C++ map和set
Posted qnbk
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++ map和set相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
map和set
关联式容器

序列式容器:底层为线性序列的数据结构,里面存储的是元素本身
关联式容器也是用来存储数据的,与序列式容器不同的是,里面存储的是<key,value>的键值对,在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高
键值对
用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,该结构一般只包含两个成员变量key和value,key代表键值,value表示与key对应的信息
树形结构的关联式容器
STL总共实现了两种不同结构的管理式容器:树形结构与哈希结构。树形结构的关联式容器:map,set,multimap,multiset这四种容器的共同特点是:使用平衡搜索树(红黑树)作为底层结果,容器中的元素是一个有序序列
set
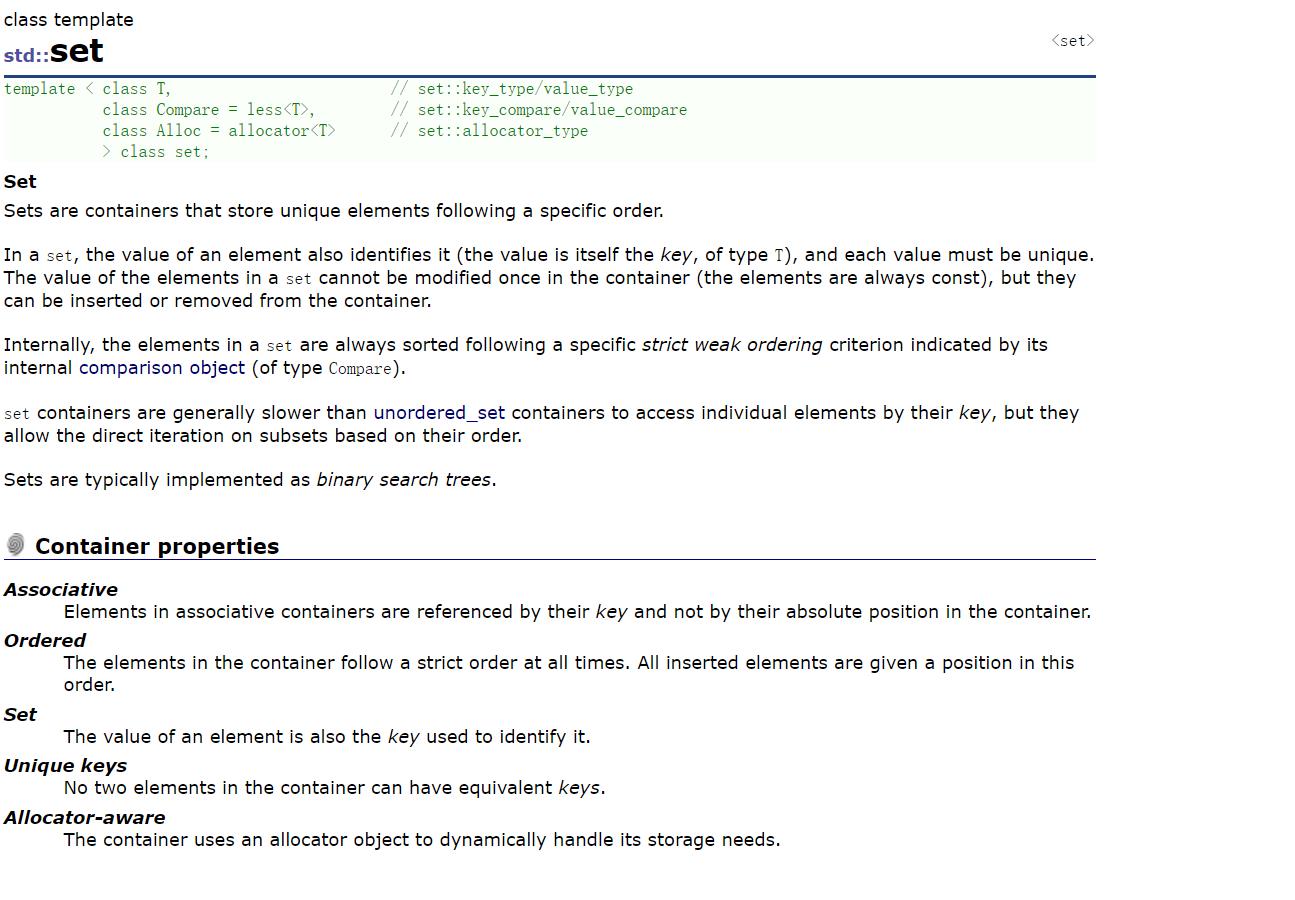
- set是按照一定次序存储元素的容器
- 在set中,元素的value也标识它(value就是key,类型为T),并且每个value必须是唯一的。set中的元素不能在容器中修改(元素总是const),但是可以从容器中插入或删除它们。
- 在内部,set中的元素总是按照其内部比较对象(类型比较)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序。
- set容器通过key访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_set容器慢,但它们允许根据顺序对子集进行直接迭代。
- .set在底层是用二叉搜索树(红黑树)实现的。
注意: - 与map/multimap不同,map/multimap中存储的是真正的键值对<key,value>,set中只放value,但在底层实际存放的是由<value,value>构成的键值对。
- set中插入元素时,只需要插入value即可,不需要构造键值对。
- set中的元素不可以重复(因此可以使用set进行去重)。
- 使用set的迭代器遍历set中的元素,可以得到有序序列
- set中的元素默认按照小于来比较
- set中查找某个元素,时间复杂度为:log2^n
- set中的元素不允许修改
set的使用
