2.BIO与NIO区别
Posted PacosonSWJTU
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2.BIO与NIO区别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【README】
- 1.本文总结自B站《netty-尚硅谷》,很不错;
- 2.本文介绍 BIO, NIO的知识;
【1】BIO(传统java IO模型)
1)BIO-Blocking IO:同步阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理;
2)原理图如下:
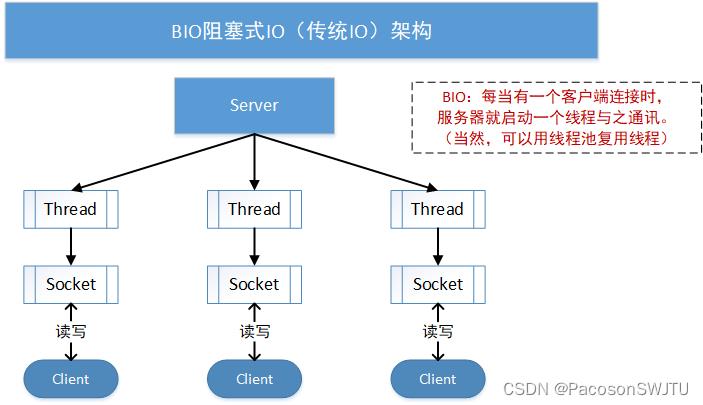
【图解】
- 1.client: 可以使用 telnet 作为客户端连接服务器;
- 2.BIO:每当有一个客户端连接时,服务器就启动一个新线程与之通讯(当然可以复用线程池)。
【代码实现】
/**
* @Description 阻塞式IO服务器
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月13日
*/
public class Bioserver
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
// 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
int order = 0;
// 创建 服务器 套接字
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功.");
while(true)
System.out.println("等待客户端请求");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 没有客户端请求,accept阻塞
System.out.printf("客户端[%d]请求建立连接\\n", ++order);
final int orderCopy = order;
threadPool.execute(()->
handler(socket, orderCopy);
);
/**
* @description 与客户端通讯
* @param socket 连接套接字
* @author xiao tang
* @date 2022/8/13
*/
public static void handler(Socket socket, int order)
byte[] byteArr = new byte[1024];
try
// 读取客户端发送的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
int length = 0;
// 客户端没有数据,read阻塞
// while( ( length = inputStream.read(byteArr))!= -1)
// System.out.println(new String(byteArr, 0, length));
//
while(true)
System.out.printf("线程id[%s],等待客户端[%d]发送数据\\n", Thread.currentThread().getId(), order);
length = inputStream.read(byteArr);
if (length == -1) break;
System.out.printf("线程id[%s],客户端[%d]:" + new String(byteArr, 0, length) + "\\n", Thread.currentThread().getId(), order);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
// 关闭与客户端的连接
try
socket.close();
System.out.printf("关闭与客户端[%d]的连接\\n", order);
catch (IOException e)
【2】NIO (同步非阻塞IO)
【2.0】NIO概述
- 1)Java NIO 全称 java non-blocking IO,是指 JDK 提供的新API。从 JDK1.4 开始,Java 提供了一系列改进的输入/输出的新特性,被统称为 NIO(即 New IO),是同步非阻塞的;
- 2)NIO 相关类都被放在 java.nio 包及子包下,并且对原java.io 包中的很多类进行改写。
- 3)NIO 有三大核心部分: Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器) ;
- 4)NIO是 面向缓冲区 ,或者面向块编程的。数据读取到缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动,这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性,使用它可以提供非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络;
5)NIO非阻塞IO处理架构:
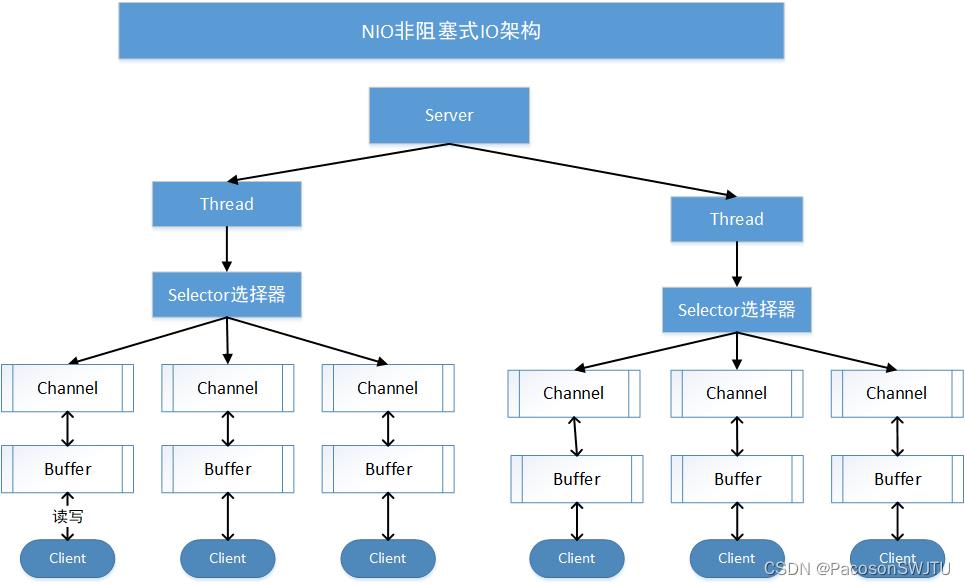
【图解】
- 1.使用NIO,服务器启动一个线程可以处理多个客户端请求。假设有10000个请求过来,根据实际情况,可以分配50或者100个线程来处理。不像之前的阻塞IO那样,非得分配10000个。
- 2.通道Channel 是封装在 java输入输出流中的对象;
【小结】
- NIO 有三大核心部分: Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器) ;
【比较】NIO 与 BIO的比较
- 1)BIO 以流的方式处理数据,而 NIO 以块的方式处理数据, 块I/O 的效率比流I/O高很多;
