二叉树寻找前驱的普通方法和线索二叉树对比
Posted 肥学
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树寻找前驱的普通方法和线索二叉树对比相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录标题
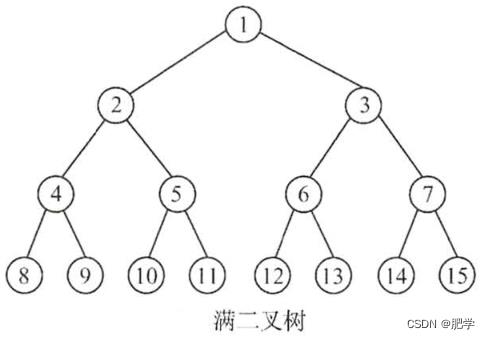
普通方法
//结构体
typedef struct TreeNode
int data;
struct TreeNode* lchild;
struct TreeNode* rchild;
*BT,TN;
//寻找二叉树中序遍历的前驱
BT pre;
void findPreInorder(BT root,int p)
if (!root)return;
findPreInorder(root->lchild,p);
if (root->data == p)
printf("%d\\n", pre->data);
return;
else
pre = root;
findPreInorder(root->rchild,p);
//寻找二叉树中序遍历的后继
TN pre1 = -1;
BT pre2 = &pre1;
void findSubInorder(BT root, int p)
if (!root)return;
findSubInorder(root->lchild, p);
if (pre2->data == p) //当前驱等于要找的节点的时候该节点就是要寻找的后继
printf("%d\\n", root->data);
pre2->data = -1;//防止下次再进入if
return;
else
pre2 = root;
findSubInorder(root->rchild, p);
//中序遍历该树用作对比,看看一会我们求得前驱和后继对不对
void inorder(BT temphead)
if (!temphead)return;
inorder(temphead->lchild);
printf("%d ", temphead->data);
inorder(temphead->rchild);
//广度优先初始化二叉树,图像和上面图片一样
void order(BT head)
queue<BT> q;
BT node = (BT)malloc(sizeof(BT));
q.push(head);
int i = 2;
while (i < 16)
BT lnode = (BT)malloc(sizeof(BT));
lnode->data = i;
lnode->lchild = NULL;
lnode->rchild = NULL;
i++;
BT rnode = (BT)malloc(sizeof(BT));
rnode->data = i;
rnode->lchild = NULL;
rnode->rchild = NULL;
i++;
q.front()->lchild = lnode;
q.front()->rchild = rnode;
q.pop();
q.push(lnode);
q.push(rnode);
int main()
BT head = (BT)malloc(sizeof(BT));
head->data = 1;
order(head);
BT temphead = head;//避免一会树得根节点地址丢失
printf("中序遍历:\\n");
inorder(temphead);
printf("\\n寻找节点5的前驱:");
temphead = head;
findPreInorder(temphead, 5);
printf("\\n寻找节点5的后继:");
temphead = head;
findSubInorder(temphead, 5);
缺点
每次寻找某节点前驱还要再遍历一次二叉树不能直接得到某节点的前驱
线索二叉树
之前我们提到了,二叉树的是存在n+1个空链域的,反正这些内存空着也是空着大佬们就想到了利用这些空的链域搞点事情,弄出了一个线索二叉树。
//建立
typedef struct TreeNode
int data;
bool tagClueLChild=false;
bool tagClueRChild=false;
struct TreeNode* lChild=NULL;
struct TreeNode* rChild=NULL;
*BT;
//中序遍历线索二叉树
void cluePreInorder(BT root)
if (!root)return;
cluePreInorder(root->lChild);
visit(root);
cluePreInorder(root->rChild);
//建立一个全局前驱节点
static BT pre;
void visit(BT root)
if (root->lChild == NULL)
root->lChild = pre;
root->tagClueLChild = true;
if (pre != NULL && pre->rChild == NULL)
pre->rChild = root;
pre->tagClueRChild = true;
pre = root;
然后我们就可以愉快的直接从某个节点直接找到它的前驱和后继了不用再去遍历一遍二叉树了。
注意
这里我们只给出了中序的线索二叉树实现,但是再实现先序线索二叉树的时候要避免死循环的情况
//先序遍历线索二叉树
void cluePrePreorder(BT root)
if (!root)return;
visit(root);
cluePrePreorder(root->lChild);
cluePrePreorder(root->rChild);
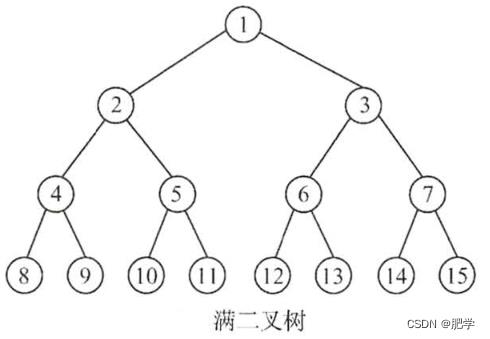
也就是当root的节点为8的时候,二叉树的前驱pre为4,再visit的时候会把8的lChild指向4节点在进行下一句cluePrePreorder(root->lChild);又会回到8节点此时8节点以经访问过了。所以代码要改进为
//先序遍历线索二叉树
void cluePrePreorder(BT root)
if (!root)return;
visit(root);
if(root->tagClueLChild)//当不是线索二叉树的时候
cluePrePreorder(root->lChild);
cluePrePreorder(root->rChild);
要对最后一个节点的tagClueLChild修改为true
以上是关于二叉树寻找前驱的普通方法和线索二叉树对比的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章