Tungsten Fabric SDN — 与 Kubernetes 的集成部署(CN)
Posted 范桂飓
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tungsten Fabric SDN — 与 Kubernetes 的集成部署(CN)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
文章目录
部署架构
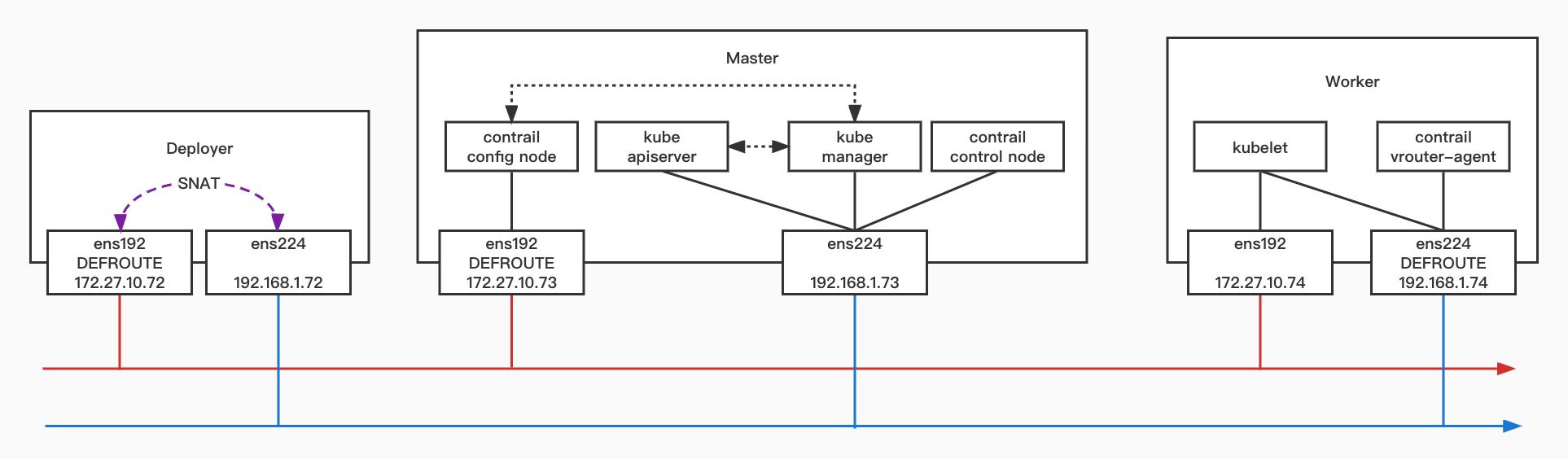
软件版本
- CentOS 7.9 2009:CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-2003.iso
- Kubernetes v1.14.8
- Tungsten fabric R21.3
部署 Kubernetes & TF
基础环境设置
-
使用 CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-2009.iso 镜像,安装操作系统。
-
配置 Underlay 网络。
- Mgmt Net 互通
- Control & Data Net 互通
-
配置各个节点的操作系统环境。
# CentOS 7.X (kernel >= 3.10.0-693.17.1)
$ uname -r
3.10.0-1127.el7.x86_64
# Python2.7
$ python -V
Python 2.7.5
# 分别设置各个节点的 hosts 解析
$ cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF
172.27.10.72 deployer
172.27.10.73 master
172.27.10.74 worker01
EOF
# 分别关闭各个节点的 FW
$ sudo systemctl disable firewalld && systemctl stop firewalld
# 分别关闭各个节点的 SELinux
$ sudo setenforce 0
$ sudo sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
- 配置 Deployer 节点
# 安装 PIP
$ curl "https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py" -o "get-pip.py"
$ python get-pip.py
# 安装 Ansible (==2.7.18)
$ pip install ansible==2.7.18
# 下载 tf-ansible-deployer 代码仓库
$ yum install git -y
$ git clone -b R21.3 http://github.com/tungstenfabric/tf-ansible-deployer
# 搭建本地 NTP 服务器
$ yum -y install ntp ntpdate
$ vi /etc/ntp.conf
...
