(数据分析三板斧)第二斧Pandas-第二节:Pandas基本数据操作与运算
Posted 快乐江湖
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了(数据分析三板斧)第二斧Pandas-第二节:Pandas基本数据操作与运算相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一:基本数据操作
(1)索引操作
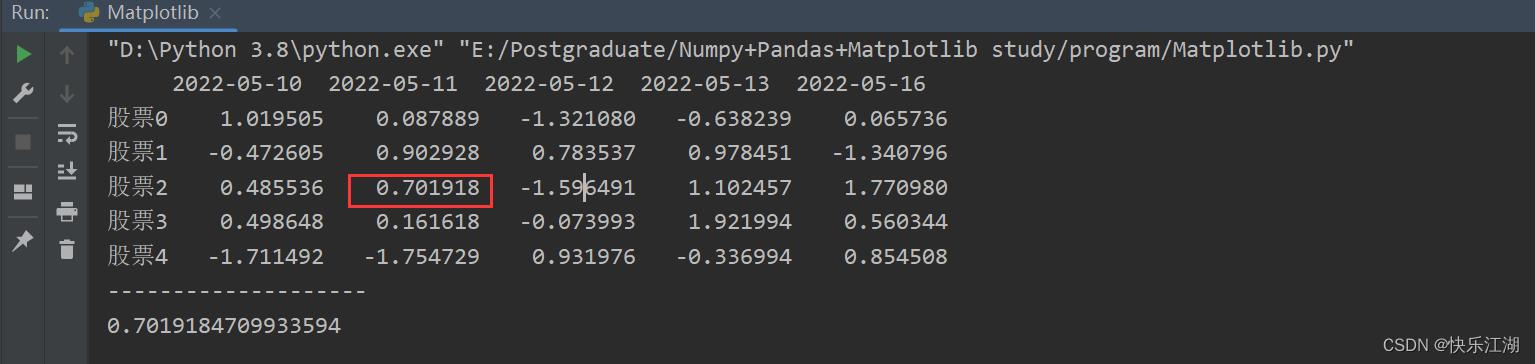
A:直接索引
这里的直接索引和Numpy中有所区别,也即不能执行如a[0, 1]这样的操作,正确的写法是先列再行,如下
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head())
print("-"*20)
print(a["2022-05-11"]["股票2"])
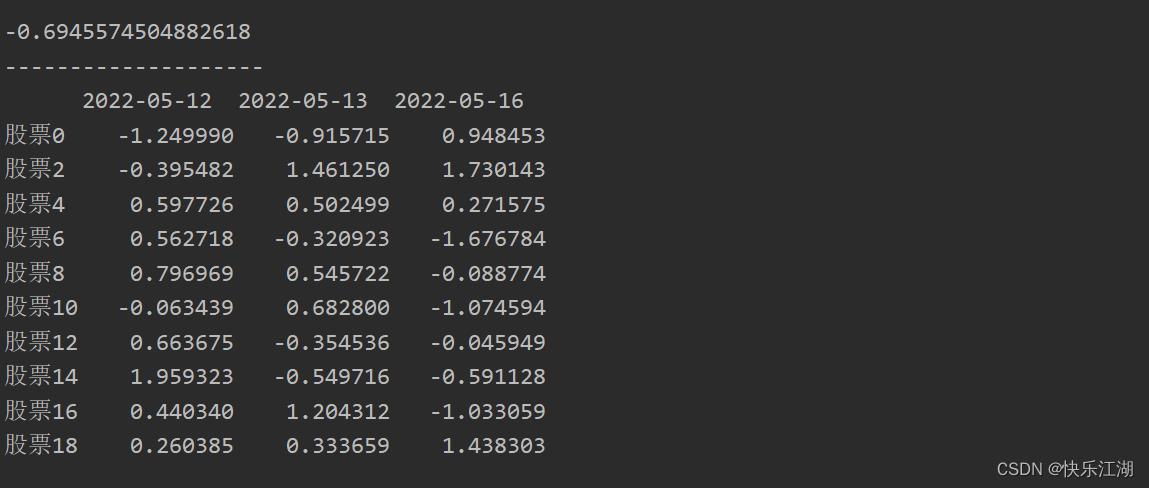
B:使用iloc进行索引
这一点其实在上一小节说到过,而且使用频次非常高,它和Numpy中的索引、切片操作类似
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head())
print("-"*20)
print(a.iloc[2, 1]) # 索引
print("-"*20)
print(a.iloc[0::2, 2:]) # 切片
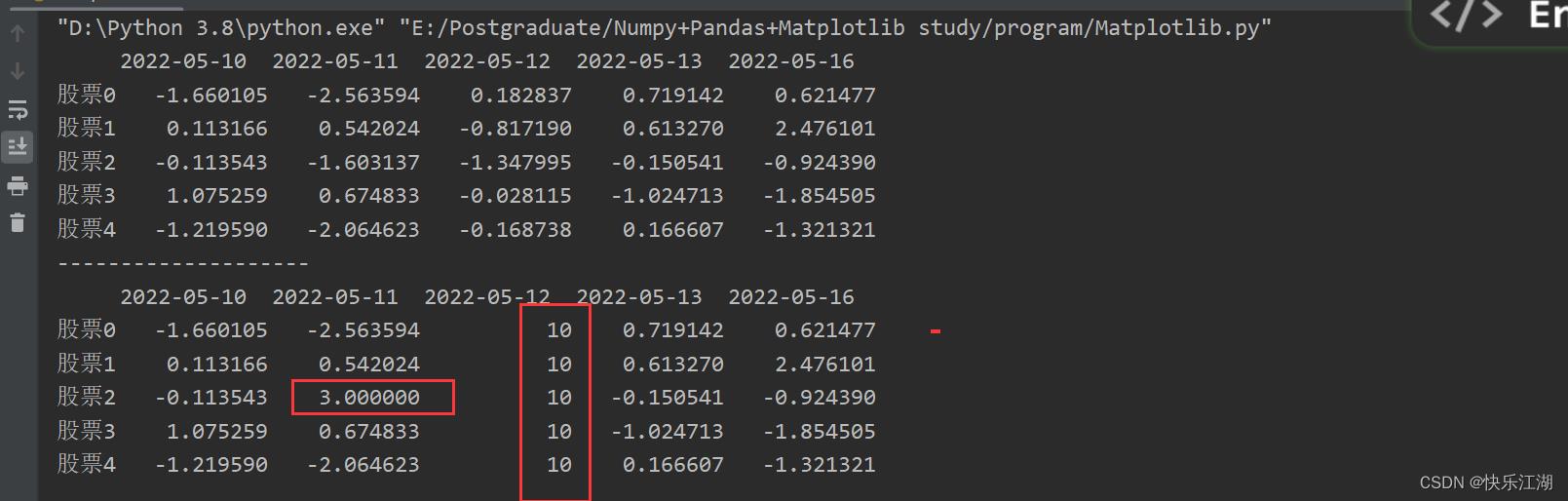
(2)赋值操作
赋值操作会和索引操作结合,这里不再多少;不够需要注意的是,Pandas中可以为某列属性统一设值
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head())
print("-"*20)
a.iloc[2, 1] = 3
a["2022-05-12"] = 10
print(a.head())
(3)排序操作
A:DataFrame
①:按内容排序
使用DataFrame.set_values()可以按照内容对DataFrame排序,内含两个参数
by:指定依据哪个列进行排序(注意:可以传入列表,此时前面的列就类似于Excel中的主要关键字,后面的就类似于次要关键字)ascending:默认为True,表示升序;设置为False表示降序
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head())
print("-"*20)
b = a.sort_values(by='2022-05-11', ascending=False) # 按2022-05-11交易额从大到小排序
print(b)
################################结果
2022-05-10 2022-05-11 2022-05-12 2022-05-13 2022-05-16
股票0 1.140266 -0.335673 -0.609860 1.455295 -1.404658
股票1 0.536550 1.236006 0.190541 -1.317378 -0.723883
股票2 -0.470633 -1.443694 -0.000648 0.033552 0.892974
股票3 0.624107 1.194269 1.430418 -0.457140 0.422416
股票4 1.151253 0.480178 2.920191 2.672906 -0.946110
--------------------
2022-05-10 2022-05-11 2022-05-12 2022-05-13 2022-05-16
股票8 0.345007 2.247404 0.343531 -0.713948 1.312751
股票1 0.536550 1.236006 0.190541 -1.317378 -0.723883