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/set/
(C++官网上的文档介绍)
set的模板参数列表
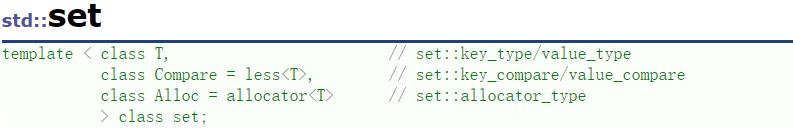
T:set 中存放元素的类型,实际在底层存储<value,value>的键值对
Compare:set元素中默认按照小于比较
Alloc:set元素空间的管理方式,使用STL提供的空间配置器管理
set的构造

set的迭代器

set的其他操作
set的应用举例
插入数据
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void test_set()
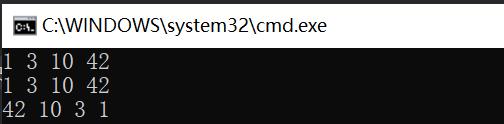
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(42);
s.insert(3);
//排序 + 去重
//遍历方式1:迭代器
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
cout << endl;
//while (it != s.end())
//
// *it += 1;//错误,不能修改已经插入的值
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
//
//cout << endl;
//遍历方式2:范围for
for (auto e : s)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
//排降序
set<int>::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
cout << endl;
int main()
test_set();
return 0;
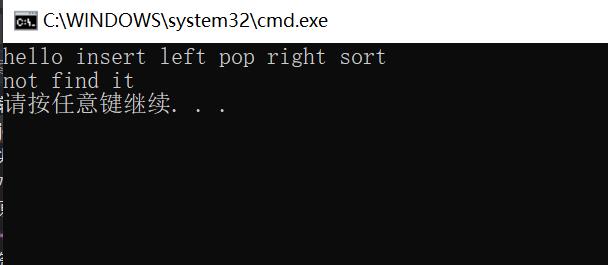
检查单词拼写是否正确
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test_set()
//检查单词是否正确
//思路:词库的单词放入set的对象中,把写出来的单词去set中查找看是否存在
set<string> strSet;
strSet.insert("insert");
strSet.insert("sort");
strSet.insert("left");
strSet.insert("right");
strSet.insert("pop");
strSet.insert("hello");
// ......
