MyBatis-Plus 使用这么方便,底层是如何处理的呢?
Posted Java知音_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MyBatis-Plus 使用这么方便,底层是如何处理的呢?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
点击关注公众号,实用技术文章及时了解
文章目录
Mapper 对象方法映射为 SQL 语句
Mapper 操作数据库的流程
前言
MyBatis-plus是完全基于MyBatis开发的一个增强工具,是在MyBatis的基础上做增强的框架,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
它在MyBatis原本的框架上增加了很多实用性功能,比如乐观锁插件、字段自动填充功能、分页插件、条件构造器、sql 注入器等等。使用 MyBatis-plus 可以完全不写任何 XML 文件,直接使用继承了BaseMapper 接口的类对象完成对数据库的映射操作
基于映射的原理,MyBatis-plus 必然要实现 Mapper中的方法与 SQL 语句的对应转化,以下即为 MyBatis-plus 重要流程图例
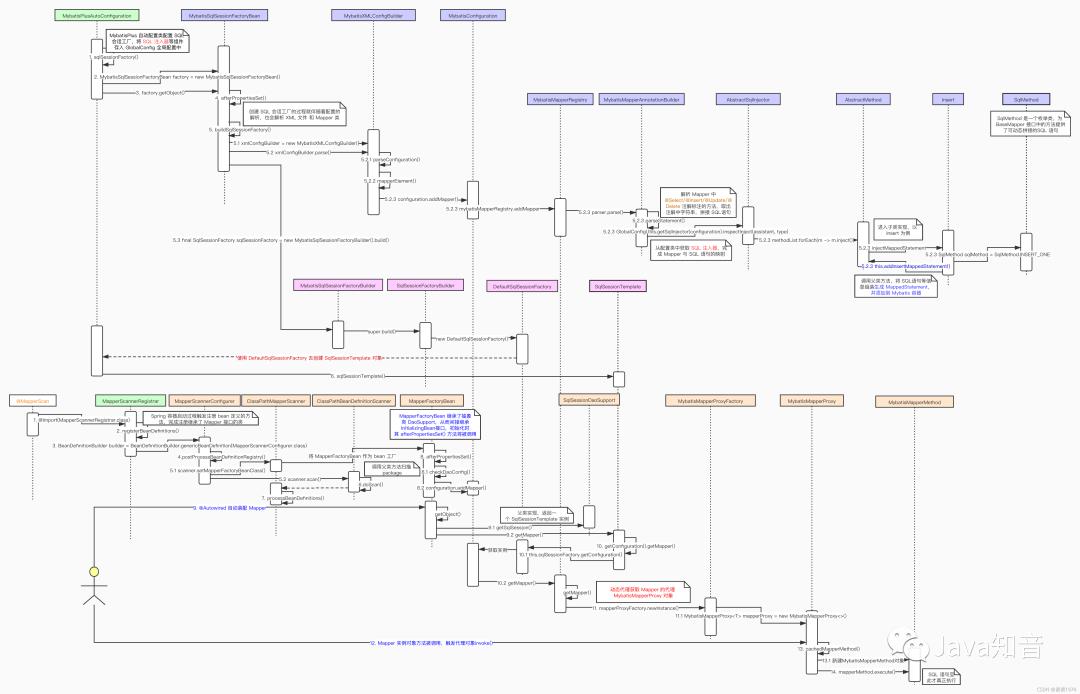
1. Mapper 对象方法映射为 SQL 语句
1.在 MyBatis-plus 中, MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration 自动配置类的 sqlSessionFactory()方法为 Spring提供创建 sqlSession的工厂类对象,对 sqlSessionFactory 进行定义的定义类变为了 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean。
在 sqlSessionFactory()方法中,除了注入 MyBatis本身的组件,还会注入MyBatis-plus 的 主键生成器、SQL 注入器等组件,最后通过 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject() 方法获取到 sqlSessionFactory 对象
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception
// TODO 使用 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean 而不是 SqlSessionFactoryBean
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation()))
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
applyConfiguration(factory);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null)
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
......
// TODO 自定义枚举包
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeEnumsPackage()))
factory.setTypeEnumsPackage(this.properties.getTypeEnumsPackage());
// TODO 此处必为非 NULL
GlobalConfig globalConfig = this.properties.getGlobalConfig();
// TODO 注入填充器
if (this.applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(MetaObjectHandler.class,
false, false).length > 0)
MetaObjectHandler metaObjectHandler = this.applicationContext.getBean(MetaObjectHandler.class);
globalConfig.setMetaObjectHandler(metaObjectHandler);
// TODO 注入主键生成器
if (this.applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(IKeyGenerator.class, false,
false).length > 0)
IKeyGenerator keyGenerator = this.applicationContext.getBean(IKeyGenerator.class);
globalConfig.getDbConfig().setKeyGenerator(keyGenerator);
// TODO 注入sql注入器
if (this.applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(ISqlInjector.class, false,
false).length > 0)
ISqlInjector iSqlInjector = this.applicationContext.getBean(ISqlInjector.class);
globalConfig.setSqlInjector(iSqlInjector);
// TODO 设置 GlobalConfig 到 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean
factory.setGlobalConfig(globalConfig);
return factory.getObject();
2.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean#getObject() 执行懒加载策略,最后通过 buildSqlSessionFactory() 方法创建 SqlSessionFactory 工厂类对象。这个方法的流程很长,不过大致可以分为两个步骤:
创建
MybatisXMLConfigBuilder对象,调用其parse()方法去解析 XML 配置文件及 Mapper解析获得的信息存储在
targetConfiguration对象中,根据其信息创建SqlSessionFactory对象
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception
final MybatisConfiguration targetConfiguration;
// TODO 使用 MybatisXmlConfigBuilder 而不是 XMLConfigBuilder
MybatisXMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
......
