结合Binder机制看ActivityManager
Posted Jason_Lee155
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了结合Binder机制看ActivityManager相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、前言
本文主要分析android系统的进程间通信 (Binder机制) 在应用框架层的Java源代码;相关文章网上很多,我们尽量少代码多流程。
Binder是一种基于C/S的架构,主要包含四个部分:
- 服务端 Server;
- 客户端 Client;
- Binder驱动;
- ServiceManager 管理远程服务;
二、流程图
先看一些 Binder 通信的流程图:

流程图说明
- Binder 是一种基于 C/S的架构,分为 Client、Service、Binder驱动 三部分;
- 客户端持有一个 Binder 的代理对象 BinderProxy,用于和远程服务的通信;
- 关于Client端为什么持有一个 BinderProxy 对象,请参考 《Android Binder框架实现源码深入分析》;
看一下 IBinder 类的说明,可得出以下结论:
- IBinder 是一个轻量级的远程对象接口,它具备很高的性能;
- IBinder 的核心Api Binder.transact() 会自动关联到 Binder.onTransact();
- Binder.transact() 方法允许我们发送一个数据到 Binder 对象中,也能从一个 Binder 对象中接收数据;
- Binder.transact() 方法是一个同步的方法,直到远程对象(Service端)从 Binder.onTransact() 返回数据时,Binder.transact() 才能拿到数据;
- 在 transact() 中,通过 Parcel 来进行数据传输,且将数据写入到一个公共的缓存区当中;
- 系统在每个进程当中都维护了一个线程池,当有IPC通信时,该线程池就分发出一条线程来执行这个通信操作;
- 判断远程服务失效的方法有3中:
1,transact() 方法接收到 RemoteException 异常,说明远程服务失效;
2,调用 IBinder.pingBinder() 方法,如果返回 false 就说明远程服务失效;
3,调用 IBinder.linkToDeath() 方法,可以向Binder中注册一个 DeathRecipient 接口作为参数,当远程服务失效时,就会触发这个接口参数的回调;
三、类图
3.1 Binder机制在 IActivityManager 中的应用
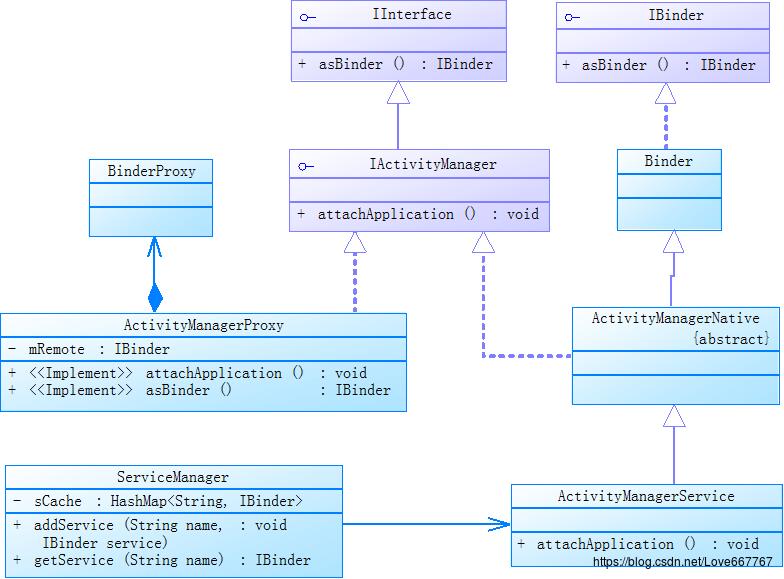
具体分析,请查看《结合Binder机制看ActivityManager(二)》
3.2 Binder机制在 AIDL 中的应用
AIDL能实现进程间通信,其实质仍然是 Binder机制 的使用;
AIDL文件所生成 class 文件的类的关系图
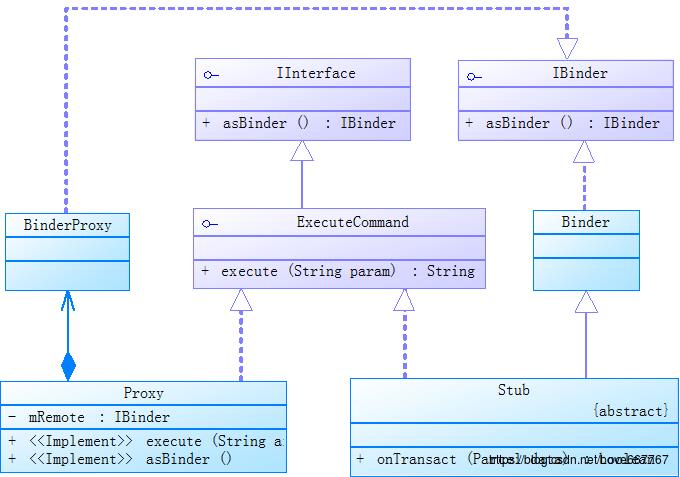
分析AIDL文件生成的 class 文件的代码
1,ExecuteCommand.aidl 文件
// AIDL文件
interface ExecuteCommand
String execute(String param);
2,ExecuteCommand.class 文件
public interface ExecuteCommand extends android.os.IInterface
// Stub就相当于是IActivityManager类图中的ActivityManagerNative类;
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand";
public Stub()
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
/**
* asInterface()传入一个BinderProxy作为参数;
*/
public static com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
if ((obj == null))
return null;
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand)))
return ((com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand) iin);
// 返回一个`ExecuteCommand` 接口的远程服务代理对象;
return new com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand.Stub.Proxy(obj);
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
return this;
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
switch (code)
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
case TRANSACTION_execute:
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
java.lang.String _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readString();
java.lang.String _result = this.execute(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
// 这里就是向reply中写入数据,将结果返回给调用的客户端;
reply.writeString(_result);
return true;
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
// `Proxy` 对象是 `ExecuteCommand` 接口的远程服务代理对象;
private static class Proxy implements com.example.aidl.interfaze.ExecuteCommand
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote)
mRemote = remote;
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
return mRemote;
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
return DESCRIPTOR;
@Override
public java.lang.String execute(java.lang.String param) throws android.os.RemoteException
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
java.lang.String _result;
try
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeString(param);
// 这个方法时同步的,需要等待远程服务端返回,返回的结果在_reply中读取;