#server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
#server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 127.127.1.0
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
$ systemctl enable ntpd && systemctl restart ntpd && systemctl status ntpd
$ ntpq -p
# Deployer 作为 Master 和 Worker 的 SNAT GW
$ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -o ens192 -j SNAT --to 172.27.10.72
创建 Deployment instance
$ tf-ansible-deployer/config/instances.yaml
global_configuration:
CONTAINER_REGISTRY: tungstenfabric
REGISTRY_PRIVATE_INSECURE: True
provider_config:
bms:
ssh_user: root
ssh_pwd: 1qaz@WSX
ntpserver: deployer
domainsuffix: cluster02
instances:
master:
provider: bms
ip: 172.27.10.73
roles:
config:
config_database:
control:
webui:
analytics:
analytics_database:
analytics_alarm:
analytics_snmp:
k8s_master:
kubemanager:
worker01:
provider: bms
ip: 172.27.10.74
roles:
vrouter:
PHYSICAL_INTERFACE: ens224
VROUTER_GATEWAY: 192.168.1.75
k8s_node:
contrail_configuration:
KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_PROJECT:
KUBERNETES_API_NODES: 192.168.1.73
KUBERNETES_API_SERVER: 192.168.1.73
KUBEMANAGER_NODES: 192.168.1.73
KUBERNETES_POD_SUBNETS: 10.0.1.0/24
KUBERNETES_SERVICE_SUBNETS: 10.0.2.0/24
CONTRAIL_VERSION: R21.3-latest
CONTRAIL_CONTAINER_TAG: R21.3-latest
CONTROLLER_NODES: 172.27.10.73
CONTROL_NODES: 192.168.1.73
ENCAP_PRIORITY: VXLAN,MPLSoUDP,MPLSoGRE
CONFIG_NODEMGR__DEFAULTS__minimum_diskGB: 2
DATABASE_NODEMGR__DEFAULTS__minimum_diskGB: 2
CONFIG_DATABASE_NODEMGR__DEFAULTS__minimum_diskGB: 2
ANALYTICS_DATA_TTL: 1
ANALYTICS_STATISTICS_TTL: 1
ANALYTICS_FLOW_TTL: 1
DEVICE_MANAGER__DEFAULTS__push_mode: 0
LOG_LEVEL: SYS_DEBUG
执行 Playbooks
$ yum install sshpass -y
$ cd /root/tf-ansible-deployer
ansible-playbook -e orchestrator=kubernetes -i inventory/ playbooks/configure_instances.yml
ansible-playbook -e orchestrator=kubernetes -i inventory/ playbooks/install_k8s.yml
ansible-playbook -e orchestrator=kubernetes -i inventory/ playbooks/install_contrail.yml
环境检查
-
登陆 WebGUI(初始密码为 contrail123):https://172.27.10.73:8143
-
查看 K8s 集群状态。
$ kubectl get pods -A -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
kube-system coredns-6dcc67dcbc-4wklk 1/1 Running 0 6h11m 10.0.1.252 worker01 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-6dcc67dcbc-m4lc4 1/1 Running 0 6h11m 10.0.1.251 worker01 <none> <none>
kube-system etcd-master 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 172.27.10.73 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 172.27.10.73 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 172.27.10.73 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-fg2b6 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 192.168.1.74 worker01 <none> <none>
kube-system kube-proxy-rmp7j 1/1 Running 0 6h11m 172.27.10.73 master <none> <none>
kube-system kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 172.27.10.73 master <none> <none>
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard-7d7d775b7b-gp7cc 1/1 Running 0 6h10m 192.168.1.74 worker01 <none> <none>
$ kubectl get node -A -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master NotReady master 6h12m v1.14.8 172.27.10.73 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://18.3.1
worker01 Ready <none> 6h11m v1.14.8 192.168.1.74 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 docker://18.3.1
配置记录
Control Plane
- kube-apiserver
kube-apiserver
--advertise-address=192.168.1.73
--allow-privileged=true
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
--client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true
--etcd-cafile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--etcd-certfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.crt
--etcd-keyfile=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-etcd-client.key
--etcd-servers=https://127.0.0.1:2379
--insecure-port=0
--kubelet-client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.crt
--kubelet-client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver-kubelet-client.key
--kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
--proxy-client-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.crt
--proxy-client-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-client.key
--requestheader-allowed-names=front-proxy-client
--requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt
--requestheader-extra-headers-prefix=X-Remote-Extra-
--requestheader-group-headers=X-Remote-Group
--requestheader-username-headers=X-Remote-User
--secure-port=6443
--service-account-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.pub
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.0.2.0/24
--tls-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt
--tls-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.key
- kube-controller-manager
kube-controller-manager
--allocate-node-cidrs=true
--authentication-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--authorization-kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--bind-address=127.0.0.1
--client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--cluster-cidr=10.0.1.0/24
--cluster-signing-cert-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--cluster-signing-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.key
--controllers=*,bootstrapsigner,tokencleaner
--kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/controller-manager.conf
--leader-elect=true
--node-cidr-mask-size=24
--requestheader-client-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/front-proxy-ca.crt
--root-ca-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
--service-account-private-key-file=/etc/kubernetes/pki/sa.key
--use-service-account-credentials=true
- kube-manager
$ cat /etc/contrail/contrail-kubernetes.conf
[DEFAULTS]
host_ip=192.168.1.73
orchestrator=kubernetes
...
