPrice());
System.out.println("订单总额:¥" + order.getTotal());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------");
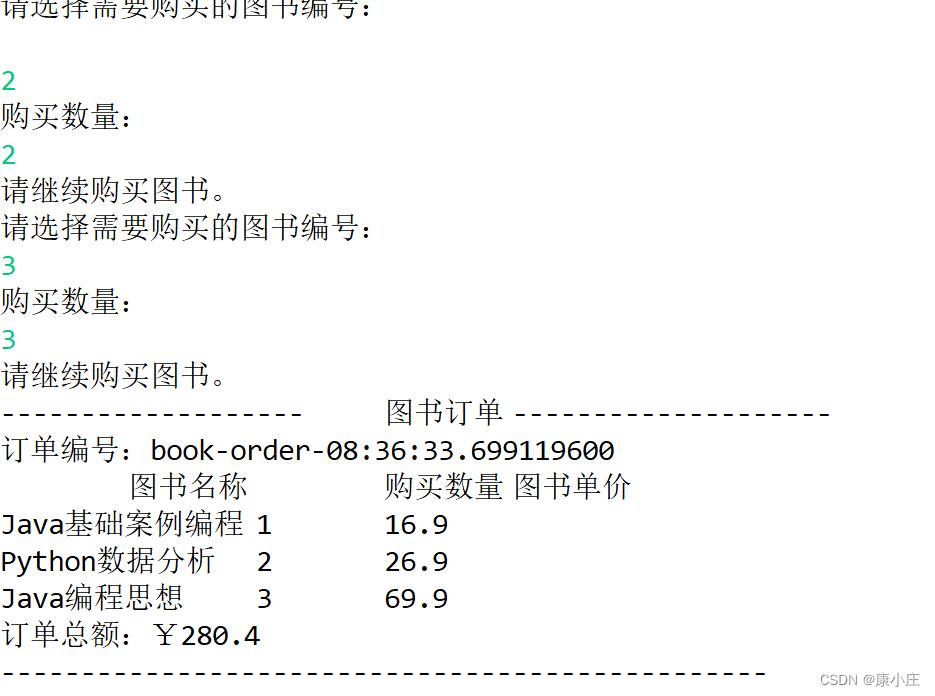
运行截图
【案例3-2】银行存取款程序设计
【案例介绍】
- 案例描述
银行存取款的流程是人们非常熟悉的事情,用户可在银行对自己的资金账户进行存款、取款、查询余额等操作,极大的便利了人民群众对资金的管理。
本任务要求,使用所学知识编写一个银行存取款程序,实现存取款功能。编写一个帐户类实现银行帐户的概念,创建帐户类的对象ba,假设ba的账号为:123456,初始的存款余额为500元。首先向该账户存入1000元,再取出800元。
【案例目标】
l 学会分析“银行存取款”程序任务实现的逻辑思路。
l 能够独立完成“银行存取款”程序的源代码编写、运行及编译。
l 理解Java语言是如何体现面向对象编程基本思想的。
l 掌握类的声明以及对象的创建。
l 了解类的成员变量和成员方法的特性以及类的构造方法的使用。
【案例分析】
(1)通过任务描述可知,需要定义一个银行帐户类BankAccount实现银行帐户的概念。
(2)账户的属性包括账号和存款余额,所以还需要在BankAccount类中定义两个变量:“帐号” (account_number) 和“存款余额”(leftmoney)。
(3)对账户的操作包括存款、取款、查询余额,所以再定义四个方法:“存款”(savemoney)、“取款”(getmoney) 、“查询余额”(getleftmoney)以及构造方法(BankAccount)。
(4)最后,编写测试类,在main()方法中创建一个BankAccount类的对象ba,假设ba的账号为:123456,初始的存款余额为500元。首先向该账户存入1000元,再取出2000元。
【案例实现】
BankAccount.Java
上述代码中,声明了一个int类型的account_number属性设一个double类型的leftmoney属性,并编写了其存款方法savemoney()、取款方法getmoney()、查询余额方法getleftmoney()以及用来初始化变量的构造方法BankAccount()。最后,在main()方法中进行测试:创建了一个ba对象,账号为123456,初始余额为200元,首先向该账户存入了1000元,随后又取出800元。
BookAccount
public class BankAccount
/**
* 账户号码
*/
private int account_number;
/**
* 剩余钱
*/
private double leftmoney;
public int getAccount_number()
return account_number;
public void setAccount_number(int account_number)
this.account_number = account_number;
public double getLeftmoney()
return leftmoney;
public void setLeftmoney(double leftmoney)
this.leftmoney = leftmoney;
public BankAccount(int account_number, double leftmoney)
super();
this.account_number = account_number;
this.leftmoney = leftmoney;
public void saveMoney(double money)
this.leftmoney += money;
public void getMoney(double money)
this.leftmoney -= money;
public BankAccount()
super();
BookClient
public class BankAccountClient
public static void main(String[] args)
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
int money = 1000;
bankAccount.saveMoney(money);
System.out.println("已存入" + money + "元,还剩下" + bankAccount.getLeftmoney() + "元");
int money1 = 800;
bankAccount.getMoney(money1);
