树的浅析与实现
Posted chenshikun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了树的浅析与实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、基本概念
树是一种简单的非线性结构,所有元素之间具有明显的层次特性。在树结构中,每一个结点只有一个前驱节点,称为父结点,没有前驱节点的结点只有一个,称为树的根结点,简称树的根。每一个结点可以有多个后继节点,称为该结点的子结点。没有后继节点的结点称为叶子结点。在树结构中,一个结点所拥有的后件的个数称为该结点的度,所有结点中最大的度称为树的度。树的最大层次称为树的深度。
二、二叉树
定义:二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。二叉树通常分为满二叉树和完全二叉树。
(1)满二叉树:一个深度为K且有2k+1-1个节点的二叉树。
(2)完全二叉树:只多有最下面的两层的节点的度数可以小于2,其余各层节点的度数都等于2,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。
性质:
(1)对于非空二叉树,其i层最大的节点数目为2i,其中i>=0。
(2)深度为k的二叉树之多有2k+1-1个节点,其中k>=-1。
(3)在任意一棵非空二叉树中,若终端节点的个数为n0,度为2的节点数为n2,则存在n0 = n2 +1。
(4)具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为k等于log2(n+1)向上取整再减1。
(5)如将一棵有n个节点的完全二叉树子上(根节点)向下(叶节点),同一层,子做向右连续赋予节点编号0,1,2,3,4....,n-1则对任意下标为i的节点有:
1、若i=0,则i为根节点,无父节点;若i>0,i>0,则i的父节点下标为(i-1)/2向下取整。
2、若2*i+1<n,则i的左子女为2*i+1。
3、若2*i+2<n,则i的右子女为2*i+2。
4、若i为偶数,且i≠0,则左兄弟为i-1。
5、若i为奇数,且i≠n-1,则右兄弟为i+1。
6、节点i所在的层次为log2(i+1)向下取整。
实现:
树节点定义

1 #pragma once 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <assert.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 template <class T> 6 class BinaryTreeNode 7 { 8 public: 9 BinaryTreeNode(); 10 BinaryTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode* node); 11 void setData(const T &value); //设置节点值 12 void setParent(BinaryTreeNode<T>*parent); //设置父节点 13 void setLeftChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>*leftchild); //设置左孩子节点 14 void setRightChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>*rightchild); //设置右孩子节点 15 T& getData(); //获取节点值 16 BinaryTreeNode<T>* getparent(); //获取父节点 17 BinaryTreeNode<T>* getLeftChild(); //获取左孩子节点 18 BinaryTreeNode<T>* getRightChild(); //获取右孩子节点 19 20 private: 21 T m_value; //存储值 22 BinaryTreeNode<T>* m_parent; //指向父节点 23 BinaryTreeNode<T>* m_leftChilde; //指向左孩子节点 24 BinaryTreeNode<T>* m_rightChilde; //指向右孩子节点 25 }; 26 27 28 29 30 template <class T> 31 BinaryTreeNode<T>::BinaryTreeNode() 32 { 33 m_parent = NULL; 34 m_leftChilde = NULL; 35 m_rightChilde = NULL; 36 } 37 38 template <class T> 39 BinaryTreeNode<T>::BinaryTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode* node) 40 { 41 m_value = node->getData(); 42 m_parent = node->getparent(); 43 m_leftChilde = node->getLeftChild(); 44 m_rightChilde = node->getRightChild(); 45 } 46 47 template <class T> 48 void BinaryTreeNode<T>::setData(const T &value) 49 { 50 m_value = value; 51 } 52 53 template <class T> 54 void BinaryTreeNode<T>::setParent(BinaryTreeNode<T>*parent) 55 { 56 m_parent = parent; 57 } 58 59 template <class T> 60 void BinaryTreeNode<T>::setRightChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>*rightchild) 61 { 62 m_rightChilde = rightchild; 63 } 64 65 template <class T> 66 void BinaryTreeNode<T>::setLeftChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>*leftchild) 67 { 68 m_leftChilde = leftchild; 69 } 70 71 template <class T> 72 T& BinaryTreeNode<T>::getData() 73 { 74 return m_value; 75 } 76 77 template <class T> 78 BinaryTreeNode<T>* BinaryTreeNode<T>::getparent() 79 { 80 return m_parent; 81 } 82 83 template <class T> 84 BinaryTreeNode<T>* BinaryTreeNode<T>::getRightChild() 85 { 86 return m_rightChilde; 87 } 88 89 template <class T> 90 BinaryTreeNode<T>* BinaryTreeNode<T>::getLeftChild() 91 { 92 return m_leftChilde; 93 }
树定义