for (auto e : strSet)//ascii码比较大小排序
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
set<string>::iterator ret = strSet.find("helloc");
if (ret != strSet.end())
cout << "find it!" << endl;
else
cout << "not find it" << endl;
int main()
test_set();
return 0;
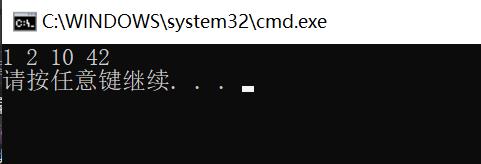
删除
oid test_set2()
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(42);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(3);
//先查找,找到了删,没找到也删-》报错
//auto pos = s.find(30);
auto pos = s.find(7);
if (pos != s.end())
s.erase(pos);
//在就删除,不在不处理
s.erase(3);
s.erase(30);
for (auto e : s)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
int main()
//test_set();
test_set2();
return 0;
multiset
- multiset是按照特定顺序存储元素的容器,其中元素是可以重复的。
- 在multiset中,元素的value也会识别它(因为multiset中本身存储的就是<value,value>组成的键值对,因此value本身就是key,key就是value,类型为T).multiset元素的值不能在容器中进行修改(因为元素总是const的),但可以从容器中插入或删除。
- 在内部,multiset中的元素总是按照其内部比较规则(类型比较)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序。
注意: - multiset中再底层中存储的是<value,value>的键值对
- multiset的插入接口中只需要插入即可
- 与set的区别是,multiset中的元素可以重复,set是中value是唯一的
- 使用迭代器对multiset中的元素进行遍历,可以得到有序的序列
- multiset中的元素不能修改
- 在multiset中找某个元素,时间复杂度为O(log2^N)
- multiset的作用:可以对元素进行排序