- 2) BIO 是阻塞的,NIO 则是非阻塞的;
- 3) BIO基于字节流和字符流进行操作,而 NIO 基于Channel(通道)和Buffer(缓冲区)进行操作;磁盘数据借助通道读入到缓冲区,或者从缓冲区写出到磁盘。
补充:NIO中,Selector(选择器) 用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接请求,数据到达等),因此使用单个线程就可以监听多个客户端通道;
【3】NIO3大核心部分
1)NIO 有三大核心部分: Buffer(缓冲区), Channel(通道),Selector(选择器) ;
2)3个模块关联关系如下:
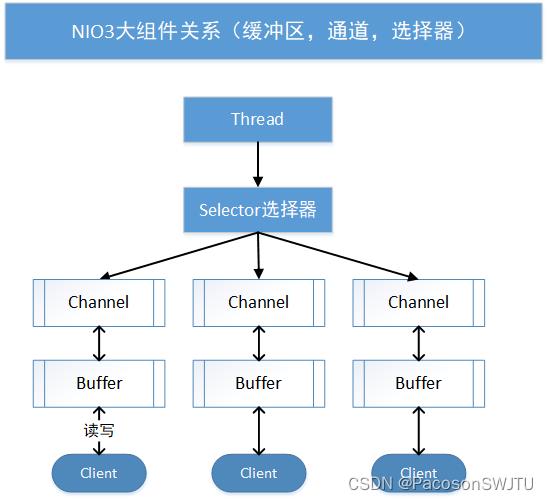
【图解】
- 1)一个服务器线程对应一个选择器;一个选择器对应多个通道(因为多个通道可以注册到同一个选择器);
- 2)一个通道对应一个缓冲区 buffer;
- 4)cpu切换到哪个channel运行 ,是由事件决定的;事件 event 是一个很重要的概念(如 ACCEPT, READ 事件);
- 5)Selector 会根据不同事件,在各个通道上切换;
- 6)Buffer 本质上就是一个内存块,底层是由一个数组实现;
- 7)数据读取或写入,是通过buffer来完成,这个和 BIO 是有本质不同的;此外,BIO要么是输入流,要么是输出流,不能双向;但NIO的buffer是可读可写的,需要flip方法进行切换;
- 8)Channel 是双向的,可以反应底层操作系统的情况,如 linux底层的操作系统通道就是双向的;
【3.1】NIO中的Buffer缓冲
【3.1.1】buffer缓冲概述
1)缓冲区(Buffer):
- 缓冲区本质上是一个可以读写数据的内存块(如字节数组),可以更轻松地使用内存块;
- 缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况。
2)Channel 提供读写文件的接口、都必须经由Buffer,如下图所示。
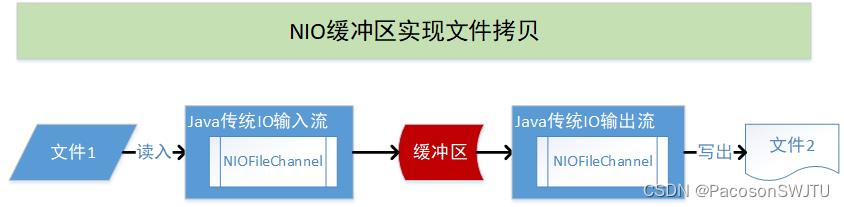
参见 FileChannel读写文件代码( NIOFileChannel015.java ,下文有)
【代码】NIO中缓冲区的使用
/**
* @Description 缓冲区使用
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月13日
*/
public class BasicBuffer
/**
* @description Buffer的使用
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
// 创建一个buffer
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
// 向buffer存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++)
intBuffer.put(i*2);
// 从buffer 读取数据
// 需要先把 buffer 转换,读写切换(写模式切换到读模式)
intBuffer.flip();
intBuffer.position(1);
while(intBuffer.hasRemaining())
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
【3.1.2】buffer子类及属性
1)子类
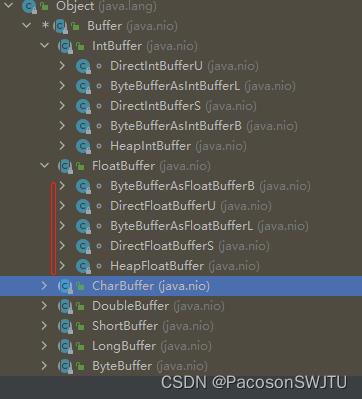
【图解】
- ByteBuffer,存储字节数据到缓冲区(常用)-字节缓冲区;
- ShortBuffer,存储短整型数据到缓冲区;
- CharBuffer,存储字符数据到缓冲区;
- IntBuffer,存储整数数据到缓冲区;
- LongBuffer,存储长整型数据到缓冲区;
- DoubleBuffer,存储双精度到缓冲区;
- FloatBuffer,存储单精度到缓冲区;
2)buffer的4个属性
public abstract class Buffer
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;| 序号 | 属性 | 描述 |
| 1 | Capacity | 容量,即缓冲区大小,定长不能改变。 |
| 2 | Position | 当前位置;表示下一个要被读写的元素的下标(索引) |
| 3 | limit | 表示缓冲区最大可用位置,读写时不能超过极限位置。 |
| 4 | Mark | 标记,不修改。 |
【3.1.3】只读buffer
/**
* @Description 只读 buffer
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOReadOnly017
public static void main(String[] args)
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
buffer.put((byte) i);
// 读取
buffer.flip();
// 得到一个只读buffer
ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.getClass()); // java.nio.HeapByteBufferR
// 读取
while (readOnlyBuffer.hasRemaining())
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.get());
readOnlyBuffer.flip();
readOnlyBuffer.put((byte)0); // 抛出异常-ReadOnlyBufferException
【3.1.4】 get与put() 方法操作 数据类型要一致