[KUBERNETES]
kubernetes_api_server=192.168.1.73
kubernetes_api_port=8080
kubernetes_api_secure_port=6443
...
- contrail config api
$ cat /etc/contrail/contrail-api-0.conf
[DEFAULTS]
listen_ip_addr=172.27.10.73
listen_port=8082
http_server_port=8084
http_server_ip=0.0.0.0
- contrail control node
$ cat /etc/contrail/contrail-control.conf
[DEFAULT]
hostip=192.168.1.73
Worker Node
- kubelet
$ cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
address: 0.0.0.0
- cni
$ cat /etc/cni/net.d/10-contrail.conf
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"contrail" :
"cluster-name" : "k8s",
"meta-plugin" : "multus",
"vrouter-ip" : "127.0.0.1",
"vrouter-port" : 9091,
"config-dir" : "/var/lib/contrail/ports/vm",
"poll-timeout" : 5,
"poll-retries" : 15,
"log-file" : "/var/log/contrail/cni/opencontrail.log",
"log-level" : "4"
,
"name": "contrail-k8s-cni",
"type": "contrail-k8s-cni"
- vrouter-agent
$ cat /etc/contrail/contrail-vrouter-agent.conf
[CONTROL-NODE]
servers=192.168.1.73:5269
[DEFAULT]
http_server_ip=0.0.0.0
collectors=172.27.10.73:8086
log_file=/var/log/contrail/vrouter-agent/contrail-vrouter-agent.log
physical_interface_mac=00:50:56:88:43:77
...
[NETWORKS]
control_network_ip=192.168.1.74
[DNS]
servers=192.168.1.73:53
[VIRTUAL-HOST-INTERFACE]
name=vhost0
ip=192.168.1.74/24
compute_node_address=192.168.1.74
physical_interface=ens224
gateway=192.168.1.75
环境卸载
# 卸载 Contrail
ansible-playbook -e orchestrator=kubernetes -i inventory/ playbooks/contrail_destroy.yml
TS
问题 1:
TASK [k8s : make cache to import gpg keys] ***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
[WARNING]: Consider using the yum module rather than running 'yum'. If you need to use command because yum is insufficient you can add 'warn: false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in ansible.cfg to get rid of this
message.
fatal: [172.27.10.74]: FAILED! => "changed": true, "cmd": ["yum", "-q", "makecache", "-y", "--disablerepo=*", "--enablerepo=Kubernetes"], "delta": "0:00:00.943399", "end": "2022-06-13 12:14:42.859957", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 1, "start": "2022-06-13 12:14:41.916558", "stderr": "https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - \\"Peer's Certificate has expired.\\"\\n正在尝试其它镜像。\\nIt was impossible to connect to the CentOS servers.\\nThis could mean a connectivity issue in your environment, such as the requirement to configure a proxy,\\nor a transparent proxy that tampers with TLS security, or an incorrect system clock.\\nYou can try to solve this issue by using the instructions on https://wiki.centos.org/yum-errors\\nIf above article doesn't help to resolve this issue please use https://bugs.centos.org/.\\n\\n\\n\\n One of the configured repositories failed (k8s repo),\\n and yum doesn't have enough cached data to continue. At this point the only\\n safe thing yum can do is fail. There are a few ways to work \\"fix\\" this:\\n\\n 1. Contact the upstream for the repository and get them to fix the problem.\\n\\n 2. Reconfigure the baseurl/etc. for the repository, to point to a working\\n upstream. This is most often useful if you are using a newer\\n distribution release than is supported by the repository (and the\\n packages for the previous distribution release still work).\\n\\n 3. Run the command with the repository temporarily disabled\\n yum --disablerepo=Kubernetes ...\\n\\n 4. Disable the repository permanently, so yum won't use it by default. Yum\\n will then just ignore the repository until you permanently enable it\\n again or use --enablerepo for temporary usage:\\n\\n yum-config-manager --disable Kubernetes\\n or\\n subscription-manager repos --disable=Kubernetes\\n\\n 5. Configure the failing repository to be skipped, if it is unavailable.\\n Note that yum will try to contact the repo. when it runs most commands,\\n so will have to try and fail each time (and thus. yum will be be much\\n slower). If it is a very temporary problem though, this is often a nice\\n compromise:\\n\\n yum-config-manager --save --setopt=Kubernetes.skip_if_unavailable=true\\n\\nfailure: repodata/repomd.xml from Kubernetes: [Errno 256] No more mirrors to try.\\nhttps://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - \\"Peer's Certificate has expired.