linux内核源码分析之sysfs文件系统
Posted 为了维护世界和平_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了linux内核源码分析之sysfs文件系统相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
源码结构
源码中sysfs目录结构,文件比较少,根据文件名即可知其含义。
创建目录
任何 kobject 在系统中注册,就会有一个目录在 sysfs 中被创建。这个目录是作为该 kobject 的父对象所在目录的子目录创建的。sysfs 中的顶层目录代表着内核对象层次的共同祖先;例如:某些对象属于某个子系统。
Sysfs 在与其目录关联的 kernfs_node 对象中内部保存一个指向实现目录的 kobject 的指针。
属性
kobject 的属性可在文件系统中以普通文件的形式导出。Sysfs 为属性定义了面向文件 I/O 操作的方法,以提供对内核属性的读写。一个简单的属性结构定义如下:
struct attribute
char * name;
struct module *owner;
umode_t mode;
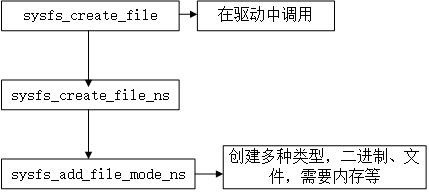
;int sysfs_create_file(struct kobject * kobj, const struct attribute * attr);
void sysfs_remove_file(struct kobject * kobj, const struct attribute * attr);
一个单独的属性结构并不包含读写其属性值的方法。子系统最好为特定对象类型的属性定义自己的属性结构体和封装函数。
在驱动中的数据结构组织方式
struct device_attribute
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
;
int device_create_file(struct device *, const struct device_attribute *);
void device_remove_file(struct device *, const struct device_attribute *);
宏定义的使用
static DEVICE_ATTR(foo, S_IWUSR | S_IRUGO, show_foo, store_foo);等同于如下代码:
static struct device_attribute dev_attr_foo =
.attr =
.name = "foo",
.mode = S_IWUSR | S_IRUGO,
.show = show_foo,
.store = store_foo,
,
;
子系统的回调函数
当定义一个新的属性类型时,必须实现一系列的 sysfs 操作,以帮助读写调用实现属性所有者的显示和储存方法。
struct sysfs_ops
ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, char *);
ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *, struct attribute *, const char *, size_t);
;示例:
#define to_dev(obj) container_of(obj, struct device, kobj)
#define to_dev_attr(_attr) container_of(_attr, struct device_attribute, attr)
static ssize_t dev_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
struct device_attribute *dev_attr = to_dev_attr(attr);
struct device *dev = to_dev(kobj);
ssize_t ret = -EIO;
if (dev_attr->show)
ret = dev_attr->show(dev, dev_attr, buf);
if (ret >= (ssize_t)PAGE_SIZE)
printk("dev_attr_show: %pS returned bad count\\n",
dev_attr->show);
return ret;
读写属性数据
在声明属性时,必须指定 show() 或 store() 方法,以实现属性的读或写。
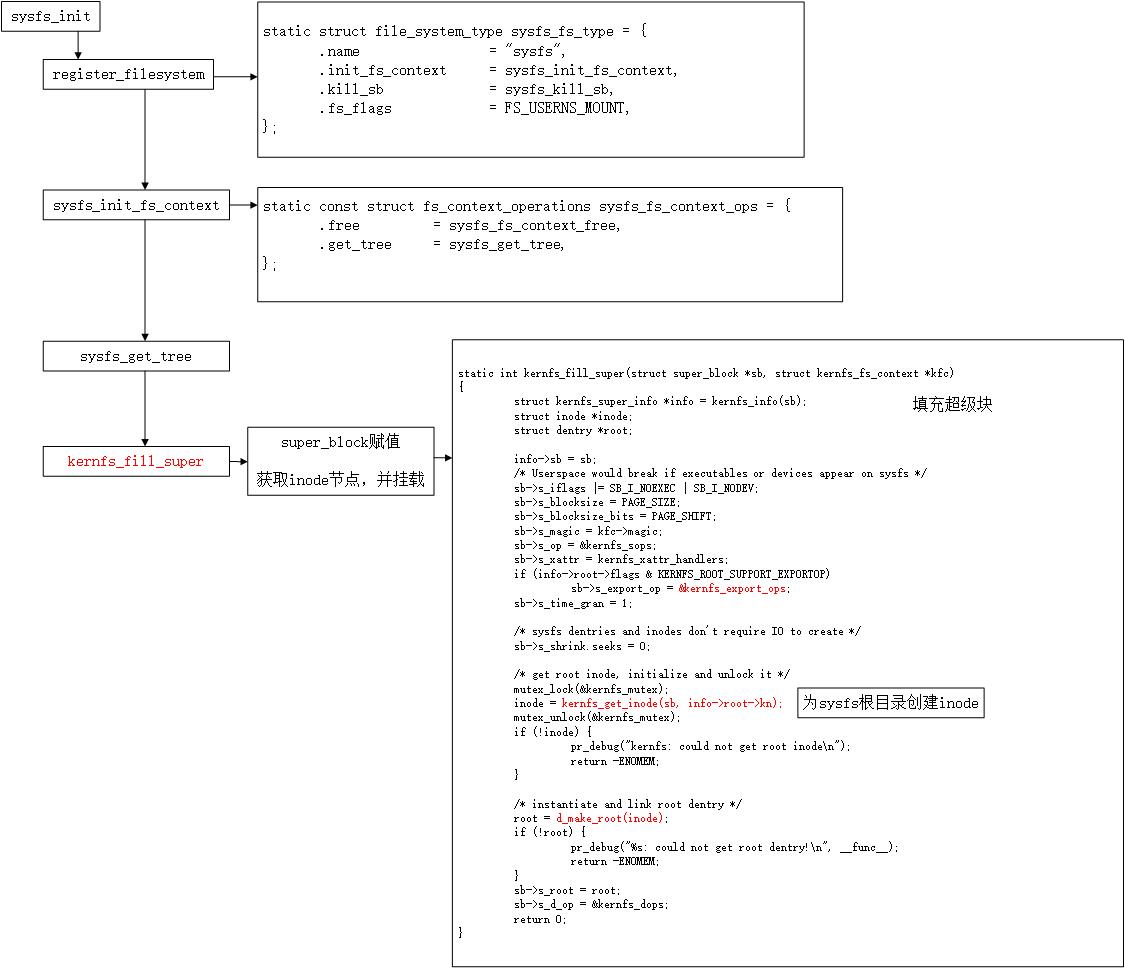
sysfs文件系统注册
static struct file_system_type sysfs_fs_type =
.name = "sysfs",
.init_fs_context = sysfs_init_fs_context,
.kill_sb = sysfs_kill_sb,
.fs_flags = FS_USERNS_MOUNT,
;
int __init sysfs_init(void)
int err;