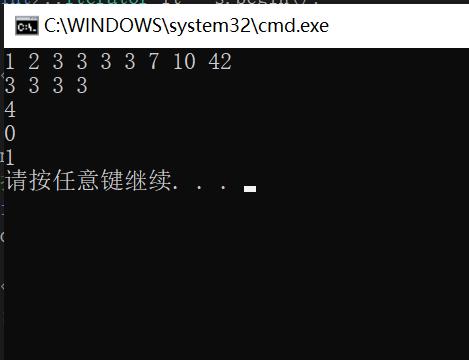
void multiset_test()
//multiset 允许键值冗余,使用方法基本与set一致
//下面几个地方有些差异
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(42);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(3);
multiset<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
cout << endl;
//find 查找的val有多个的时候,它找的是中序的第一个
multiset<int>::iterator pos = s.find(3);
while (*pos == 3)
cout << *pos << " ";
pos++;
cout << endl;
cout << s.count(3) << endl;//查找val的个数
cout << s.count(30) << endl;
cout << s.count(7) << endl;
s.erase(3);//删除所有的
//相当于:
//multiset<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
//while (it != s.end()
//
// //删除
//
int main()
multiset_test();
return 0;
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/multiset/
(C++官网的multiset文档)
map
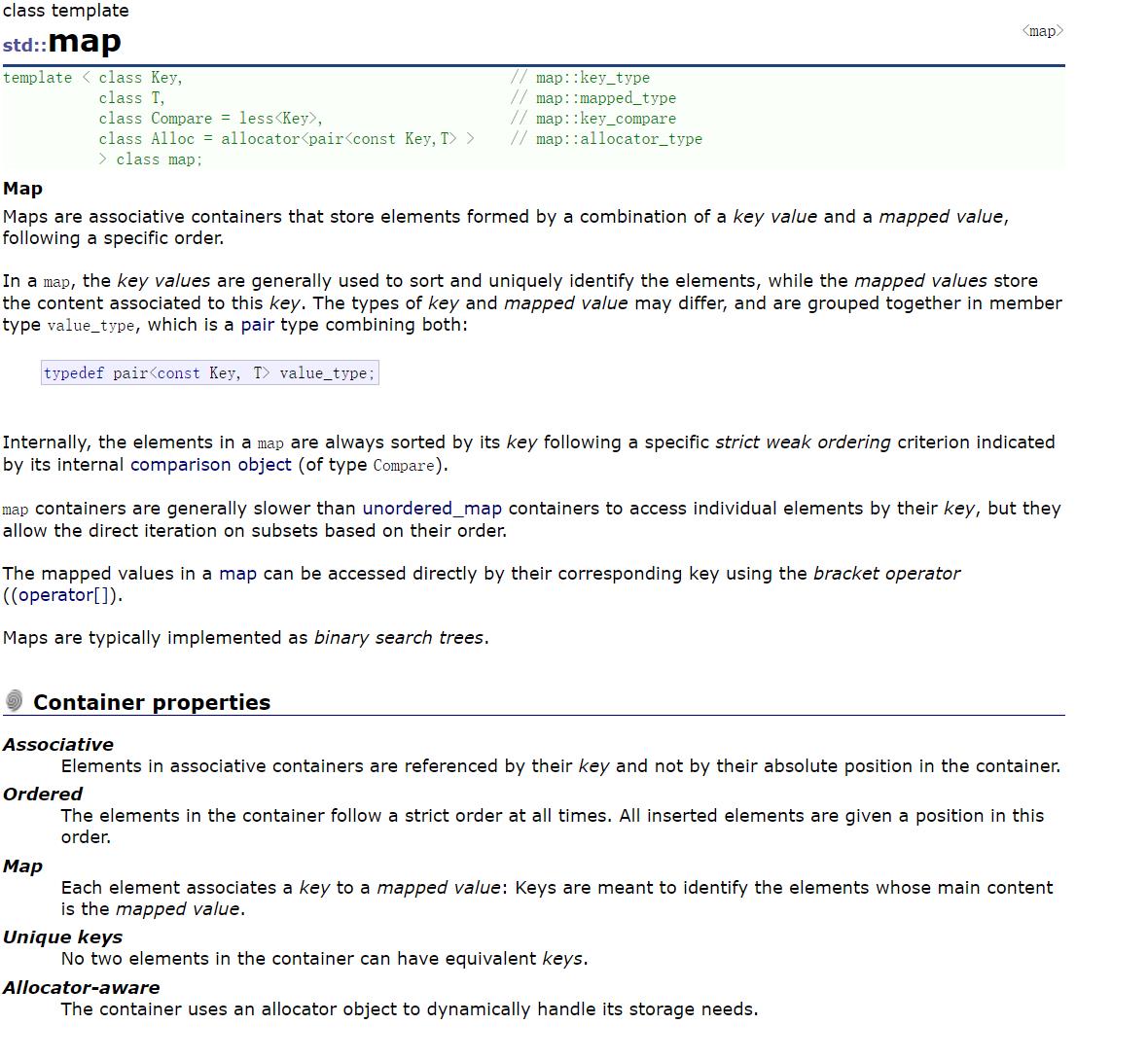
- map是关联容器,它按照特定的次序(按照key来比较)存储由键值key和值value组合而成的元素。
- 在map中,键值key通常用于排序和惟一地标识元素,而值value中存储与此键值key关联的内容。键值key和值value的类型可能不同,并且在map的内部,key与value通过成员类型value_type绑定在一起,为其取别名称为pair:
typedef pair value_type; - 在内部,map中的元素总是按照键值key进行比较排序的。
- map中通过键值访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_map容器慢,但map允许根据顺序对元素进行直接迭代(即对map中的元素进行迭代时,可以得到一个有序的序列)。