buffer缓冲中 get与put() 方法操作 数据类型要一致 :
/**
* @Description buffer put 与 get 操作的数据类型要一致
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOByteBufferPugGet017
public static void main(String[] args)
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
// 类型化方式放入数据
buffer.putInt(100);
buffer.putLong(4);
buffer.putChar('中');
buffer.putShort((short)4);
// 取出
buffer.flip();
System.out.println();
System.out.println(buffer.getInt());
System.out.println(buffer.getChar());
System.out.println(buffer.getLong());
System.out.println(buffer.getLong()); // 抛出异常
【3.1.5】 Buffer的分散与聚集(buffer数组读写数据)
前面我们讲的读写操作,都是通过一个Buffer 完成的,NIO还支持通过多个Buffer (即 Buffer 数组) 完成读写操作,即 Scattering 和Gathering;
2)buffer的分散与聚集( Scattering 与 Gathering )
- Scattering: 将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入。
- Gathering: 从buffer读取数据时, 可以采用buffer数组,依次读取。
/**
* @Description buffer的分散与聚集( Scattering 与 Gathering )
* Scattering: 将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入。
* Gathering: 从buffer读取数据时, 可以采用buffer数组,依次读取。
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class ScatterAndGatherBuffer019
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 使用 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
// 绑定端口到socket 并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
// 等待客户端连接(telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 循环读取
int msgLength = 8; // 假定从客户端接收8个字节
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead < msgLength)
long singleLength = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += singleLength;
System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead);
// 流打印,查看当前buffer的position 和 limit
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).stream()
.map(buffer -> "position = " + buffer.position() + ", limit=" + buffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println);
// 将所有buffer反转-flip
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(x -> x.flip());
// 将数据读出显示到客户端
long byteWrite = 0;
while (byteWrite < msgLength)
long length = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += length;
// 将所有buffer 清空
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(x -> x.clear());
System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead + ", byteWrite = " + byteWrite);
【3.2】channel 通道的代码示例
1)写出到文件
/**
* @Description nio文件通道读文件
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOFileChannel013
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
String text = "hello 世界";
// 创建一个输出流
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(
new File("D://temp/netty/nio_file_channel01.txt")))