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_execute, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readString();
finally
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
return _result;
static final int TRANSACTION_execute = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
public java.lang.String execute(java.lang.String param) throws android.os.RemoteException;
四、类 Binder、BinderProxy
Binder、BinderProxy 类都是 IBinder 接口的实现类,我们看一下其内部的方法;
4.1 BinderProxy
final class BinderProxy implements IBinder
// 在接口远程服务的代理对象的方法中调用transact()
// 如在ActivityManagerProxy对象的方法中调用transact()
public boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException
Binder.checkParcel(this, code, data, "Unreasonably large binder buffer");
// 最终直接调用Native层接口;
return transactNative(code, data, reply, flags);
// 调用Native层代码
public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException;
BinderProxy()
mSelf = new WeakReference(this);
4.2 类 Binder
public class Binder implements IBinder
/**
* Add the calling thread to the IPC thread pool. This function does
* not return until the current process is exiting.
*/
public static final native void joinThreadPool();
/**
* Default implementation always returns true -- if you got here,
* the object is alive.
*/
public boolean pingBinder()
return true;
/**
* Default implementation is a stub that returns false. You will want
* to override this to do the appropriate unmarshalling of transactions.
*
* <p>If you want to call this, call transact().
*/
protected boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException
if (code == INTERFACE_TRANSACTION)
reply.writeString(getInterfaceDescriptor());
return true;
else if (code == DUMP_TRANSACTION)
ParcelFileDescriptor fd = data.readFileDescriptor();
String[] args = data.readStringArray();
if (fd != null)
try
dump(fd.getFileDescriptor(), args);
finally
try
fd.close();
catch (IOException e)
// swallowed, not propagated back to the caller
// Write the StrictMode header.
if (reply != null)
reply.writeNoException();
else
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
return true;
return false;
/**
* Local implementation is a no-op.
*/
public void linkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags)
// Entry point from android_util_Binder.cpp's onTransact
// 在android_util_Binder.cpp的onTransact()方法会调用调这个方法;
// 即在调用BinderProxy.transact()方法后,经过Native层的调用后,最终调用execTransact()方法;
private boolean execTransact(int code, long dataObj, long replyObj,
int flags)
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(dataObj);
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(replyObj);
boolean res;
try
// 调用Binder子类的onTransact()方法;
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
catch (Exception e)
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(e);
res = true;
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return res;
五、类似的结构
| Interface | Native | Proxy | Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| IActivityManager | ActivityManagerNative | ActivityManagerProxy | ActivityManagerService |
| IApplicationThread | ApplicationThreadNative | ApplicationThreadProxy | ApplicationThread |
| IServiceManager | ServiceManagerNative | ServiceManagerProxy | / |
| IPackageManager | IPackageManager.Stub | IPackageManager.Stub.Proxy | PackageManagerService |
以上是关于结合Binder机制看ActivityManager的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章