1 #pragma once 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <assert.h> 4 #include <stack> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include "binaryTreeNode.h" 7 using namespace std; 8 template <class T> 9 class BinaryTree 10 { 11 public: 12 BinaryTree(T &value); 13 BinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode<T>* node); 14 BinaryTreeNode<T>* getRoot(); //获取根节点 15 void insertLeftChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root, T &value); //插入左孩节点 16 void insertRightChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root,T &value); //插入右孩子节点 17 bool isEmpty(); //判断是否为空 18 //树的遍历 19 //前序遍历 20 void preOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用递归实现 21 void preOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用栈结构实现 22 //中序遍历 23 void inOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用递归实现 24 void inOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用栈结构实现 25 //后序遍历 26 void postOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用递归实现 27 void postOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; //使用栈结构实现 28 //层序遍历 29 void levelOrderTraverse(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const; 30 private: 31 BinaryTreeNode<T>* m_root; //根节点 32 }; 33 34 35 36 37 38 //构造函数 39 template <class T> 40 BinaryTree<T>::BinaryTree(T &value) 41 { 42 m_root = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(); 43 m_root->setData(value); 44 } 45 46 template <class T> 47 BinaryTree<T>::BinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode<T>* node) 48 { 49 m_root = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(); //创建一个新的节点 50 m_root = node; 51 } 52 53 //设置子节点函数 54 template <class T> 55 void BinaryTree<T>::insertRightChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root, T &value) 56 { 57 BinaryTreeNode<T>* childNode = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(); 58 childNode->setData(value); 59 childNode->setParent(root); 60 root->setRightChild(childNode); 61 } 62 63 template <class T> 64 void BinaryTree<T>::insertLeftChild(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root, T &value) 65 { 66 BinaryTreeNode<T>* childNode = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(); 67 childNode->setData(value); 68 childNode->setParent(root); 69 root->setLeftChild(childNode); 70 } 71 72 //获取根节点函数 73 template <class T> 74 BinaryTreeNode<T>* BinaryTree<T>::getRoot() 75 { 76 return m_root; 77 } 78 79 template <class T> 80 bool BinaryTree<T>::isEmpty() 81 { 82 return m_root->getparent(); 83 } 84 85 //遍历函数 86 //1、前序遍历 87 template <class T> 88 void BinaryTree<T>::preOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 89 { 90 if (NULL !=root) 91 { 92 cout << root->getData() << "->"; 93 preOrderTraverse1(root->getLeftChild()); 94 preOrderTraverse1(root->getRightChild()); 95 } 96 } 97 98 template <class T> 99 void BinaryTree<T>::preOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 100 { 101 stack<BinaryTreeNode<T>*> s; 102 BinaryTreeNode<T>* p = root; 103 while (!s.empty() || p!=NULL) 104 { 105 while (p) 106 { 107 s.push(p); 108 cout << p->getData() << "->"; 109 p = p->getLeftChild(); 110 } 111 p = s.top(); 112 s.pop(); 113 p = p->getRightChild(); 114 115 } 116 } 117 118 //2、中序遍历 119 template <class T> 120 void BinaryTree<T>::inOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 121 { 122 if (NULL != root) 123 { 124 inOrderTraverse1(root->getLeftChild()); 125 cout << root->getData() << "->"; 126 inOrderTraverse1(root->getRightChild()); 127 } 128 } 129 130 template <class T> 131 void BinaryTree<T>::inOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 132 { 133 stack<BinaryTreeNode<T>*> s; 134 BinaryTreeNode<T>*p = root; 135 while (!s.empty() || p != NULL) 136 { 137 while (p) 138 { 139 s.push(p); 140 p = p->getLeftChild(); 141 } 142 p = s.top(); 143 s.pop(); 144 cout << p->getData()<<"->"; 145 p = p->getRightChild(); 146 } 147 } 148 149 //2、后序遍历 150 template <class T> 151 void BinaryTree<T>::postOrderTraverse1(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 152 { 153 if (NULL!