else if (this.configLocation != null)
// TODO 使用 MybatisXMLConfigBuilder
// 1.1 创建 MybatisConfiguration 对象
xmlConfigBuilder = new MybatisXMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
// 2.1 将解析获得的信息的引用传递给 targetConfiguration 对象
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
else
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
// TODO 使用 MybatisConfiguration
targetConfiguration = new MybatisConfiguration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
// TODO 无配置启动所必须的
this.globalConfig = Optional.ofNullable(this.globalConfig).orElseGet(GlobalConfigUtils::defaults);
this.globalConfig.setDbConfig(Optional.ofNullable(this.globalConfig.getDbConfig()).orElseGet(GlobalConfig.DbConfig::new));
// TODO 初始化 id-work 以及 打印骚东西
targetConfiguration.setGlobalConfig(this.globalConfig);
......
// 1.2 开始解析 XML 配置文件 及 Mapper 接口
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null)
try
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
catch (Exception ex)
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.class.getSimpleName(),
this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory,
this.dataSource));
if (this.mapperLocations != null)
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0)
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
else
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations)
if (mapperLocation == null)
continue;
try
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
catch (Exception e)
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
else
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
// 2.2 根据 targetConfiguration 对象中保存的信息创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(targetConfiguration);
......
return sqlSessionFactory;
3.MybatisXMLConfigBuilder#parse() 会去解析配置文件,最后会调用到其内部方法 mapperElement()。这个方法完成解析 Mapper工作,并将其添加到配置类 MybatisConfiguration 中
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception
/*
* 定义集合 用来分类放置mybatis的Mapper与XML 按顺序依次遍历
*/
if (parent != null)
//指定在classpath中的mapper文件
Set<String> resources = new HashSet<>();
//指向一个mapper接口
Set<Class<?>> mapperClasses = new HashSet<>();
setResource(parent, resources, mapperClasses);
// 依次遍历 首先 resource 然后 mapper
for (String resource : resources)
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//TODO
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
for (Class<?> mapper : mapperClasses)
// 主要关注此处
configuration.addMapper(mapper);
4.MybatisConfiguration#addMapper()方法其实是去调用 MybatisMapperRegistry#addMapper() 方法,其核心是MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder#parse()
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type)
if (type.isInterface())
if (hasMapper(type))
// TODO 如果之前注入 直接返回
return;
// TODO 这里就不抛异常了
// throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try
// TODO 这里也换成 MybatisMapperProxyFactory 而不是 MapperProxyFactory
knownMappers.put(type, new MybatisMapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// TODO 这里也换成 MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder 而不是 MapperAnnotationBuilder
MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
finally
if (!loadCompleted)
knownMappers.remove(type);
5.MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder#parse() 方法真正开始完成 Mapper 接口中的方法与 SQL 语句的映射,其中 parseStatement()方法是解析 @Select/@Update 等注解写入的 SQL语句,而代码 GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type) 通过 MaBatis-plus的 SQL 注入器完成 Mapper 方法与 SQL 语句的转化
@Override
public void parse()
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource))
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
final String typeName = type.getName();
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(typeName);
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
SqlParserHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(type);
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods)
try
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge())
// 解析 @Select 注解写入的 SQL
parseStatement(method);
SqlParserHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(typeName, method);
catch (IncompleteElementException e)
// TODO 使用 MybatisMethodResolver 而不是 MethodResolver
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MybatisMethodResolver(this, method));
// TODO 注入 CURD 动态 SQL , 放在在最后, because 可能会有人会用注解重写sql
if (GlobalConfigUtils.isSupperMapperChildren(configuration, type))
GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type);
parsePendingMethods();
6.AbstractSqlInjector#inspectInject() 会完成 BaseMapper 接口中提供的通用方法对应的 SQL 语句准备,这部分主要通过 AbstractMethod#inject()方法完成
@Override
public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass)
Class<?> modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass);
if (modelClass != null)
String className = mapperClass.toString();
Set<String> mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration());
if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className))
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = this.getMethodList(mapperClass);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(methodList))
TableInfo tableInfo = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass);
// 循环注入自定义方法
methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo));
else
logger.debug(mapperClass.toString() + ", No effective injection method was found.");
mapperRegistryCache.add(className);
7.AbstractMethod#inject()方法并没有什么特别的操作,只是调用其子类实现 injectMappedStatement()方法。以 SelectOne#injectMappedStatement() 为例,其 SQL 语句的核心在于 SqlMethod 类,这个枚举类中缓存了可以动态拼接的 SQL 语句脚本,只需要填上参数 format 就可以得到 SQL 语句的执行脚本。