- map支持下标访问符,即在[]中放入key,就可以找到与key对应的value。
- map通常被实现为二叉搜索树(平衡二叉搜索树(红黑树))。
map的使用
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/
(C++官网的map文档)
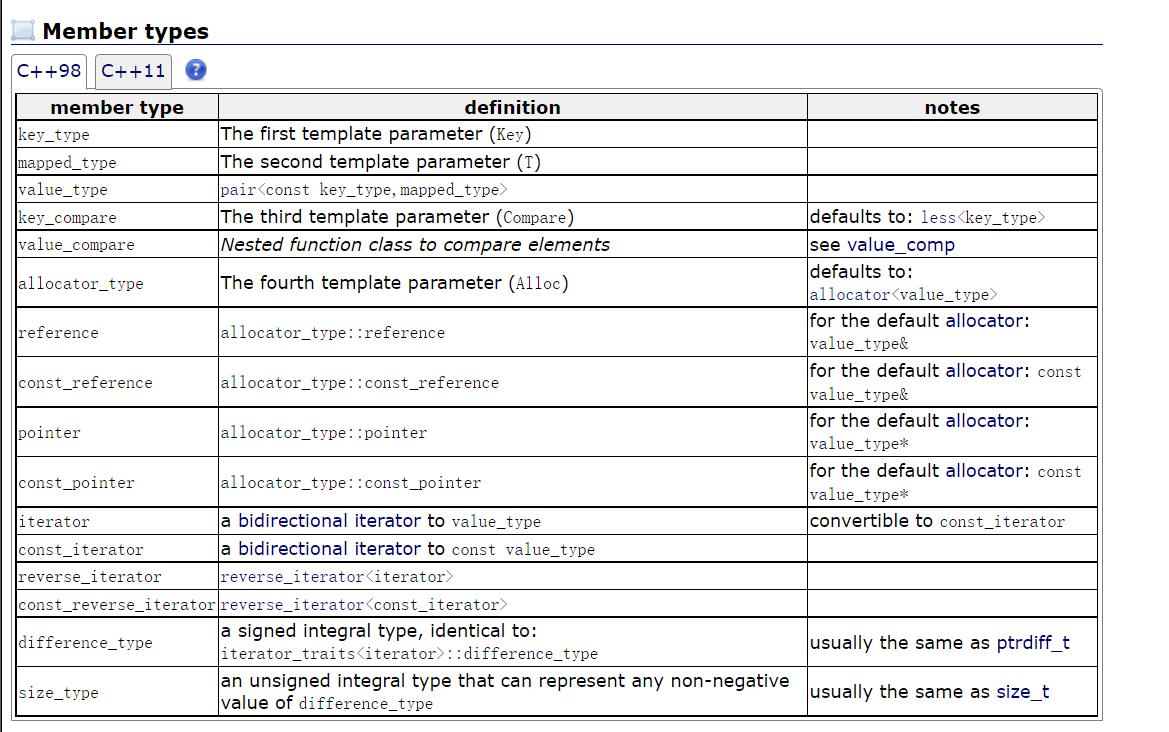
map的模板参数说明
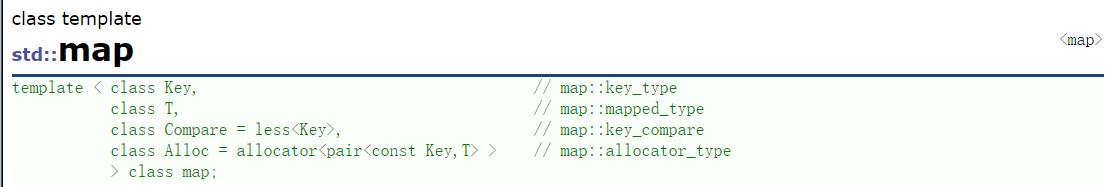
key:键值对中key的类型
T:键值对中value的类型
Compare:比较器的类型,map中的元素是按照key来比较的,缺省情况下按照小于来比较,一般情况下(内置类型元素)该参数不需要传递,如果无法比较时(自定义类型),需要用户自己显式传递比较规则(一般情况下按照函数指针或者仿函数来传递)
Alloc:通过空间配置器来申请底层空间,不需要用户传递,除非用户不想使用标准库提供的空间配置器
注意:在使用map时,需要包含头文件。
map构造
函数声明: map()
功能介绍:构造一个空的map
map迭代器
map容量与元素访问
empty()
bool empty()const
功能:检测map中的元素是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false
size()
size_type size() const
功能:返回map中有效元素的个数
operator[]
mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& k)
功能:返回key对应的value

注意:
在元素访问时,有一个与operator[]类似的操作at()(该函数不常用)函数,都是通过key找到与key对应的value然后返回其引用,不同的是:当key不存在时,operator[]用默认value与key构造键值对然后插入,返回该默认value,at()函数直接抛异常。
map中元素的其他操作
map应用
插入和修改
//template <class T1,class T2>
//struct pair
//
// typedef T1 first_type;
// typedef T2 second_type;
// T1 first;
// T2 second;
// pair() :first(T1()), second(T2())
//
// pair(const T1& t1, const T2& t2) :first(t1), first(t2)
//
//;
//template<class T1,class T2>
//pair<T1, T2>make_pair(T1 x, T2 y)