\\"", "stderr_lines": ["https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - \\"Peer's Certificate has expired.\\"", "正在尝试其它镜像。", "It was impossible to connect to the CentOS servers.", "This could mean a connectivity issue in your environment, such as the requirement to configure a proxy,", "or a transparent proxy that tampers with TLS security, or an incorrect system clock.", "You can try to solve this issue by using the instructions on https://wiki.centos.org/yum-errors", "If above article doesn't help to resolve this issue please use https://bugs.centos.org/.", "", "", "", " One of the configured repositories failed (k8s repo),", " and yum doesn't have enough cached data to continue. At this point the only", " safe thing yum can do is fail. There are a few ways to work \\"fix\\" this:", "", " 1. Contact the upstream for the repository and get them to fix the problem.", "", " 2. Reconfigure the baseurl/etc. for the repository, to point to a working", " upstream. This is most often useful if you are using a newer", " distribution release than is supported by the repository (and the", " packages for the previous distribution release still work).", "", " 3. Run the command with the repository temporarily disabled", " yum --disablerepo=Kubernetes ...", "", " 4. Disable the repository permanently, so yum won't use it by default. Yum", " will then just ignore the repository until you permanently enable it", " again or use --enablerepo for temporary usage:", "", " yum-config-manager --disable Kubernetes", " or", " subscription-manager repos --disable=Kubernetes", "", " 5. Configure the failing repository to be skipped, if it is unavailable.", " Note that yum will try to contact the repo. when it runs most commands,", " so will have to try and fail each time (and thus. yum will be be much", " slower). If it is a very temporary problem though, this is often a nice", " compromise:", "", " yum-config-manager --save --setopt=Kubernetes.skip_if_unavailable=true", "", "failure: repodata/repomd.xml from Kubernetes: [Errno 256] No more mirrors to try.", "https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - \\"Peer's Certificate has expired.\\""], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []
[root@master ~]# yum -q makecache -y --disablerepo=* --enablerepo=Kubernetes
https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - "Peer's Certificate has expired."
正在尝试其它镜像。
It was impossible to connect to the CentOS servers.
This could mean a connectivity issue in your environment, such as the requirement to configure a proxy,
or a transparent proxy that tampers with TLS security, or an incorrect system clock.
You can try to solve this issue by using the instructions on https://wiki.centos.org/yum-errors
If above article doesn't help to resolve this issue please use https://bugs.centos.org/.
One of the configured repositories failed (k8s repo),
and yum doesn't have enough cached data to continue. At this point the only
safe thing yum can do is fail. There are a few ways to work "fix" this:
1. Contact the upstream for the repository and get them to fix the problem.
2. Reconfigure the baseurl/etc. for the repository, to point to a working
upstream. This is most often useful if you are using a newer
distribution release than is supported by the repository (and the
packages for the previous distribution release still work).
3. Run the command with the repository temporarily disabled
yum --disablerepo=Kubernetes ...
4. Disable the repository permanently, so yum won't use it by default. Yum
will then just ignore the repository until you permanently enable it
again or use --enablerepo for temporary usage:
yum-config-manager --disable Kubernetes
or
subscription-manager repos --disable=Kubernetes
5. Configure the failing repository to be skipped, if it is unavailable.
Note that yum will try to contact the repo. when it runs most commands,
so will have to try and fail each time (and thus. yum will be be much
slower). If it is a very temporary problem though, this is often a nice
compromise:
yum-config-manager --save --setopt=Kubernetes.skip_if_unavailable=true
failure: repodata/repomd.xml from Kubernetes: [Errno 256] No more mirrors to try.
https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#60 - "Peer's Certificate has expired."