以上过程结束,只需要将所有信息通过 addInsertMappedStatement()方法封装成 MappedStatement对象并将其加入到容器中,这样 Mapper接口方法调用时,就可以通过 动态代理 的方式找到其对应执行的 SQL 脚本,至此 SQL 语句准备及配置解析就完成了。
最后拼接的 SQL 语句 脚本形式如下示例,实际执行数据库操作时会解析这个脚本完成变量替换,从而得到可执行的 SQL 语句
<script>
<choose>
<when test="ew != null and ew.sqlFirst != null">
$ew.sqlFirst
</when>
<otherwise></otherwise>
</choose>
SELECT
<choose>
<when test="ew != null and ew.sqlSelect != null">
$ew.sqlSelect
</when>
<otherwise>id,name,type</otherwise>
</choose>
FROM node
<if test="ew != null">
<where>
<if test="ew.entity != null">
<if test="ew.entity.id != null">id=#ew.entity.id</if>
<if test="ew.entity['name'] != null">AND name=#ew.entity.name</if>
<if test="ew.entity['type'] != null">AND type=#ew.entity.type</if>
</if>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.nonEmptyOfWhere">
<if test="ew.nonEmptyOfEntity and ew.nonEmptyOfNormal">AND</if>
$ew.sqlSegment
</if>
</where>
<if test="ew.sqlSegment != null and ew.sqlSegment != '' and ew.emptyOfWhere">
$ew.sqlSegment
</if>
</if>
<choose>
<when test="ew != null and ew.sqlComment != null">
$ew.sqlComment
</when>
<otherwise></otherwise>
</choose>
</script>@Override
public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo)
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_ONE;
SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(),
sqlFirst(), sqlSelectColumns(tableInfo, true), tableInfo.getTableName(),
sqlWhereEntityWrapper(true, tableInfo), sqlComment()), modelClass);
return this.addSelectMappedStatementForTable(mapperClass, getMethod(sqlMethod), sqlSource, tableInfo);
8.SqlSessionFactory对象的创建需要回到 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory()方法中,很容易追踪到 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build()方法,最后其实是通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build()方法创建了一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象返回
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config)
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
2. Mapper 操作数据库的流程
1.@MapperScan 注解通过 @Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class) 引入扫描注册的类MapperScannerRegistrar,该类实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口并重写registerBeanDefinitions()方法,在该方法中注册了 MapperScannerConfigurer 类
void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName)
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);
......
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, builder.getBeanDefinition());
2.MapperScannerConfigurer 是 Mapper接口的扫描配置类,实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,其 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法会在容器启动过程中被回调,通过 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan()方法完成 Mapper 的扫描注册
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders)
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization))
scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization));
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
3.ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions() 将扫描到的 Mapper接口生成的对应 BeanDefinition 的 beanClass 属性替换为 MapperFactoryBean,这样每次获取 Mapper 实例实际是通过 MapperFactoryBean 的实例去获取
此处体现了 FactoryBean 的定位,即用于获取同一类 bean 的工厂 bean
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions)
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions)
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + beanClassName
+ "' mapperInterface");
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName))
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null)
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName))
if (explicitFactoryUsed)
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null)
if (explicitFactoryUsed)
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
if (!explicitFactoryUsed)
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
definition.setLazyInit(lazyInitialization);
4.@Autowired 自动注入 Mapper 触发容器获取 bean 的方法,调用到 MapperFactoryBean#getObject()方法,最终调用到 sqlSessionTemplate#getMapper()方法
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type)
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
5.MyBatis-plus 使用的配置类是MybatisConfiguration,最终调用到 MybatisMapperRegistry#getMapper()方法,这里就进入了动态代理获取 MapperProxy 实例的流程
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession)
// TODO 这里换成 MybatisMapperProxyFactory 而不是 MapperProxyFactory
final MybatisMapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MybatisMapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null)
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MybatisPlusMapperRegistry.");
try
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
catch (Exception e)
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
6.MybatisMapperProxyFactory#newInstance()方法给自动注入返回一个 MybatisMapperProxy 代理对象
protected T newInstance(MybatisMapperProxy<T> mapperProxy)
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]mapperInterface, mapperProxy);
7.调用 Mapper 接口的方法触发代理对象的 MybatisMapperProxy#invoke(),此时根据 Mapper 对象被调用的方法生成 MybatisMapperMethod 对象,通过MybatisMapperMethod#execute()去真正地执行 SQL 语句,从而完成数据库操作。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
try
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass()))
return method.invoke(this, args);
else if (method.isDefault())
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
catch (Throwable t)
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
final MybatisMapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
来源:blog.csdn.net/weixin_45505313/article/
details/104855453
推荐
PS:因为公众号平台更改了推送规则,如果不想错过内容,记得读完点一下“在看”,加个“星标”,这样每次新文章推送才会第一时间出现在你的订阅列表里。点“在看”支持我们吧!
以上是关于MyBatis-Plus 使用这么方便,底层是如何处理的呢?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章