FlinkFlink 批处理模式Map端数据聚合 NormalizedKeySorter
Posted 九师兄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FlinkFlink 批处理模式Map端数据聚合 NormalizedKeySorter相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

1.概述
在flink的批处理模式下,数据的计算也有着map/reduce两端的计算模型,这一点和MR、spark计算框架是类似的。在数据进行分组计算的过程中,都有着map和reduce两端的聚合过程,map的聚合称之为combiner,这一过程的目的是将数据进行预聚合,减少中间的数据传输量,也减轻了reduce端数据计算的压力。
在《Batch模式JobGraph的创建》中我们分析了在数据聚合的map端,数据最终会经过combiner算子处理,在batch模式下,chain在一起的算子都被封装成ChainedDriver,这个combiner算子就被封装成了SynchronousChainedCombineDriver,数据的核心处理也在这个类里面。在本文中,我们还以WordCount为示例,代码可以参考《Batch模式JobGraph的创建》
2.combiner算子SynchronousChainedCombineDriver
public class SynchronousChainedCombineDriver<IN, OUT> extends ChainedDriver<IN, OUT>
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SynchronousChainedCombineDriver.class);
/** Fix length records with a length below this threshold will be in-place sorted, if possible. */
private static final int THRESHOLD_FOR_IN_PLACE_SORTING = 32;
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
private InMemorySorter<IN> sorter;
private GroupCombineFunction<IN, OUT> combiner;
private TypeSerializer<IN> serializer;
private TypeComparator<IN> groupingComparator;
private AbstractInvokable parent;
private final QuickSort sortAlgo = new QuickSort();
private List<MemorySegment> memory;
private volatile boolean running = true;
-
sorter:flink定义的一种数据结构,用作数据缓存区,将数据先写入到sorter中,并对数据按照key进行排序操作。这个结构非常重要 -
combiner:数据聚合的函数 -
serializer:序列化工具,用于对象数据的序列化和反序列化 -
groupingComparator:分组比较器,比较key,比较两个数据是否属于同一个分组。 -
parent:Flink中的任务类型,例如BatchTask -
sortAlgo:快速排序算子,用来对sorter中的数据进行排序,排序是基于key进行的 -
memory:对内存空间的封装,将内存拆分成一个个的内存段MemorySegment,缓冲的数据写入到这些MemorySegment中。sorter会持有这些MemorySegment
每个算子是有生命周期的,在生命周期内,会依次调用ChainedDriver的setup()、openTask()、collect()方法,setup()、openTask()方法一般是作为算子的初始化操作,数据的处理在collect()中。
2.1 setup()方法
首先看setup()方法
这一步主要就是从配置中实例化数据聚合函数
//SynchronousChainedCombineDriver
public void setup(AbstractInvokable parent)
this.parent = parent;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final GroupCombineFunction<IN, OUT> combiner =
BatchTask.instantiateUserCode(this.config, userCodeClassLoader, GroupCombineFunction.class);
this.combiner = combiner;
FunctionUtils.setFunctionRuntimeContext(combiner, getUdfRuntimeContext());
2.2 openTask()方法
再看openTask()方法
openTask()方法主要的实现:
-
分配用于数据缓冲的内存MemorySegment,MemorySegment是flink管理的一片内存区域,在逻辑上就是一个buffer,每个buffer的大小(也就是每个MemorySegment的segmentSize)默认是32k
-
创建sorter,sorter持有这些MemorySegment,数据写入sorter就是往这些MemorySegment里写。一般情况下这个sorter是NormalizedKeySorter,sorter还持有一个sortingComparator,用来对写入的数据按照key进行排序。
public void openTask() throws Exception
// open the stub first
final Configuration stubConfig = this.config.getStubParameters();
BatchTask.openUserCode(this.combiner, stubConfig);
// ----------------- Set up the sorter -------------------------
// instantiate the serializer / comparator
final TypeSerializerFactory<IN> serializerFactory = this.config.getInputSerializer(0, this.userCodeClassLoader);
final TypeComparatorFactory<IN> sortingComparatorFactory = this.config.getDriverComparator(0, this.userCodeClassLoader);