股票3 0.624107 1.194269 1.430418 -0.457140 0.422416
股票16 -0.022314 0.978442 -0.385441 0.425358 0.256676
股票14 -0.095465 0.825514 -2.102140 0.140338 0.682775
股票4 1.151253 0.480178 2.920191 2.672906 -0.946110
股票9 -0.248780 0.304714 0.785853 0.443867 2.091956
股票11 -0.764729 0.227958 0.095879 0.003024 -2.472051
股票18 -1.805458 0.199713 1.305307 -0.016038 0.866450
股票7 0.009133 0.033530 1.766141 -1.305760 -0.550846
股票15 0.013513 0.023848 -1.593861 -0.895160 -0.257068
股票10 0.394090 -0.025457 0.119109 0.507042 -0.631266
股票5 -0.314802 -0.087573 -0.287413 -0.258240 -0.398647
股票13 -0.545517 -0.258856 1.314928 -0.270260 -0.986413
股票12 -0.218475 -0.291619 -0.454326 0.886155 0.692385
股票0 1.140266 -0.335673 -0.609860 1.455295 -1.404658
股票17 -1.350691 -0.450121 0.285704 -0.004896 -2.870467
股票2 -0.470633 -1.443694 -0.000648 0.033552 0.892974
股票6 1.376071 -1.948821 -0.562346 -1.127938 -1.017620
股票19 1.800965 -2.048083 -0.740680 -0.407289 0.226595
再比如传入列表
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head())
print("-"*20)
b = a.sort_values(by=['2022-05-11', '2022-05-12'], ascending=False) # 按2022-05-11交易额从大到小排序,如果相同再按'2022-05-12'排序
print(b)
################################结果
2022-05-10 2022-05-11 2022-05-12 2022-05-13 2022-05-16
股票0 -0.696859 1.135797 -0.198742 -0.686441 0.647720
股票1 -0.791635 1.277678 0.324301 0.557662 0.959444
股票2 -0.002558 -0.010332 0.407265 -0.312768 -1.287430
股票3 0.310360 -0.614057 0.017131 -0.718071 -0.076585
股票4 0.772929 -0.518885 -1.159284 1.296433 -1.623409
--------------------
2022-05-10 2022-05-11 2022-05-12 2022-05-13 2022-05-16
股票18 -0.136648 1.755186 -0.741259 -0.636747 0.887794
股票8 1.400976 1.564791 0.353867 -2.015033 -1.505703
股票6 -0.253795 1.526582 -0.434713 0.200566 -1.073504