sysfs_root = kernfs_create_root(NULL, KERNFS_ROOT_EXTRA_OPEN_PERM_CHECK,
NULL);
if (IS_ERR(sysfs_root))
return PTR_ERR(sysfs_root);
sysfs_root_kn = sysfs_root->kn;
err = register_filesystem(&sysfs_fs_type);
if (err)
kernfs_destroy_root(sysfs_root);
return err;
return 0;
文件操作ops
struct kernfs_ops
int (*open)(struct kernfs_open_file *of);
void (*release)(struct kernfs_open_file *of);
int (*seq_show)(struct seq_file *sf, void *v);
void *(*seq_start)(struct seq_file *sf, loff_t *ppos);
void *(*seq_next)(struct seq_file *sf, void *v, loff_t *ppos);
void (*seq_stop)(struct seq_file *sf, void *v);
ssize_t (*read)(struct kernfs_open_file *of, char *buf, size_t bytes,
loff_t off);
size_t atomic_write_len;
bool prealloc;
ssize_t (*write)(struct kernfs_open_file *of, char *buf, size_t bytes,
loff_t off);
__poll_t (*poll)(struct kernfs_open_file *of,
struct poll_table_struct *pt);
int (*mmap)(struct kernfs_open_file *of, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
;文件类型操作,实例分为多种
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_file_kfops_empty =
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_file_kfops_ro =
.seq_show = sysfs_kf_seq_show,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_file_kfops_wo =
.write = sysfs_kf_write,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_file_kfops_rw =
.seq_show = sysfs_kf_seq_show,
.write = sysfs_kf_write,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_prealloc_kfops_ro =
.read = sysfs_kf_read,
.prealloc = true,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_prealloc_kfops_wo =
.write = sysfs_kf_write,
.prealloc = true,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_prealloc_kfops_rw =
.read = sysfs_kf_read,
.write = sysfs_kf_write,
.prealloc = true,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_bin_kfops_ro =
.read = sysfs_kf_bin_read,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_bin_kfops_wo =
.write = sysfs_kf_bin_write,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_bin_kfops_rw =
.read = sysfs_kf_bin_read,
.write = sysfs_kf_bin_write,
;
static const struct kernfs_ops sysfs_bin_kfops_mmap =
.read = sysfs_kf_bin_read,
.write = sysfs_kf_bin_write,
.mmap = sysfs_kf_bin_mmap,
;
内核参考学习连接
Linux内核源码/内存调优/文件系统/进程管理/设备驱动/网络协议栈-学习视频教程-腾讯课堂
以上是关于linux内核源码分析之sysfs文件系统的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章