final TypeComparatorFactory<IN> groupingComparatorFactory = this.config.getDriverComparator(1, this.userCodeClassLoader);
this.serializer = serializerFactory.getSerializer();
//sortingComparator用在sorter里,用来对key进行排序
TypeComparator<IN> sortingComparator = sortingComparatorFactory.createComparator();
//groupingComparator用在聚合的过程中,对sorter中读的数据进行分组比较
this.groupingComparator = groupingComparatorFactory.createComparator();
MemoryManager memManager = this.parent.getEnvironment().getMemoryManager();
final int numMemoryPages = memManager.computeNumberOfPages(this.config.getRelativeMemoryDriver());
//MemoryManager分配内存,以一个个内存段的形式当做数据的缓存空间
this.memory = memManager.allocatePages(this.parent, numMemoryPages);
// instantiate a fix-length in-place sorter, if possible, otherwise the out-of-place sorter
if (sortingComparator.supportsSerializationWithKeyNormalization() &&
this.serializer.getLength() > 0 && this.serializer.getLength() <= THRESHOLD_FOR_IN_PLACE_SORTING)
this.sorter = new FixedLengthRecordSorter<IN>(this.serializer, sortingComparator.duplicate(), this.memory);
else
//通常情况下都是NormalizedKeySorter,sorter持有很多个内存段MemorySegment
this.sorter = new NormalizedKeySorter<IN>(this.serializer, sortingComparator.duplicate(), this.memory);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled())
LOG.debug("SynchronousChainedCombineDriver object reuse: " + (this.objectReuseEnabled ? "ENABLED" : "DISABLED") + ".");
2.3 collect()方法
接下来看collect()方法
collect()方法的主要实现大致:
-
将数据先写到缓冲区里,就是写入到sorter里
-
如果缓冲区写不下了,也就是写满了,就对缓冲区的数据进行按key排序并分组聚合,然后写出去,也就是写到ResultPartition里去
-
缓冲区的数据处理完之后,重置sorter,重新写到sorter里去。
public void collect(IN record)
this.numRecordsIn.inc();
// try writing to the sorter first
try
if (this.sorter.write(record))
return;
catch (IOException e)
throw new ExceptionInChainedStubException(this.taskName, e);
// do the actual sorting
try
//对缓冲的数据进行排序并进行数据聚合,写出去
sortAndCombine();
catch (Exception e)
throw new ExceptionInChainedStubException(this.taskName, e);
this.sorter.reset();
try
if (!this.sorter.write(record))
throw new IOException("Cannot write record to fresh sort buffer. Record too large.");
catch (IOException e)
throw new ExceptionInChainedStubException(this.taskName, e);
private void sortAndCombine() throws Exception
final InMemorySorter<IN> sorter = this.sorter;
if (objectReuseEnabled)
//和下面未使用对象重用的逻辑类似
...
else
if (!sorter.isEmpty())
//先用快速排序对sorter中的数据按key进行排序,然后分组聚合
this.sortAlgo.sort(sorter);
// run the combiner
final NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator<IN> keyIter = new NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator<IN>(sorter.getIterator(), this.groupingComparator);
// cache references on the stack
final GroupCombineFunction<IN, OUT> stub = this.combiner;
final Collector<OUT> output = this.outputCollector;
// run stub implementation
while (this.running && keyIter.nextKey())
stub.combine(keyIter.getValues(), output);
由上可以看到,数据的核心在数据是怎么样写到的缓存区里的,又是怎么进行排序和合并的。这些关键的实现都在sorter中,所以了解sorter是必须的。
3. 内存数据存储原理
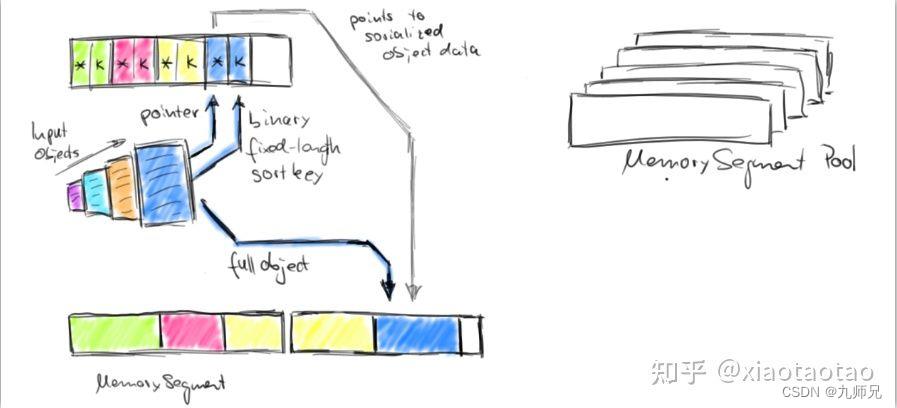
在分析sorter之前,先总结说一下sorter的数据存储的原理,以便更好的分析源码。flink在存储数据时,是将对象数据分为两部分存储,一部分存储真实的对象数据,一部分存储对象数据存放位置(即指针)+ 对象的key。反应在sorter持有的那些MemorySegment上,就是一部分的MemorySegment存放真实数据,一部分MemorySegment存放数据指针 + 数据的key,这样做的好处是排序的过程可以更加的高效,只需要对指针数据(包括指针和key)进行排序即可,因为排序过程需要进行数据交换,指针数据占用内存更少,对指针数据的交换更加高效。