股票1 -0.791635 1.277678 0.324301 0.557662 0.959444
股票9 0.955544 1.228857 -0.862442 -0.713909 0.777751
股票0 -0.696859 1.135797 -0.198742 -0.686441 0.647720
股票17 -1.090038 1.069987 -0.598334 0.788517 0.213765
股票12 0.056584 1.019725 0.562919 -1.080408 0.250403
股票14 0.273654 0.573102 0.946956 -1.462846 -0.848182
股票19 -1.265085 0.524326 1.168115 -0.032979 1.396737
股票16 1.731010 0.326501 1.378928 0.513753 0.263608
股票13 0.602576 0.205295 0.740936 0.833047 0.604638
股票5 0.744839 0.010035 1.732724 -0.443837 0.405501
股票2 -0.002558 -0.010332 0.407265 -0.312768 -1.287430
股票7 1.025292 -0.309240 0.763632 -0.340627 -0.695329
股票15 -1.267292 -0.349368 1.162461 0.902893 -0.213027
股票4 0.772929 -0.518885 -1.159284 1.296433 -1.623409
股票3 0.310360 -0.614057 0.017131 -0.718071 -0.076585
股票10 2.136984 -1.087719 0.237653 1.366751 0.270767
股票11 -1.583523 -1.269841 1.655004 -0.526091 0.661879
②:按索引排序
使用DataFrame.sort_index()可以依据索引对DataFrame进行排序,比较简单就不再演示了
B:Series
Series就更简单了,因为它只有一列,所有你只需要指定ascending即可
二:数据运算
- Pandas运算函数非常多,用到再查也不迟:文档
A:算数运算
算数运算很简单,就是常见的+、-、*、\\等,对不同的对象操作就有不同的结果(也即它可以整体对DataFrame或者Series操作或者索引,很多时候也会和索引、切片结合)
stock_change = np.random.normal(0, 1, (20, 5))
stock_index = ["股票".format(i) for i in range(20)] # 行索引
date_index = pd.date_range(start='20220510', periods=5, freq='B') # 列索引
a = pd.DataFrame(stock_change, index=stock_index, columns=date_index)
print(a.head(3))
print("-"*20)
b = a.add(10) # 全部加10
print(b.head(3))
print("-"*20)
c = a["2022-5-10"].sub(3) # 某列减3
print(c.head(3))
print("-"*20)
d = a["2022-5-10"].sub(a["2022-5-13"]) # 列运算
print(c.head(3))
print("-"*20)
print(d.head(3))
B:逻辑运算
C:统计运算
D:自定义运算
以上是关于(数据分析三板斧)第二斧Pandas-第二节:Pandas基本数据操作与运算的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章