遗传算法和禁忌搜索解TSP
Posted hellobigorange
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了遗传算法和禁忌搜索解TSP相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
原始数据
计算从城市1出发,通过每个城市,最终回到城市1的最短距离,及路径
city_list = [[1, (1150.0, 1760.0)], [2, (630.0, 1660.0)], [3, (40.0, 2090.0)], [4, (750.0, 1100.0)],
[5, (750.0, 2030.0)], [6, (1030.0, 2070.0)], [7, (1650.0, 650.0)], [8, (1490.0, 1630.0)],
[9, (790.0, 2260.0)], [10, (710.0, 1310.0)], [11, (840.0, 550.0)], [12, (1170.0, 2300.0)],
[13, (970.0, 1340.0)], [14, (510.0, 700.0)], [15, (750.0, 900.0)], [16, (1280.0, 1200.0)],
[17, (230.0, 590.0)], [18, (460.0, 860.0)], [19, (1040.0, 950.0)], [20, (590.0, 1390.0)],
[21, (830.0, 1770.0)], [22, (490.0, 500.0)], [23, (1840.0, 1240.0)], [24, (1260.0, 1500.0)],
[25, (1280.0, 790.0)], [26, (490.0, 2130.0)], [27, (1460.0, 1420.0)], [28, (1260.0, 1910.0)],
[29, (360.0, 1980.0)]]
路径开头和结尾都是1,只要全排列2,…,29看怎么排列路径最短即可。
遗传算法
遗传算法_geatpy
写好代价函数和参数,直接调用geatpy包。
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""MyProblem.py"""
import geatpy as ea
import numpy as np
city_list = [[1, (1150.0, 1760.0)], [2, (630.0, 1660.0)], [3, (40.0, 2090.0)], [4, (750.0, 1100.0)],
[5, (750.0, 2030.0)], [6, (1030.0, 2070.0)], [7, (1650.0, 650.0)], [8, (1490.0, 1630.0)],
[9, (790.0, 2260.0)], [10, (710.0, 1310.0)], [11, (840.0, 550.0)], [12, (1170.0, 2300.0)],
[13, (970.0, 1340.0)], [14, (510.0, 700.0)], [15, (750.0, 900.0)], [16, (1280.0, 1200.0)],
[17, (230.0, 590.0)], [18, (460.0, 860.0)], [19, (1040.0, 950.0)], [20, (590.0, 1390.0)],
[21, (830.0, 1770.0)], [22, (490.0, 500.0)], [23, (1840.0, 1240.0)], [24, (1260.0, 1500.0)],
[25, (1280.0, 790.0)], [26, (490.0, 2130.0)], [27, (1460.0, 1420.0)], [28, (1260.0, 1910.0)],
[29, (360.0, 1980.0)]]
x_point_list = [i[1][0] for i in city_list] # x坐标
y_point_list = [i[1][1] for i in city_list] # y坐标
# 计算两城市间的距离
def city_distance(city1, city2):
distance = ((float(x_point_list[city1] - x_point_list[city2])) ** 2 + (
float(y_point_list[city1] - y_point_list[city2])) ** 2) ** 0.5
return distance
# 计算线路路径长度
def aim_func(road_list):
current_point = 0
dist = 0
for i in road_list:
next_point = i - 1
dist += city_distance(current_point, next_point)
current_point = i - 1
dist += city_distance(current_point, 0)
return dist
class MyProblem(ea.Problem): # 继承Problem父类
def __init__(self):
name = 'MyProblem' # 初始化name(函数名称,可以随意设置)
M = 1 # 初始化M(目标维数)
maxormins = [1] # 初始化maxormins(目标最小最大化标记列表,1:最小化该目标;-1:最大化该目标)
Dim = len(city_list) - 1 # 初始化Dim(决策变量维数)
varTypes = [1] * Dim # 初始化varTypes(决策变量的类型,元素为0表示对应的变量是连续的实数;1表示是离散的整数)
lb = [2] * Dim # 决策变量下界
ub = [Dim + 1] * Dim # 决策变量上界
lbin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量下边界,1表示包含上边界;0表示不包含上边界
ubin = [1] * Dim # 决策变量上边界
# 调用父类构造方法完成实例化
ea.Problem.__init__(self, name, M, maxormins, Dim, varTypes, lb, ub, lbin, ubin)