注:下面我说的 指针数据(也叫索引数据) 包括数据指针+key,数据指针 才仅表示long型的offset
另外,指针数据在内存中所占的长度是定长的,指针是long型,占8个字节,key在组合情况下(例如一个元组中的两个或多个字段)最多占16个字节,单个(一个字段)情况最多占8个字节。例如使用string字符串作为key,那最多只截取前8位。有的key不足8位,那就用0补齐,如此一来,每个元素将使用16个字节作为指针数据。
因为key最多截取的前8位,那么不同的key前8位可能是相同的,那么在排序过程中如果两个key相同,就去比较对象数据,按照对象数据的key来做比较,这一步有一个反序列化的过程。
在读数据的时候,也是读取的指针数据,从指针数据中得到对象数据所在MemorySegment的位置,然后从对应的位置读取并反序列化成对象,所以这个指针数据也可以叫作索引数据。
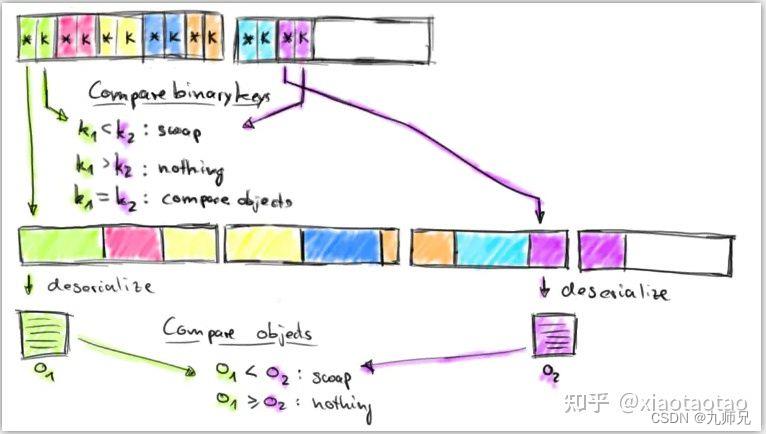
下面的两幅图说明了数据的存储和排序比较过程
存储:
排序比较:
4.NormalizedKeySorter
数据缓冲区NormalizedKeySorter
接下来我们来看这个InMemorySorter的实现,这里我们看通常情况下的NormalizedKeySorter
4.1 结构
首先我们看一下它的结构
public final class NormalizedKeySorter<T> implements InMemorySorter<T>
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NormalizedKeySorter.class);
//指针数据所占的字节长度
private static final int OFFSET_LEN = 8;
//key所占的最大长度
private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_NORMALIZED_KEY_LEN = 16;
//单个字段的key所占最大长度
private static final int MAX_NORMALIZED_KEY_LEN_PER_ELEMENT = 8;
//最少的MemorySegment个数
private static final int MIN_REQUIRED_BUFFERS = 3;
//大数据元素的阈值,超过这个阈值认为是大数据记录
private static final int LARGE_RECORD_THRESHOLD = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
private static final long LARGE_RECORD_TAG = 1L << 63;
private static final long POINTER_MASK = LARGE_RECORD_TAG - 1;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Members
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
//在排序过程中用于数据交换的buffer
private final byte[] swapBuffer;
//序列化器,用于将对象数据进行序列化存储和反序列化比较
private final TypeSerializer<T> serializer;
//比较器,用在排序比较过程
private final TypeComparator<T> comparator;
//存储数据的数据收集器,存储反序列化后的真实对象数据
private final SimpleCollectingOutputView recordCollector;
//用于从MemorySegment读取数据
private final RandomAccessInputView recordBuffer;
private final RandomAccessInputView recordBufferForComparison;
//当前存放指针数据的MemorySegment,SortIndex就是指的指针数据
private MemorySegment currentSortIndexSegment;
//总共的MemorySegment,就是一个个的buffer
private final ArrayList<MemorySegment> freeMemory;
//这里放的是所有存放指针数据的MemorySegment
private final ArrayList<MemorySegment> sortIndex;
//这里存放的是所有存储对象真实数据的MemorySegment
private final ArrayList<MemorySegment> recordBufferSegments;
//当前对象数据所在MemorySegment的位置,即数据指针
private long currentDataBufferOffset;
//指针数据的总大小
private long sortIndexBytes;
//指针数据在MemorySegment的位置
private int currentSortIndexOffset;
//总共记录条数
private int numRecords;
//key的字节大小
private final int numKeyBytes;
//每个元素指针数据的大小,包括指针+key
private final int indexEntrySize;
//每个MemorySegment可以存放多少个指针数据
private final int indexEntriesPerSegment;
//指针数据在MemorySegment最大的offset位置
private final int lastIndexEntryOffset;
//每个MemorySegment的buffer大小
private final int segmentSize;
//总共多少个MemorySegment
private final int totalNumBuffers;
private final boolean normalizedKeyFullyDetermines;
private final boolean useNormKeyUninverted;
从结构上我们看到了NormalizedKeySorter里定义了每个指针数据的大小,定义了专门用于存放指针数据的MemorySegment列表和专门用于存放对象数据的MemorySegment列表,定义了指针数据和对象数据在MemorySegment中的位置游标等等。
4.2 构造方法
下面来看NormalizedKeySorter的构造方法