//
// return (pair<T1, T2>(x, y));
//
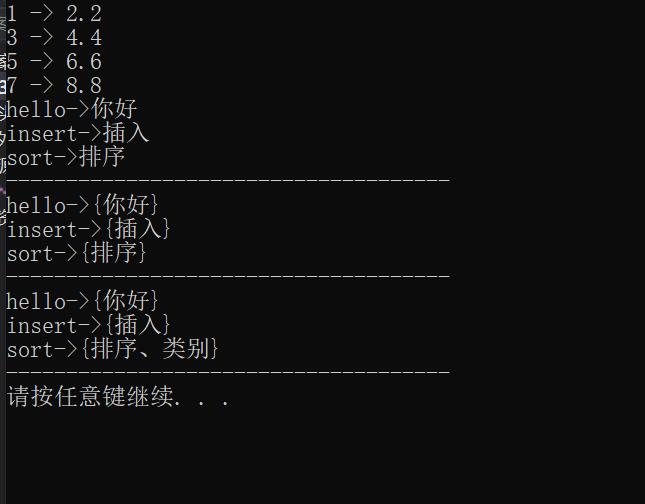
void map_test1()
map<int, double> m;
//调用pair的构造函数,构造一个匿名对象插入
m.insert(pair<int, double>(1, 2.2));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(3, 4.4));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(5, 6.6));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(5, 9.9));//key值相同就会插入失败
//调用函数模板,构造对象。好处是不需要去声明pair参数,让函数模板自己推
m.insert(make_pair(7,8.8));
map<int, double>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
//cout << (*it).first<<" -> "<<(*it).second<< endl;
cout << it->first << " -> " << it->second << endl;
it++;
//通过typedef 简化命名
typedef std::map<std::string, std::string> DICT;
typedef std::pair<std::string, std::string> DICT_KV;
typedef std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator DICT_IT;
DICT dict;
dict.insert(DICT_KV("insert", "插入"));
dict.insert(std::make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(std::make_pair("hello", "你好"));
DICT_IT dit = dict.begin();
while (dit != dict.end())
cout << dit->first << "->" << dit->second << endl;
dit++;
cout << "-------------------------------------" << endl;
DICT_IT dit2 = dict.begin();
while(dit2 != dict.end())