// 获取对应 FileChannel,FileChannel 是抽象类,具体类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fos.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 把文本写入 ByteBuffer, 并把 ByteBuffer 反转-flip
byteBuffer.put(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byteBuffer.flip();
// 把 byteBuffer 写入到 FileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println("异常");
throw e;
2)从文件读入数据
/**
* @Description FileChannel读文件
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOFileChannel014
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 创建一个输入流
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(
new File("D://temp/netty/nio_file_channel01.txt")))
// 获取对应 FileChannel,FileChannel 是抽象类,具体类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fis.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 从文件读入内容到缓冲区
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 显示
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println("异常");
throw e;
3)读写文件(拷贝)
/**
* @Description FileChannel读写文件
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOFileChannel015
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 创建一个输入流
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D://temp/netty/nio_file_channel01.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D://temp/netty/nio_file_channel02.txt"))
// 获取对应 FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel01 = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel fileChannel02 = fos.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
// 循环读取
while(fileChannel01.read(byteBuffer) != -1)
// 反转
byteBuffer.flip();
// 将buffer 中的数据写入到 02.txt
fileChannel02.write(byteBuffer);
// 清空 buffer
byteBuffer.clear();
// 显示
System.out.println("拷贝成功.");
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println("异常");
throw e;
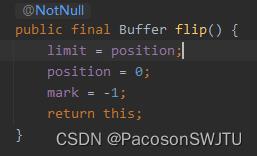
补充: Buffer.flip() 切换读写模式(如写模式切换为读模式)
4)用 transferFrom 拷贝文件
/**
* @Description 采用 transferFrom 拷贝图片
* @author xiao tang
* @version 1.0.0
* @createTime 2022年08月16日
*/
public class NIOFileChannel016
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 创建一个输入流
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D://temp/netty/image/1.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D://temp/netty/image/2.jpg"))
// 获取对应 FileChannel
FileChannel srcChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel destChannel = fos.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
// 使用 transferFrom 完成拷贝
destChannel.transferFrom(srcChannel, 0, srcChannel.size());
// 显示
System.out.println("拷贝成功.");
catch (Exception e)
System.out.println("异常");
throw e;
【3.3】选择器(Selector)
refer2
3.NIO选择器(基于NIO的服务器与客户端通讯)_PacosonSWJTU的博客-CSDN博客
以上是关于2.BIO与NIO区别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章