了解了NormalizedKeySorter的结构之后,看构造方法就比较容易了,大致的实现就是给各个定义的成员变量进行赋值,在这个过程我们大概可以看到:
-
指针数据是定长的,包含了数据的位置指针和key,位置指针8字节,单个字段key最多8字节,多个字段组合key最多16字节。所以指针数据最多是24字节,key是一个字段的最多16字节
-
指针数据的MemorySegment和对象数据的MemorySegment都是从所有的MemorySegment列表里取的,即freeMemory
-
recordCollector(写)和recordBuffer(读)都是使用的对象数据存储的MemorySegment,这也是必然的
public NormalizedKeySorter(TypeSerializer<T> serializer, TypeComparator<T> comparator,
List<MemorySegment> memory, int maxNormalizedKeyBytes)
if (serializer == null || comparator == null || memory == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (maxNormalizedKeyBytes < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Maximal number of normalized key bytes must not be negative.");
this.serializer = serializer;
this.comparator = comparator;
this.useNormKeyUninverted = !comparator.invertNormalizedKey();
// check the size of the first buffer and record it. all further buffers must have the same size.
// the size must also be a power of 2
this.totalNumBuffers = memory.size();
if (this.totalNumBuffers < MIN_REQUIRED_BUFFERS)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Normalized-Key sorter requires at least " + MIN_REQUIRED_BUFFERS + " memory buffers.");
this.segmentSize = memory.get(0).size();
this.freeMemory = new ArrayList<MemorySegment>(memory);
// create the buffer collections
this.sortIndex = new ArrayList<MemorySegment>(16);
this.recordBufferSegments = new ArrayList<MemorySegment>(16);
// the views for the record collections
this.recordCollector = new SimpleCollectingOutputView(this.recordBufferSegments,
new ListMemorySegmentSource(this.freeMemory), this.segmentSize);
this.recordBuffer = new RandomAccessInputView(this.recordBufferSegments, this.segmentSize);
this.recordBufferForComparison = new RandomAccessInputView(this.recordBufferSegments, this.segmentSize);
// set up normalized key characteristics
if (this.comparator.supportsNormalizedKey())
// compute the max normalized key length
int numPartialKeys;
try
numPartialKeys = this.comparator.getFlatComparators().length;
catch (Throwable t)
numPartialKeys = 1;
int maxLen = Math.min(maxNormalizedKeyBytes, MAX_NORMALIZED_KEY_LEN_PER_ELEMENT * numPartialKeys);
this.numKeyBytes = Math.min(this.comparator.getNormalizeKeyLen(), maxLen);
this.normalizedKeyFullyDetermines = !this.comparator.isNormalizedKeyPrefixOnly(this.numKeyBytes);
else
this.numKeyBytes = 0;
this.normalizedKeyFullyDetermines = false;
// compute the index entry size and limits
//indexEntrySize即每个指针数据(也可以叫作索引数据,包括数据指针+key)的大小
this.indexEntrySize = this.numKeyBytes + OFFSET_LEN;
this.indexEntriesPerSegment = this.segmentSize / this.indexEntrySize;
this.lastIndexEntryOffset = (this.indexEntriesPerSegment - 1) * this.indexEntrySize;
this.swapBuffer = new byte[this.indexEntrySize];
// set to initial state
//给当前的指针数据存储分配一个MemorySegment
this.currentSortIndexSegment = nextMemorySegment();
this.sortIndex.add(this.currentSortIndexSegment);
//从freeMemory里获取一个MemorySegment,获取一个就删除一个,freeMemory里就少一个
private MemorySegment nextMemorySegment()
return this.freeMemory.remove(this.freeMemory.size() - 1);
4.3 缓存数据写入
下面我们看数据的写入过程
写入过程会分为两部分,一部分是指针数据(索引数据),一部分是对象真实数据。
大致实现如下:
-
如果当前的索引数据