System.out.println("已取出" + money1 + "元,还剩下" + bankAccount.getLeftmoney() + "元");
运行截图

【案例3-3】多功能手机
【案例介绍】
- 案例描述
随着科技的发展,手机的使用已经普及到每个家庭甚至个人,手机的属性越来越强大,功能也越来越多,因此人们在生活中越来越依赖于手机。
任务要求,使用所学知识编写一个手机属性及功能分析程序设计,测试各个手机的属性及功能。使用手机时,输出当前手机的各个属性参数以及正在使用的功能。
【任务目标】
l 学会分析“手机属性及功能分析” 程序任务实现的逻辑思路。
l 能够独立完成“手机属性及功能分析”程序的源代码编写、编译及运行。
l 理解和掌握面向对象的设计过程。
l 掌握类的结构和定义过程。
l 掌握构造方法及其重载。
l 掌握对象的创建和使用。
【实现思路】
(1)通过任务描述可知,需要定义一个手机类Phone实现手机的概念。
(2)手机具有属性:品牌(brand)、型号(type)、价格(price)、操作系统(os)和内存(memory)。因此,需要在手机类中定义品牌(brand)、型号(type)、价格(price)、操作系统(os)和内存(memory)的变量。
(3)手机具有功能:查看手机信息(about())、打电话(call(String no))、玩游戏(playGame())、下载音乐(downloadMusic())、播放音乐(playMusic())。所以,可以定义对应的方法about()、call()、playGame()、downloadMusic()、playMusic()。
【实现代码】
Phone.java
上述代码中,定义了手机的品牌brand、型号type、价格price、操作系统os、内存memorySize等属性,并提供了手机类的无参和参构造,以及打电话call()、打游戏playGame()、下载音乐downloadMusic()、播放音乐playMusic()等方法。
PhoneTest.java
上述代码中,创建了两个手机对象,并输出了这两个手机对象的属性及功能。
Phone
public class Phone
/**
* 品牌
*/
private String brand;
/**
* 型号
*/
private String type;
/**
* 操作系统
*/
private String os;
/**
* 价格
*/
private int price;
/**
* 内存
*/
private int memory;
public String getBrand()
return brand;
public void setBrand(String brand)
this.brand = brand;
public String getType()
return type;
public void setType(String type)
this.type = type;
public String getOs()
return os;
public void setOs(String os)
this.os = os;
public int getPrice()
return price;
public void setPrice(int price)
this.price = price;
public int getMemory()
return memory;
public void setMemory(int memory)
this.memory = memory;
public Phone(String brand, String type, String os, int price, int memory)
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.type = type;
this.os = os;
this.price = price;
this.memory = memory;
public Phone()
super();
// 关于本机
public void about()
System.out.println("品牌:" + brand + "\\n" + "型号:" + type + "\\n" + "操作系统:" + os + "\\n" + "价格:" + price + "\\n"
+ "内存:" + memory + "\\n");
// 打电话
public void call(String num)
System.out.println("拨打电话" + num + "。。。");
// 打游戏
public void playGame()
System.out.println(