解决:
$ grep gpgcheck -inR *
playbooks/roles/k8s/tasks/RedHat.yml:8: gpgcheck: no
playbooks/roles/k8s/tasks/RedHat.yml:17: repo_gpgcheck: no
playbooks/roles/k8s/tasks/RedHat.yml:18: gpgcheck: no
部署 SDNGW
- sdngw.conf
---
HOST:
identifier : sdngw
host-management-interface : enp6s0
routing-engine-image : "/root/vmx/images/junos-vmx-x86-64-22.1R1.10.qcow2"
routing-engine-hdd : "/root/vmx/images/vmxhdd.img"
forwarding-engine-image : "/root/vmx/images/vFPC-20220223.img"
---
BRIDGES:
- type : external
name : br-mgmt-sdngw
---
CONTROL_PLANE:
vcpus : 4
memory-mb : 8192
console_port: 8601
interfaces :
- type : static
ipaddr : 172.27.10.129
macaddr : "0A:00:DD:C0:DE:0E"
---
FORWARDING_PLANE:
vcpus : 4
memory-mb : 8192
console_port: 8602
device-type : virtio
interfaces :
- type : static
ipaddr : 172.27.10.130
macaddr : "0A:00:DD:C0:DE:10"
---
JUNOS_DEVICES:
- interface : ge-0/0/0
mac-address : "02:06:0A:0E:FF:F0"
description : "ge-0/0/0 interface"
- interface : ge-0/0/1
mac-address : "02:06:0A:0E:FF:F1"
description : "ge-0/0/1 interface"
- 执行安装:
# 编译好部署配置文件之后,开始执行 VCP/VFP 安装脚本
$ cd vmx
$ nohup ./vmx.sh -lv --install --cfg /root/sdngw.conf &
# 观察日志
$ tailf nohup.out
- 初始化配置:
# 刚启动 VCP 时,需要等待 VCP 启动完成。
$ ./vmx.sh --console vcp sdngw
# root 登陆,缺省没有密码。
login: root
# 进入 CLI 模式。
$ cli
# 确认 VCP 与 VFP 之间的连通性状态(需要等待一段时间,Online 即连通)。
root> show chassis fpc
Temp CPU Utilization (%) CPU Utilization (%) Memory Utilization (%)
Slot State (C) Total Interrupt 1min 5min 15min DRAM (MB) Heap Buffer
0 Online Testing 8 0 2 0 0 511 31 0
...
# 进入配置模式。
root> configure
# 关闭自动更新。
root# delete chassis auto-image-upgrade
# 设置 VCP 的主机名。
root# set system host-name sdngw
# 设置允许 root SSH VCP 并设定 root 的密码。
root# set system root-authentication plain-text-password
root# set system services ssh root-login allow
# 保存所修改的配置。
root# commit
- sdngw-junosdev.conf
interfaces :
- link_name : vmx_link1
mtu : 1500
endpoint_1 :
- type : junos_dev
vm_name : sdngw
dev_name : ge-0/0/0
endpoint_2 :
- type : bridge_dev
dev_name : br-tenant-net
- link_name : vmx_link2
mtu : 1500
endpoint_1 :
- type : junos_dev
vm_name : sdngw
dev_name : ge-0/0/1
endpoint_2 :
- type : bridge_dev
dev_name : br-external-net
- 执行自动化脚本
# NOTE:脚本执行的是临时配置,每次重启 VM instance 都需要执行一次,或手动的进行静态配置。
$ cd vmx
$ ./vmx.sh --bind-dev --cfg /root/sdngw-junosdev.conf
# 手动将 Bridge 绑定到 pNIC。
$ brctl addif br-tenant-net enp11s0
$ brctl addif br-external-net enp26s0f0
$ brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br-external-net 8000.90e2ba8a532c no enp26s0f0
ge-0.0.1-sdngw
br-int-sdngw 8000.525400571469 yes br-int-sngw-nic
vcp-int-sdngw
vfp-int-sdngw
br-mgmt-sdngw 8000.40f2e9352cf8 yes br-mgmt-ngw-nic
enp6s0
vcp-ext-sdngw
vfp-ext-sdngw
br-tenant-net 8000.40f2e9352cf9 no enp11s0
ge-0.0.0-sdngw
virbr0 8000.525400addfe1 yes virbr0-nic
- 配置接口的 IP 地址。
# 为 ge interface 配置 IP 地址。
$ ssh root@172.27.10.129
# 登陆并进入 CLI 模式。
$ cli
root> configure
root# delete interfaces fxp0 unit 0 family inet dhcp
root# set interfaces fxp0 unit 0 family inet address 172.27.10.129/24
root# set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.128/24
root# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 172.37.10.128/24
root# commit
root# exit
# 查看接口 IP 地址
root@sdngw> show interfaces terse | grep fxp0
fxp0 up up
fxp0.0 up up inet 172.27.10.129/24
root@sdngw> show interfaces terse | grep ge-0/0/0
ge-0/0/0 up up
ge-0/0/0.0 up up inet 192.168.1.128/24
root@sdngw> show interfaces terse | grep ge-0/0/1
ge-0/0/1 up up
ge-0/0/1.0 up up inet 172.37.10.128/24
- 测试:
- master node 可以 ping 通 fxp0、ge-0/0/0。
- worker node 可以 ping 通 ge-0/0/0。
- External GW 可以 ping 通 ge-0/0/1。
以上是关于Tungsten Fabric SDN — 与 Kubernetes 的集成部署(CN)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章