MemorySegment写满了,就新获取一个MemorySegment,如果没有MemorySegment了,说明没有可用空间了,返回false -
将真实的对象数据写入到存放数据的
MemorySegment中,对象写入会进行反序列化,也就是说MemorySegment中存放的是对象的二进制数据。这个过程封装在SimpleCollectingOutputView中,如果没有空闲的MemorySegment了,就返回false -
将对象的索引数据写入到存放索引数据的
MemorySegment里,索引数据也即指针数据,记录的是对象数据所在MemorySegment中的位置和对象的key。注意这里的key是定长的,比如用一个字符串当做key,最多取前8个字符,如果不足8个字符就用0补齐
public boolean write(T record) throws IOException
//check whether we need a new memory segment for the sort index
//如果当前的索引数据MemorySegment写满了,就新获取一个MemorySegment,如果没有MemorySegment了,说明没有可用空间了,返回false
if (this.currentSortIndexOffset > this.lastIndexEntryOffset)
if (memoryAvailable())
this.currentSortIndexSegment = nextMemorySegment();
this.sortIndex.add(this.currentSortIndexSegment);
this.currentSortIndexOffset = 0;
this.sortIndexBytes += this.segmentSize;
else
return false;
// serialize the record into the data buffers
try
//将真实的对象数据写入到存放数据的MemorySegment
this.serializer.serialize(record, this.recordCollector);
catch (EOFException e)
//当没有可用空间了会抛出EOFException,返回false
return false;
final long newOffset = this.recordCollector.getCurrentOffset();
final boolean shortRecord = newOffset - this.currentDataBufferOffset < LARGE_RECORD_THRESHOLD;
if (!shortRecord && LOG.isDebugEnabled())
LOG.debug("Put a large record ( >" + LARGE_RECORD_THRESHOLD + " into the sort buffer");
// add the pointer and the normalized key
//将数据指针和对象的key写入到索引数据的MemorySegment里
this.currentSortIndexSegment.putLong(this.currentSortIndexOffset, shortRecord ?
this.currentDataBufferOffset : (this.currentDataBufferOffset | LARGE_RECORD_TAG));
if (this.numKeyBytes != 0)
this.comparator.putNormalizedKey(record, this.currentSortIndexSegment, this.currentSortIndexOffset + OFFSET_LEN, this.numKeyBytes);
this.currentSortIndexOffset += this.indexEntrySize;
this.currentDataBufferOffset = newOffset;
this.numRecords++;
return true;
简单看一下数据写入到MemorySegment的过程:
依次向MemorySegment里写入一个字节,如果MemorySegment空间不够,就获取一个新的MemorySegment,如果没有新的MemorySegment的,就抛出EOFException说明空间不足了。
//StringSerializer类
public void serialize(String record, DataOutputView target) throws IOException
StringValue.writeString(record, target);
//AbstractPagedOutputView类
public void writeByte(int v) throws IOException
if (this.positionInSegment < this.segmentSize)
this.currentSegment.put(this.positionInSegment++, (byte) v);
else
advance();
writeByte(v);
//AbstractPagedOutputView类
protected void advance() throws IOException
this.currentSegment = nextSegment(this.currentSegment, this.positionInSegment);
this.positionInSegment = this.headerLength;
//SimpleCollectingOutputView类
protected MemorySegment nextSegment(MemorySegment current, int positionInCurrent) throws EOFException
final MemorySegment next = this.memorySource.nextSegment();
if (next != null)
this.fullSegments.add(next);
this.segmentNum++;
return next;
else
throw new EOFException();
到现在,数据的写入大致的分析完毕了。
返回到SynchronousChainedCombineDriver算子,当sorter的数据写满了,就开始进行排序和数据聚合了。
5.数据排序
排序使用的是快速排序算法,flink里快速排序的算法比较复杂,这里就不分析具体实现原理了,只看看NormalizedKeySorter是如何进行比较的:
-
比较的过程是比较的索引数据,即存放索引数据的那些MemorySegment,首先比较索引数据中的key值,如果key不相等,就直接返回比较结果int值,如果key相等,就比较对象数据
-
根据数据指针从存放数据的