def aimFunc(self, pop): # 目标函数
X = pop.Phen
f = np.array([aim_func(road_list) for road_list in X]).reshape(X.shape[0], 1)
pop.ObjV = f # 计算目标函数值,赋值给pop种群对象的ObjV属性
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""main.py"""
import geatpy as ea
from MyProblem import * # 导入自定义问题接口
# 画线路图
def draw_line_pic(route, cost):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = []
y = []
route = list(route)
route.append(1)
route.insert(0,1)
for item in route:
x.append(x_point_list[item-1])
y.append(y_point_list[item-1])
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.scatter(x_point_list, y_point_list, marker="o", c='g')
plt.scatter(x_point_list[0], y_point_list[0], marker="o", c="r")
for i in range(len(city_list)):
plt.text(x_point_list[i], y_point_list[i], str(i+1), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10)
plt.title("GA_Search: " + str(cost))
plt.plot([1,2],[1,2])
plt.show()
for i in range(1):
print(str(i)+"次")
"""===============================实例化问题对象================================"""
problem = MyProblem() # 生成问题对象
"""==================================种群设置=================================="""
Encoding = 'P' # 编码方式
NIND = 500 # 种群规模
Field = ea.crtfld(Encoding=Encoding, varTypes=problem.varTypes, ranges=problem.ranges, borders=problem.borders) # 创建区域描述器
population = ea.Population(Encoding, Field, NIND) # 实例化种群对象(此时种群还没被初始化,仅仅是完成种群对象的实例化)
"""================================算法参数设置================================="""
myAlgorithm = ea.soea_SEGA_templet(problem, population) # 实例化一个算法模板对象_精英保留的遗传算法
myAlgorithm.MAXGEN = 500 # 最大进化代数
myAlgorithm.mutOper.Pm = 0.8 # 变异概率
myAlgorithm.logTras = 10 # 设置每隔多少代记录日志,若设置成0则表示不记录日志
myAlgorithm.verbose = True # 设置是否打印输出日志信息
myAlgorithm.drawing = 1 # 设置绘图方式(0:不绘图;1:绘制结果图;2:绘制目标空间过程动画;3:绘制决策空间过程动画)
"""===========================调用算法模板进行种群进化==============--==========="""
[BestIndi, population] = myAlgorithm.run() # 执行算法模板,得到最优个体以及最后一代种群
BestIndi.save() # 把最优个体的信息保存到文件中
"""==================================输出结果=================================="""
print('用时:%f 秒' % myAlgorithm.passTime)
print('评价次数:%d 次' % myAlgorithm.evalsNum)
if BestIndi.sizes != 0:
print('最优的目标函数值为:%s' % BestIndi.ObjV[0][0])
print('最优的控制变量值为:')
road_list=BestIndi.Phen[::]
print("最优路径:",road_list)
draw_line_pic(road_list[0], BestIndi.ObjV[0][0])
finally_route_list = []
for i in road_list[0]:
finally_route_list.append([i, (x_point_list[i - 1], y_point_list[i - 1])]) # 最终路径
else:
print('没找到可行解。')
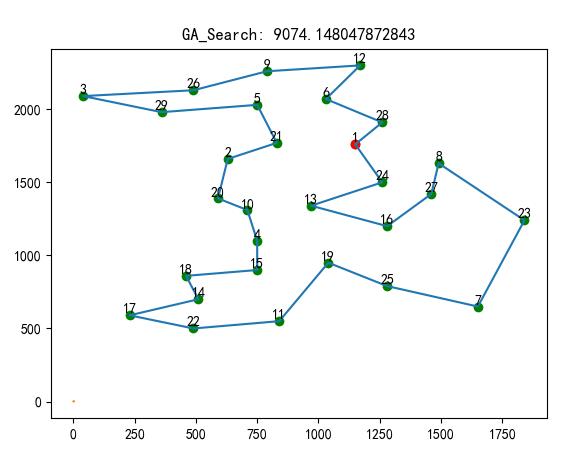
结果
用时:10.537014 秒
评价次数:250000 次
最优的目标函数值为:9076.982920396536
最优的控制变量值为:
最优路径: [1 28 6 12 9 26 3 29 5 21 2 20 10 13 4 15 18 14 17 22 11 19 25 7 23
8 27 16 24 1]
禁忌搜索
代码
结果
以上是关于遗传算法和禁忌搜索解TSP的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章