=root) 154 { 155 postOrderTraverse1(root->getLeftChild()); 156 postOrderTraverse1(root->getRightChild()); 157 cout << root->getData() << "->"; 158 } 159 } 160 161 template <class T> 162 void BinaryTree<T>::postOrderTraverse2(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 163 { 164 stack<BinaryTreeNode<T>*> s; 165 BinaryTreeNode<T> *cur; //当前节点 166 BinaryTreeNode<T> *pre = NULL; //上一次访问的节点 167 s.push(root); 168 while (!s.empty() ) 169 { 170 cur = s.top(); 171 if ((cur->getLeftChild() == NULL) && (cur->getRightChild() == NULL) 172 || (pre != NULL)&&(pre ==cur->getLeftChild()||pre==cur->getRightChild())) 173 { 174 cout << cur->getData() << "->"; //如果当前结点没有孩子结点或者孩子节点都已被访问过 175 s.pop(); 176 pre = cur; 177 } 178 else 179 { 180 if (cur->getRightChild() != NULL) 181 { 182 s.push(cur->getRightChild()); 183 } 184 if (cur->getLeftChild() != NULL) 185 { 186 s.push(cur->getLeftChild()); 187 } 188 } 189 190 } 191 192 193 } 194 //层序遍历 195 template <class T> 196 void BinaryTree<T>::levelOrderTraverse(BinaryTreeNode<T>* root) const 197 { 198 queue<BinaryTreeNode<T>* > q; 199 BinaryTreeNode<T>* p; 200 q.push(root); 201 while (!q.empty()) 202 { 203 p = q.front(); 204 if (p->getLeftChild() != NULL) 205 q.push(p->getLeftChild()); 206 if (p->getRightChild() != NULL) 207 q.push(p->getRightChild()); 208 q.pop(); 209 cout << p->getData() << "->"; 210 } 211 }
测试代码

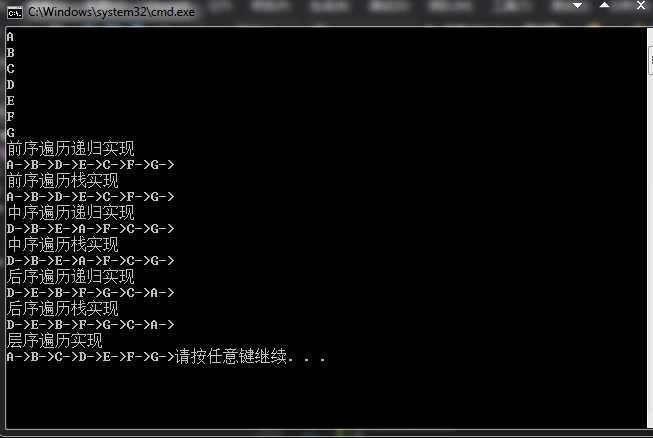
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "BinaryTree.h" 4 #include "binaryTreeNode.h" 5 using namespace std; 6 int main() 7 { 8 char value = ‘A‘; 9 BinaryTree<char> mytree(value); 10 value++; 11 mytree.insertLeftChild(mytree.getRoot(), value); 12 value++; 13 mytree.insertRightChild(mytree.getRoot(), value); 14 value++; 15 mytree.insertLeftChild(mytree.getRoot()->getLeftChild(), value); 16 value++; 17 mytree.insertRightChild(mytree.getRoot()->getLeftChild(), value); 18 value++; 19 mytree.insertLeftChild(mytree.getRoot()->getRightChild(), value); 20 value++; 21 mytree.insertRightChild(mytree.getRoot()->getRightChild(), value); 22 23 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getData() << " "; 24 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getLeftChild()->getData() << " "; 25 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getRightChild()->getData() << " "; 26 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getLeftChild()->getLeftChild()->getData() << " "; 27 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getLeftChild()->getRightChild()->getData() << " "; 28 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getRightChild()->getLeftChild()->getData() << " "; 29 cout << mytree.getRoot()->getRightChild()->getRightChild()->getData() << " "; 30 cout <<"前序遍历递归实现"<<endl; 31 mytree.preOrderTraverse1(mytree.getRoot()); 32 cout << endl; 33 cout << "前序遍历栈实现" << endl; 34 mytree.preOrderTraverse2(mytree.getRoot()); 35 cout << endl; 36 cout << "中序遍历递归实现" << endl; 37 mytree.inOrderTraverse1(mytree.getRoot()); 38 cout << endl; 39 cout << "中序遍历栈实现" << endl; 40 mytree.inOrderTraverse2(mytree.getRoot()); 41 cout << endl; 42 cout << "后序遍历递归实现" << endl; 43 mytree.postOrderTraverse1(mytree.getRoot()); 44 cout << endl; 45 cout << "后序遍历栈实现" << endl; 46 mytree.postOrderTraverse2(mytree.getRoot()); 47 cout << endl; 48 cout << "层序遍历实现" << endl; 49 mytree.levelOrderTraverse(mytree.getRoot()); 50 51 52 return 0; 53 }
测试结果
以上是关于树的浅析与实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