MemorySegment中获取对象数据,进行反序列化成对象,然后再根据对象来比较。例如用字符串当key,因为key只能取前8位,所以当key一样时需要根据对象数据的完整key来比较
由此也可以看到一个问题,如果相同的key的数据很多,那么将会进行很多次的数据反序列化操作,这会耗费一定的性能。
//NormalizedKeySorter
public int compare(int segmentNumberI, int segmentOffsetI, int segmentNumberJ, int segmentOffsetJ)
final MemorySegment segI = this.sortIndex.get(segmentNumberI);
final MemorySegment segJ = this.sortIndex.get(segmentNumberJ);
//比较索引数据中的key值,如果key不相等,就直接返回比较结果int值,如果key相等,比较对象数据
int val = segI.compare(segJ, segmentOffsetI + OFFSET_LEN, segmentOffsetJ + OFFSET_LEN, this.numKeyBytes);
if (val != 0 || this.normalizedKeyFullyDetermines)
return this.useNormKeyUninverted ? val : -val;
final long pointerI = segI.getLong(segmentOffsetI) & POINTER_MASK;
final long pointerJ = segJ.getLong(segmentOffsetJ) & POINTER_MASK;
return compareRecords(pointerI, pointerJ);
//NormalizedKeySorter
private int compareRecords(long pointer1, long pointer2)
//根据数据指针从存放数据的MemorySegment中获取对象数据,进行反序列化比较
this.recordBuffer.setReadPosition(pointer1);
this.recordBufferForComparison.setReadPosition(pointer2);
try
return this.comparator.compareSerialized(this.recordBuffer, this.recordBufferForComparison);
catch (IOException ioex)
throw new RuntimeException("Error comparing two records.", ioex);
//StringComparator
public int compareSerialized(DataInputView firstSource, DataInputView secondSource) throws IOException
String s1 = StringValue.readString(firstSource);
String s2 = StringValue.readString(secondSource);
int comp = s1.compareTo(s2);
return ascendingComparison ? comp : -comp;
//PojoComparator
public int compareSerialized(DataInputView firstSource, DataInputView secondSource) throws IOException
T first = this.serializer.createInstance();
T second = this.serializer.createInstance();
//有一个反序列化的过程
first = this.serializer.deserialize(first, firstSource);
second = this.serializer.deserialize(second, secondSource);
return this.compare(first, second);
可以看到排序过程中实际的对象数据并没有动,排序和交换的是索引数据,不同的key的索引数据按照自然顺序进行了排序,相同key的索引数据都放在了一起。之后再根据这些索引数据读实际的对象数据,相同key的数据就能放在一起进行聚合了。
6.数据聚合
经过排序之后,NormalizedKeySorter中key相同的对象数据,它们的索引数据都放在了一起,就可以开始进行数据的聚合了。
if (!sorter.isEmpty())
this.sortAlgo.sort(sorter);
// run the combiner
final NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator<IN> keyIter = new NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator<IN>(sorter.getIterator(), this.groupingComparator);
// cache references on the stack
final GroupCombineFunction<IN, OUT> stub = this.combiner;
final Collector<OUT> output = this.outputCollector;
// run stub implementation
while (this.running && keyIter.nextKey())
stub.combine(keyIter.getValues(), output);
在这个过程中,最关键的是NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator的实现,它的主要功能就是实现获取一个key的所有对象数据。
7. NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator
分组迭代器NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator
在这之前,我们先看sorter.getIterator(),NonReusingKeyGroupedIterator持有了这个iterator的引用。
可以看到这个iterator就是读取NormalizedKeySorter中排序好的索引数据,依次读索引数据,然后根据索引指针从实际数据存储中读取对象数据。
//NormalizedKeySorter类
public final MutableObjectIterator<T以上是关于FlinkFlink 批处理模式Map端数据聚合 NormalizedKeySorter的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章