//key 不能修改 value可以
dit2->second.insert(0, "");
dit2->second += "";
dit2++;
//cout << dit2->first << "->" << dit2->second << endl;
dit2 = dict.begin();
while (dit2 != dict.end())
cout << dit2->first << "->" << dit2->second << endl;
dit2++;
cout << "-------------------------------------" << endl;
//修改map里的数据
auto ret = dict.find("sort");
if(ret != dict.end())
//ret->second.insert(ret->second.size() - 1, ",类别");
//可读性的优化技巧
string& str = ret->second;
str.insert(str.size() - 1, "、类别");
DICT_IT dit3 = dict.begin();
while (dit3 != dict.end())
cout << dit3->first << "->" << dit3->second << endl;
dit3++;
cout << "-------------------------------------" << endl;
int main()
map_test1();
return 0;
pair
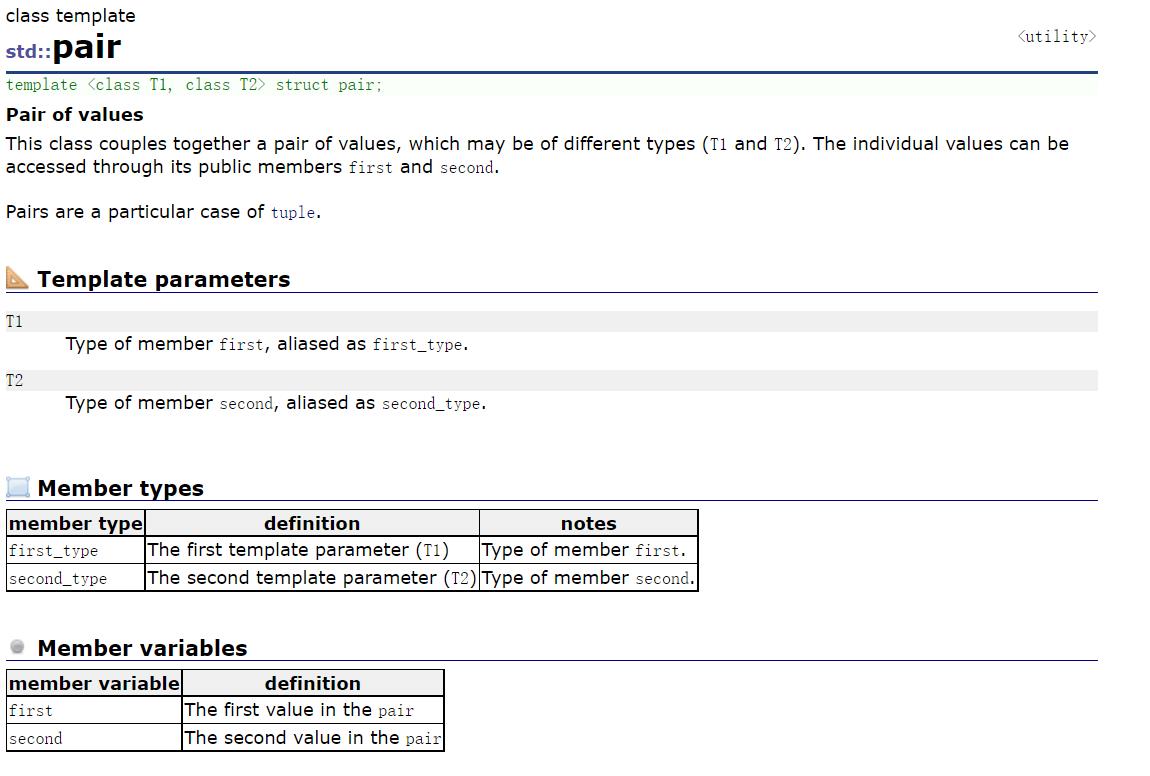
template <class T1,class T2>
struct pair
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first;
T2 second;
pair() :first(T1()), second(T2())
pair(const T1& t1, const T2& t2) :first(t1), first(t2)
;
make_pair
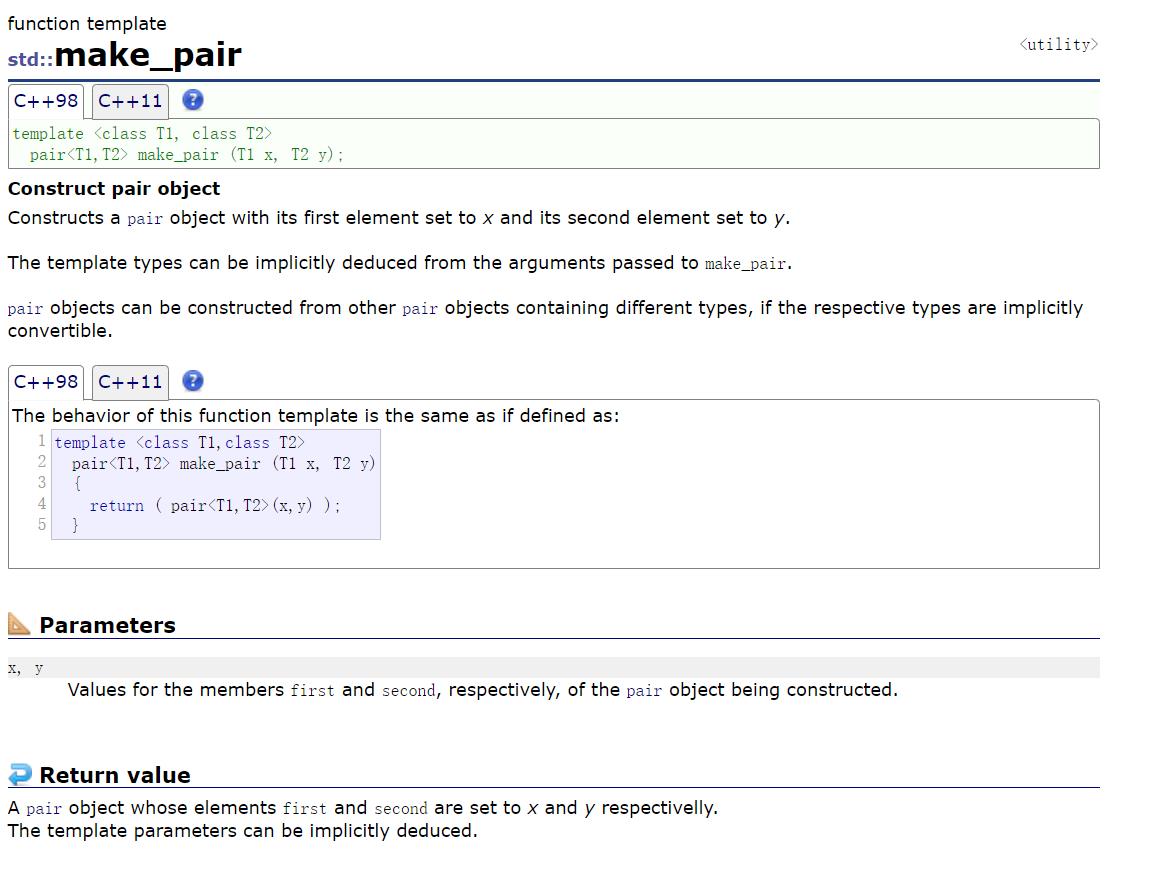
template<class T1,class T2>
pair<T1, T2>make_pair(T1 x, T2 y)
return (pair<T1, T2>(x, y));
统计次数
void map_test2()
//1、统计次数
string arr[] = "香蕉", "苹果", "菠萝", "桃子", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "榴莲", "桃子" ;
//map<string, int> countfruit;
统计次数的方式1
//for (const auto& str : arr)
//
// //第一次出现,插入<str,1>,后续再出现,次数++
// map<string, int>::iterator ret = countfruit.find(str);
// if (ret != countfruit.end())
//
// ret->second++;
//
// else
//
// countfruit.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
//
//
//for (auto& e : countfruit)
//
// cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
//
统计次数的方式2
//map<string, int> countfruit;
//for (const auto& str : arr)
//
// //先插入,如果str不在map中,insert会返回str所在节点的迭代器,次数++
// //
// //pair<map<string,int>::iterator,bool> ret = countfruit.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
// auto ret = countfruit.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
// if (ret.second == false)
//
// ret.first->second++;
//
//
//for (auto& e : countfruit)
//
// cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
//
// 统计次数的方式3
map<string, int> countfruit;
for (const auto& str : arr)
countfruit[str]++;
for (auto& e : countfruit)
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
//关于[]
map<string, string> dict;
dict["left"] = "左边"以上是关于C++ map和set的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章